
What Historical Biases against Black Hair Does the CROWN Act Address?
The CROWN Act addresses historical biases rooted in Eurocentric beauty standards that deemed Black hair unprofessional and denied opportunities.
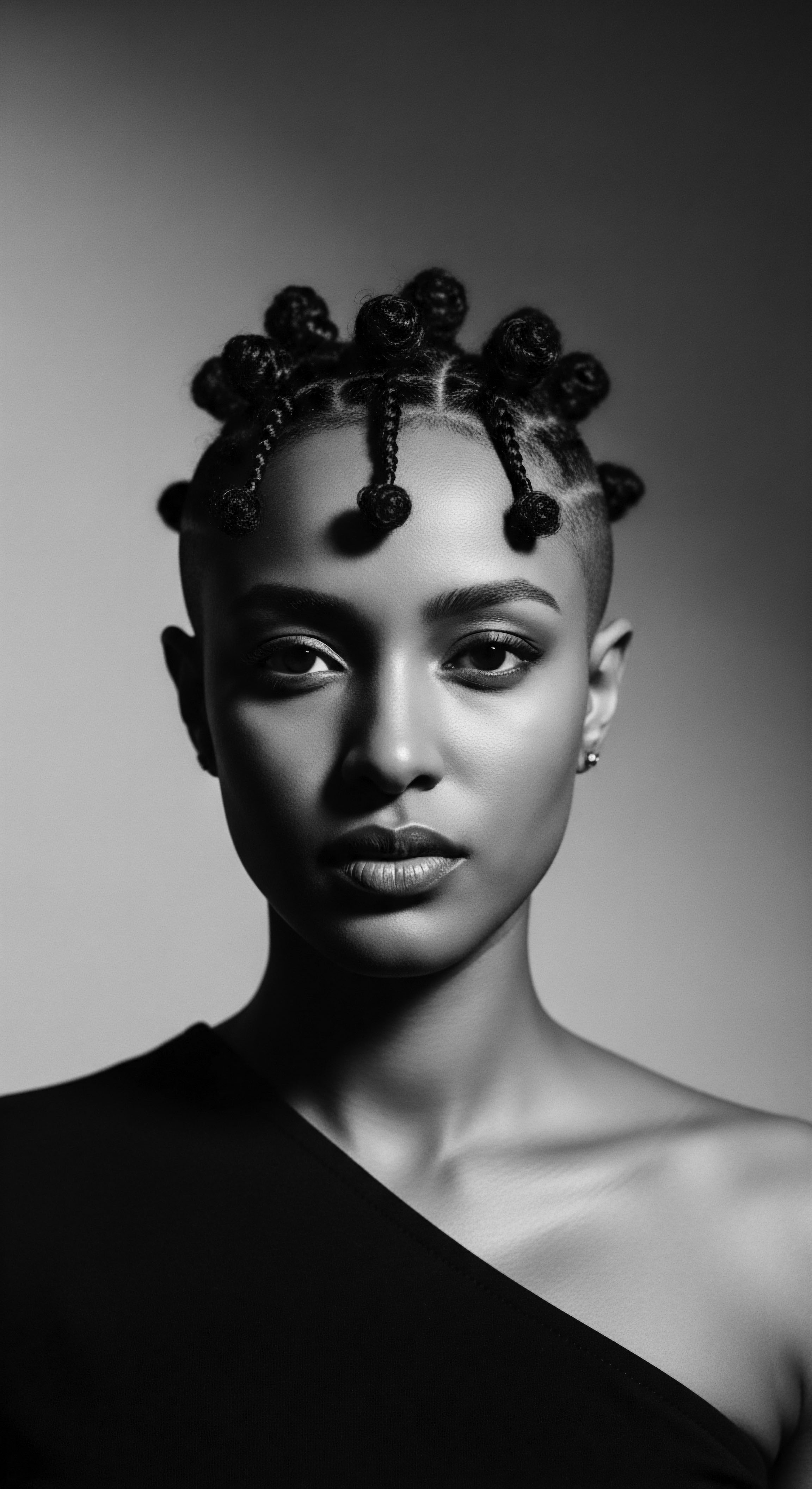

How Did Textured Hair Become Resistance?
Textured hair became resistance by embodying deep cultural heritage and self-affirmation against centuries of colonial suppression and Eurocentric beauty norms.

What Is the Historical Basis for Hair Discrimination Laws?
Hair discrimination laws stem from centuries of systemic racism, designed to control and suppress textured hair as a visible aspect of Black heritage and identity.
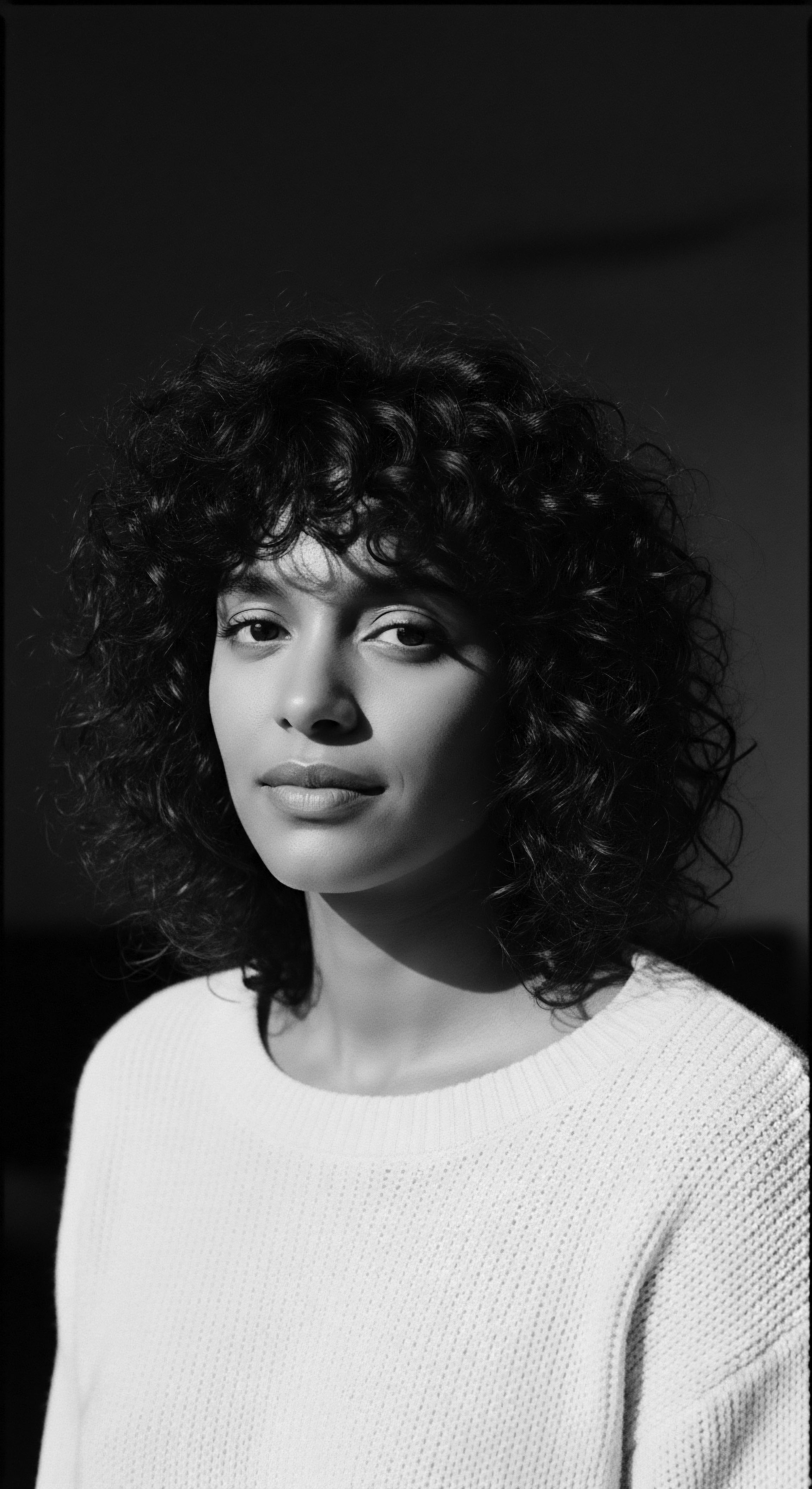

How Did Textured Hair Become a Symbol of Defiance and Collective Identity during Challenging Times?
Textured hair transformed into a symbol of defiance by embodying cultural heritage and collective identity, challenging oppressive norms.
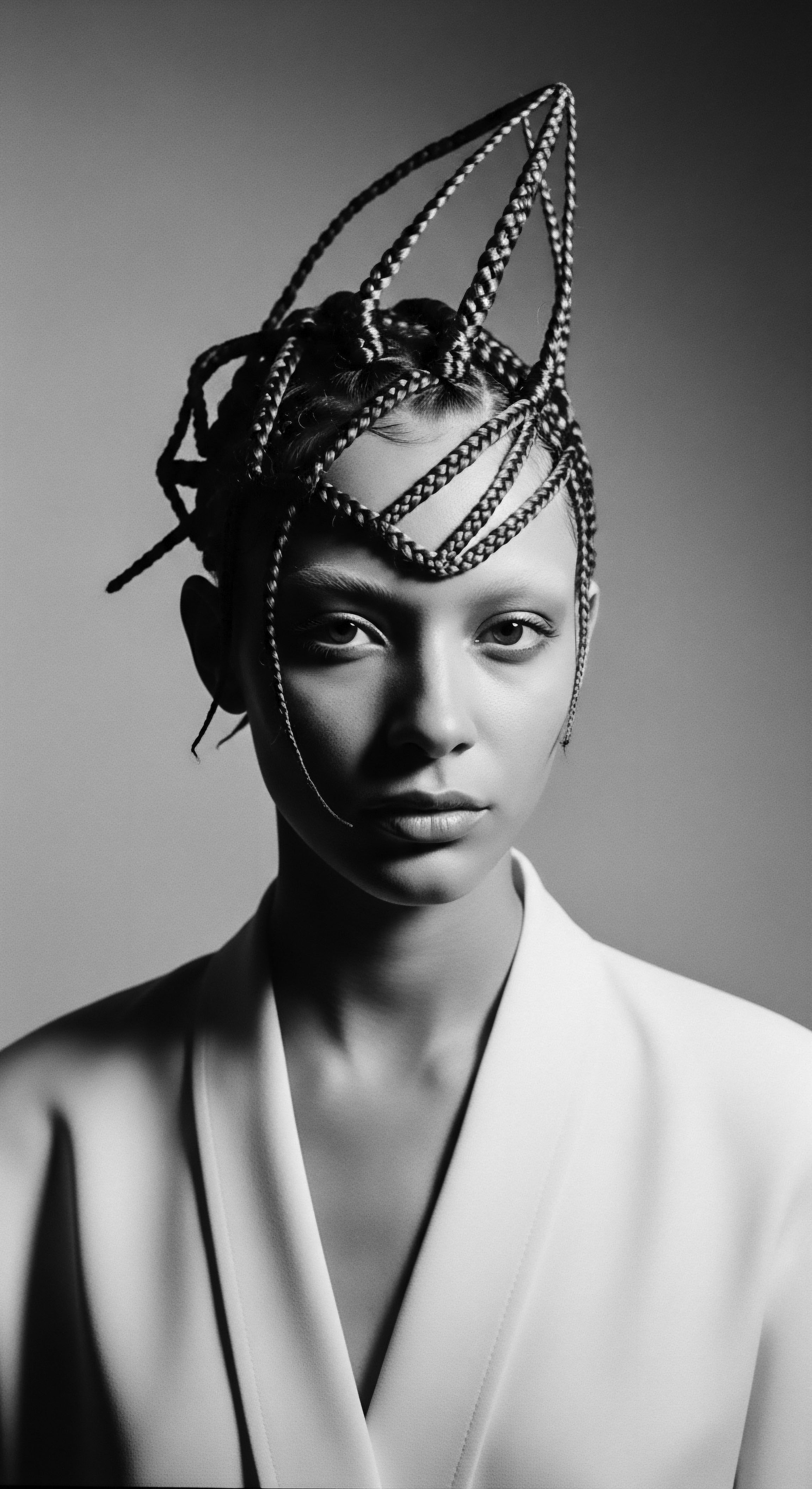

How Does CROWN Act Honor Hair Heritage?
The CROWN Act legally protects the right to wear natural, textured hair, honoring ancestral heritage and combating race-based discrimination.

How Does Hair Connect Community?
Textured hair physically and culturally binds communities through shared ancestral care practices, collective identity, and resilience.
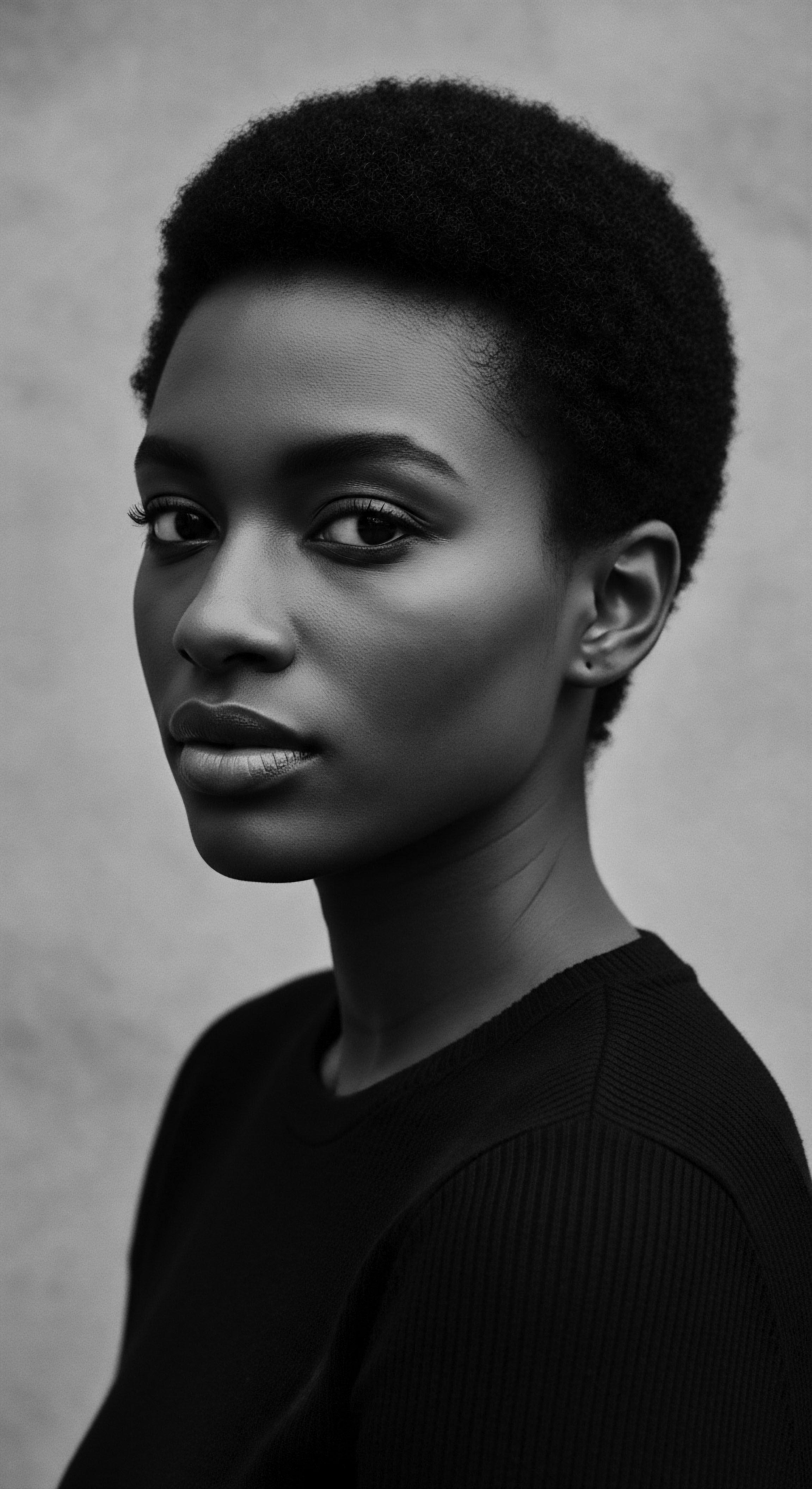
How Do Headwraps Connect Modern Care to Historical Heritage?
Headwraps connect modern textured hair care to historical heritage by serving as protective coverings, cultural markers of identity, and symbols of resilience against oppressive norms.
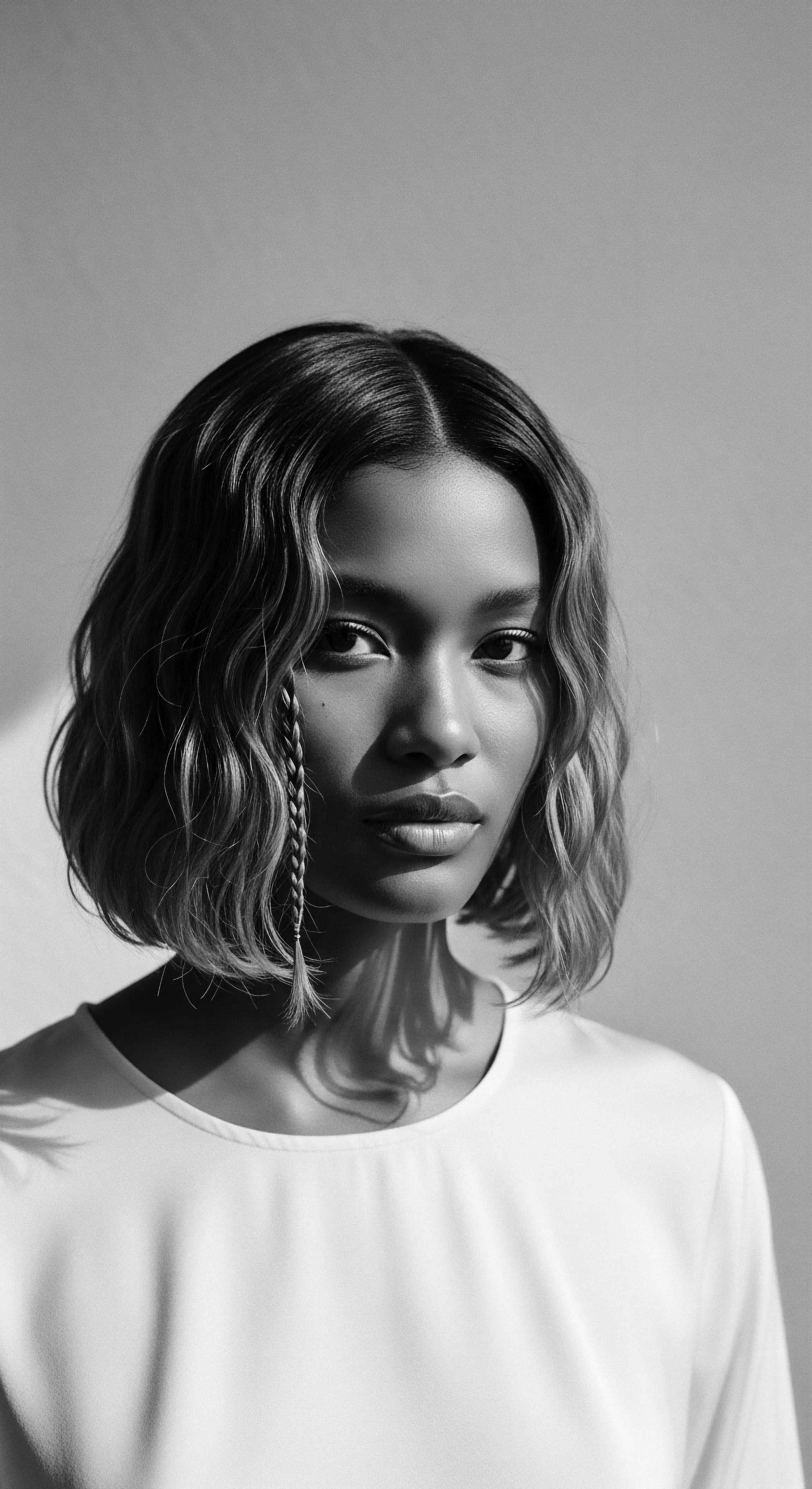

How Do Hair Rituals Define a Community?
Hair rituals within textured hair communities serve as enduring links to ancestral heritage, defining identity, transmitting knowledge, and embodying resilience.

Which States Have Recognized Hair Heritage in Anti-Discrimination Statutes?
Twenty-seven states have enacted the CROWN Act or similar legislation to prohibit hair discrimination, recognizing textured hair as a protected racial trait.

In What Ways Did Textured Hair Serve as a Symbol of Identity and Resistance Throughout History?
Textured hair has served as a powerful, enduring symbol of identity and resistance throughout history, deeply rooted in ancestral heritage and cultural affirmation.

What Is the Heritage of Cornrow Braids?
Cornrow braids carry a heritage spanning millennia, signifying identity, communication, and resilience within textured hair communities.

What Role Did Textured Hair Play in Identity Movements across the Diaspora?
Textured hair played a central role in identity movements by acting as a powerful symbol of heritage, cultural resistance, and self-affirmation.

How Do Historical Beauty Standards Relate to Textured Hair Heritage?
Historical beauty standards, rooted in Eurocentric ideals, profoundly shaped perceptions of textured hair, leading to its suppression while simultaneously fueling a powerful heritage of resilience and cultural affirmation.

How Did the Tignon Laws Reshape Hair Covering Heritage?
The Tignon Laws compelled head coverings, yet Black and mixed-race women transformed them into symbols of defiant beauty and cultural pride.

What Traditional Practices Influenced Modern Textured Hair Care Routines?
Traditional practices rooted in African heritage centered on moisture, protection, and communal care, fundamentally shaping modern textured hair routines.

Social Equity
Meaning ❉ Social Equity is the intentional redress of historical and ongoing systemic imbalances, ensuring equitable access to dignity and opportunity, particularly as it relates to textured hair heritage.

What Historical Events Influenced the Global Perception of Natural Black Hair Heritage?
Historical events shifted textured hair's perception from ancestral reverence to subjugation, eventually reclaiming its place as a symbol of identity and resilience.

How Has Textured Hair Expressed Identity through Time?
Textured hair has expressed identity by signifying social status, heritage, and resistance across centuries and cultures.

How Has Textured Hair Shaped Identity across Generations?
Textured hair profoundly shapes identity across generations through its deep cultural heritage and enduring acts of personal and communal expression.

In What Ways Did Textured Hair Serve as a Symbol of Resistance Historically?
Textured hair historically served as a profound emblem of resistance, a living testament to identity, communication, and unyielding cultural heritage.

Why Do Historical Beauty Standards Persist for Textured Hair?
Historical beauty standards persist for textured hair due to ongoing systemic legacies, economic structures, and colonial impositions impacting self-perception.

How Did Historical Laws Influence the Perception of Afro-Textured Hair?
Historical laws altered Afro-textured hair's public perception, forcing conformity but sparking powerful acts of cultural heritage preservation.

Why Did Textured Hair Straightening Become Common?
Textured hair straightening became common due to systemic pressures, societal beauty standards, and economic survival linked to perceived professionalism.

