How Did Hair Discrimination Legislation Shape Black Hair Heritage?
Hair discrimination legislation, particularly the CROWN Act, has affirmed Black hair as an integral part of racial identity, fostering cultural reclamation.

How Does Hair Biology Link to African Heritage?
African hair biology inextricably links to heritage through unique structures, ancient care practices, and enduring cultural significance.

How Does Hair Heritage Impact Workplace Confidence?
Hair heritage shapes workplace confidence by linking self-perception to ancestral beauty practices and resilience.

Hair Mutability
Meaning ❉ Hair Mutability is the dynamic capacity of textured hair to transform, reflecting biological responsiveness and cultural resilience across generations.

How Does the CROWN Act Protect Hair Heritage in Schools?
The CROWN Act legally protects students against race-based hair discrimination, upholding textured hair heritage in schools.

How Can UNESCO Support Hair Heritage?
UNESCO can support hair heritage by recognizing textured hair traditions as intangible cultural heritage, fostering intergenerational knowledge transfer, and addressing historical injustices against textured hair.

Why Is the CROWN Act Significant for Black Heritage?
The CROWN Act legally protects textured hair styles, affirming Black heritage and dismantling historical discrimination.

Cultural Hair Compounds
Meaning ❉ Cultural Hair Compounds define the interplay between hair's biological makeup and its profound cultural, historical, and social significance within communities.

How Is Hair Tied to Black Heritage?
Hair is tied to Black heritage through its role as a sacred symbol of identity, status, spirituality, and resistance across generations.

How Does Heritage Influence Modern Textured Hair Practices Today?
Heritage guides modern textured hair practices by infusing them with ancestral wisdom, cultural identity, and a legacy of resilience.

How Does Textured Hair Heritage Influence Modern Black Identity?
Textured hair heritage profoundly shapes modern Black identity through ancestral connection, cultural expression, and enduring resilience against historical oppression.

How Does Cultural Heritage Influence Textured Hair Identity Today?
Cultural heritage profoundly influences textured hair identity, grounding its meaning in ancestral wisdom, resilience, and a legacy of self-expression.
What Cultural Significance Does Textured Hair Hold in Modern Heritage Movements?
Textured hair signifies identity, resilience, and ancestral connection, acting as a living archive within modern heritage movements.

What Historical Cultural Practices Influenced Textured Hair Heritage and Care?
Historical cultural practices influenced textured hair care through ancestral wisdom, communal rituals, and acts of resistance, shaping a profound heritage.

How Have Legal Frameworks Shaped the Understanding of Textured Hair Heritage?
Legal frameworks have profoundly shaped the understanding of textured hair heritage by historically controlling its appearance and, more recently, affirming its cultural significance.

In What Ways Do Modern Anti-Discrimination Laws Safeguard Textured Hair as Cultural Heritage?
Modern laws safeguard textured hair as cultural heritage by explicitly prohibiting discrimination based on natural styles and textures, affirming ancestral ties.

Why Did Early Beauty Standards Devalue Textured Hair?
Early beauty standards devalued textured hair by severing its ancestral ties and rich cultural meaning, replacing reverence with imposed Eurocentric ideals.

How Did Early Rulings Fail Textured Hair?
Early rulings failed textured hair by enforcing Eurocentric standards, legally invalidating its ancestral forms and expressions of identity.

How Did Textured Hair Practices Serve as Resistance through History?
Textured hair practices served as resistance by embodying heritage, covertly communicating during oppression, and overtly asserting Black and mixed-race identity.

In What Ways Do Textured Hair Practices Reflect Cultural Heritage?
Textured hair practices serve as living reflections of cultural heritage, embodying ancestral wisdom, communal solidarity, and enduring resistance.

How Do Historical Styling Practices Reflect Heritage?
Historical styling practices for textured hair are living archives, revealing lineage, resilience, and profound cultural identity.

How Have Legal Frameworks Shaped Textured Hair Expression across Generations?
Legal frameworks have historically constrained and also inadvertently affirmed textured hair heritage, reflecting shifts in societal power and cultural resilience.

What Historical Laws Shaped Textured Hair?
Historical laws, such as the Tignon Laws, directly sought to control and diminish the public expression of textured hair, underscoring its deep connection to identity and cultural heritage.

Hair Trace Evidence
Meaning ❉ Hair Trace Evidence encompasses the biological and chemical stories held within each strand, revealing an individual's history and heritage.

How Have Cultural Pressures on Textured Hair Impacted Community Well-Being over Time?
Cultural pressures on textured hair significantly impacted community well-being by challenging self-identity, yet also sparked profound heritage-driven resistance and self-acceptance.

What Cultural Practices Surrounded the Use of Oils in Textured Hair Traditions?
Cultural oiling practices for textured hair honored ancestral knowledge, protected delicate strands, and asserted identity through generations.
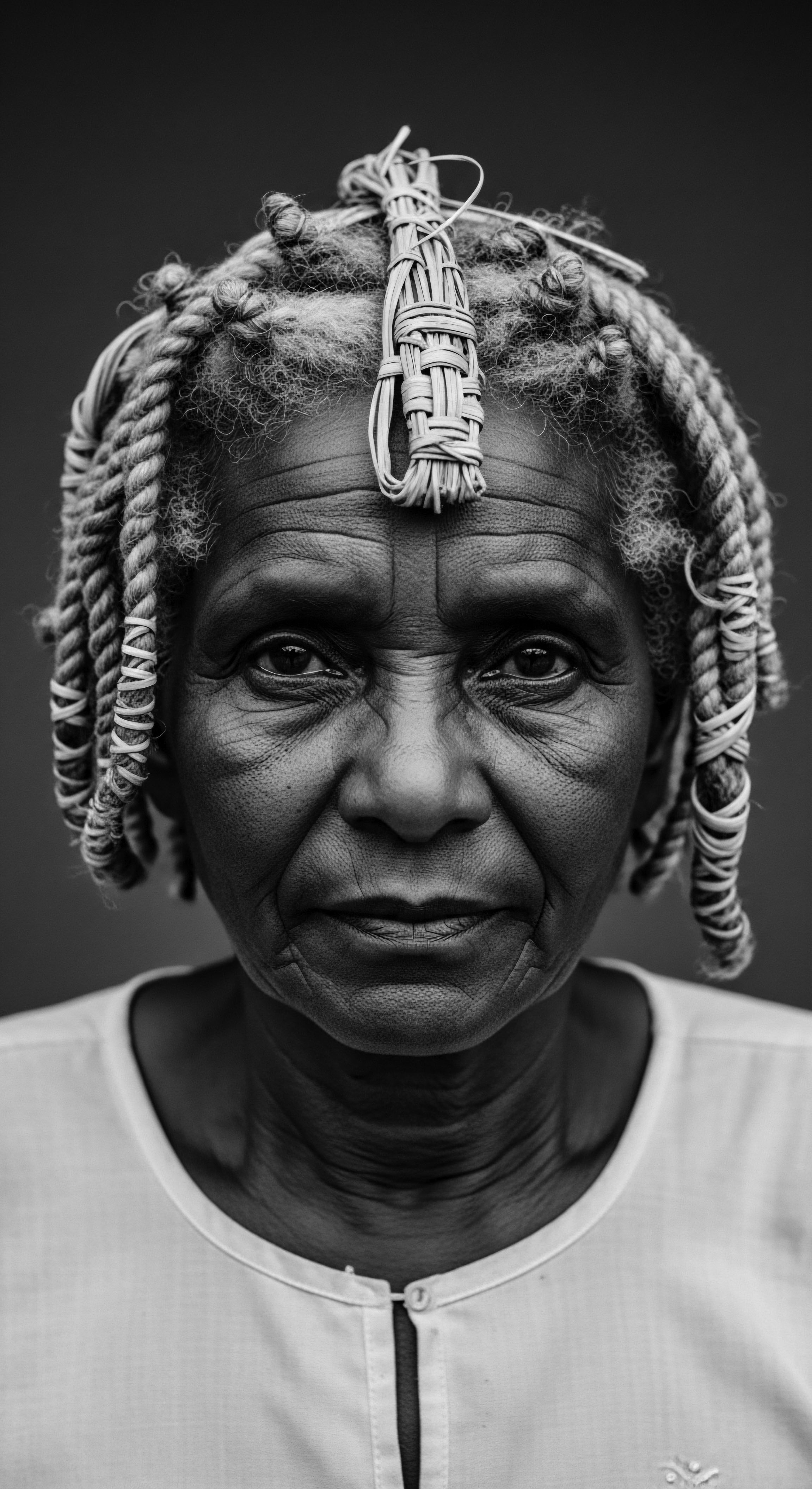

Can Appreciation for Textured Hair Dismantle Systemic Bias?
Appreciating textured hair's deep heritage dismantles systemic bias by honoring ancestral wisdom and cultural resilience.

Why Is Textured Hair Education Important for Cosmetology Students?
Textured hair education is vital for honoring its heritage, addressing past inequities, and providing respectful, competent care to all clients.

How Do Traditional Hair Care Practices Shape Modern Identity for Textured Hair?
Traditional hair care practices for textured hair act as living chronicles, profoundly shaping modern identity by anchoring individuals to their ancestral heritage.

