
How Did Ancient Communities Source Hair Oils?
Ancient communities sourced hair oils from plants, nuts, and animal fats, a practice deeply intertwined with textured hair heritage.

What Historical Records Illuminate Plant Use for Hair in the Diaspora?
Historical records show plant use for hair in the diaspora as an act of heritage preservation, adapting African botanicals to new environments for textured hair care.

Moisturize
Meaning ❉ Moisturize is the act of introducing and retaining water in the hair shaft, vital for textured hair's health and deeply rooted in ancestral care traditions.

How Do Historical African Hair Rituals Connect to Modern Textured Hair Care?
Historical African hair rituals connect to modern textured hair care through a living heritage of deep cultural reverence, protective practices, and natural ingredient use.

How Do Historical Black Hair Practices Shape Modern Care Regimens?
Historical Black hair practices shape modern care regimens by instilling enduring wisdom about protective styling, natural ingredients, and holistic well-being, deeply rooted in textured hair heritage.

African Hair Sun Adaptation
Meaning ❉ African Hair Sun Adaptation describes the unique biological and cultural resilience of coiled hair against solar radiation.

Which Traditional Ingredients Support Textured Hair Moisture?
Traditional ingredients for textured hair moisture, like shea butter and honey, offer deep hydration rooted in centuries of heritage.

Which Traditional Ingredients Protected Textured Hair from Environmental Elements?
Ancestral practices using plant oils and butters provided textured hair a protective barrier against environmental damage.

What Historical Examples Show the Resilience of Textured Hair Care?
Historical examples illuminate how textured hair care, from ancient protective styles to natural ingredient use, has consistently embodied cultural preservation and self-affirmation.

What Historical Ingredients Offered Moisture for Textured Hair?
Historical moisture for textured hair came from ancestral butters and oils like shea, coconut, and castor, rooted in deep heritage.

African Climate Adaptation
Meaning ❉ African Climate Adaptation, concerning hair, delineates ancestral knowledge and biological evolution of textured hair to environmental conditions.

What Historical Significance Did Hair Oiling Hold in African Heritage?
Hair oiling in African heritage signifies profound cultural connection, protective care, and ancestral wisdom for textured hair across generations.

How Did Ancient African Traditions Inform Modern Textured Hair Oiling Practices?
Ancient African traditions deeply inform modern textured hair oiling through inherited wisdom of protection and nourishment.
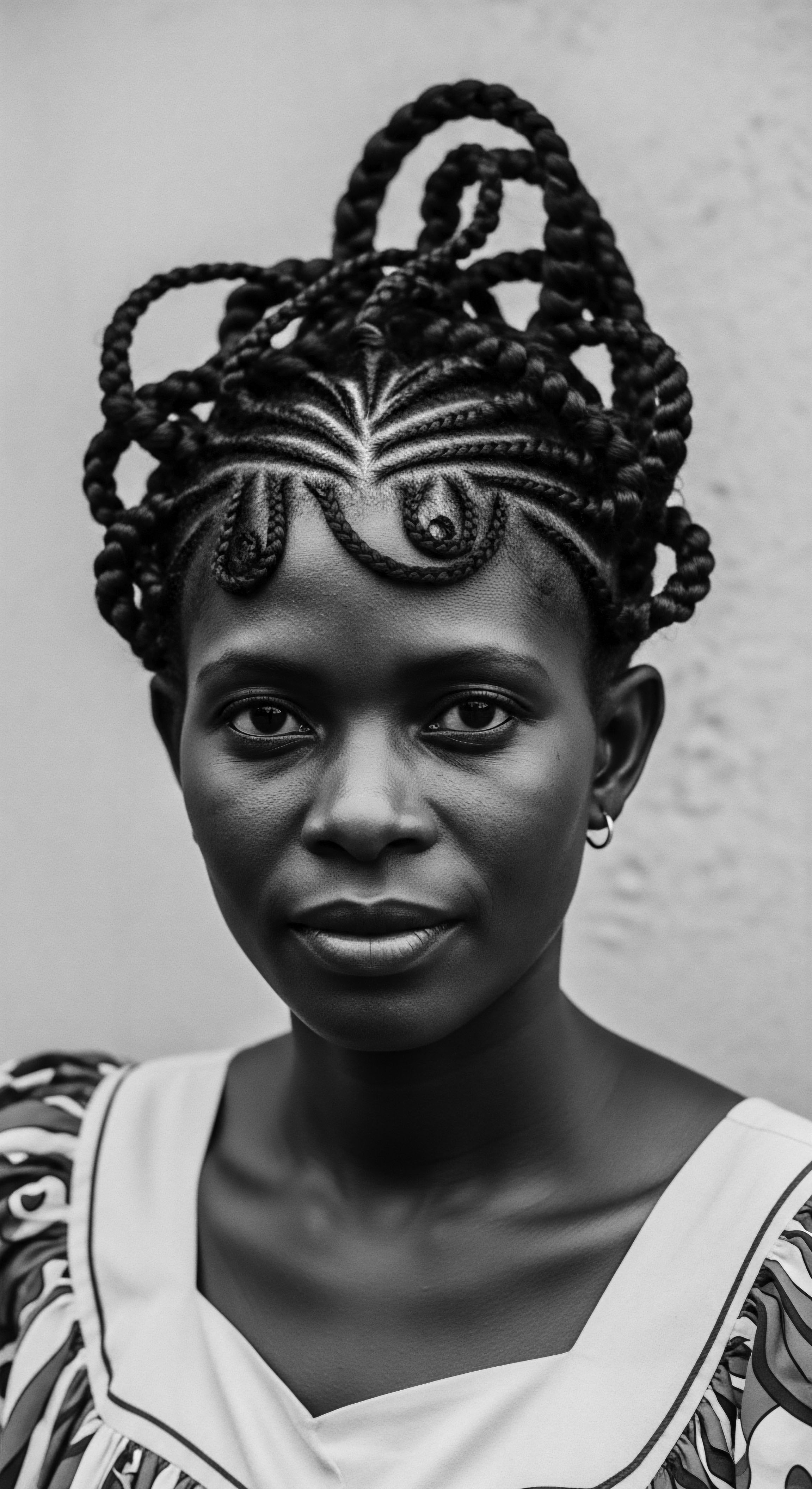

What Historical Moisture Practices Aid Textured Hair?
Historical moisture practices for textured hair centered on natural emollients and protective styles, rooted in ancestral heritage.

What Historical Care Practices Addressed Textured Hair’s Unique Scalp Needs?
Historical scalp care practices for textured hair, rooted in ancestral wisdom, prioritized natural ingredients and protective styling to foster scalp health and identity.
Why Do African Traditions Prioritize Natural Oils for Textured Hair?
African traditions prioritize natural oils for textured hair because of its unique biology and cultural heritage.
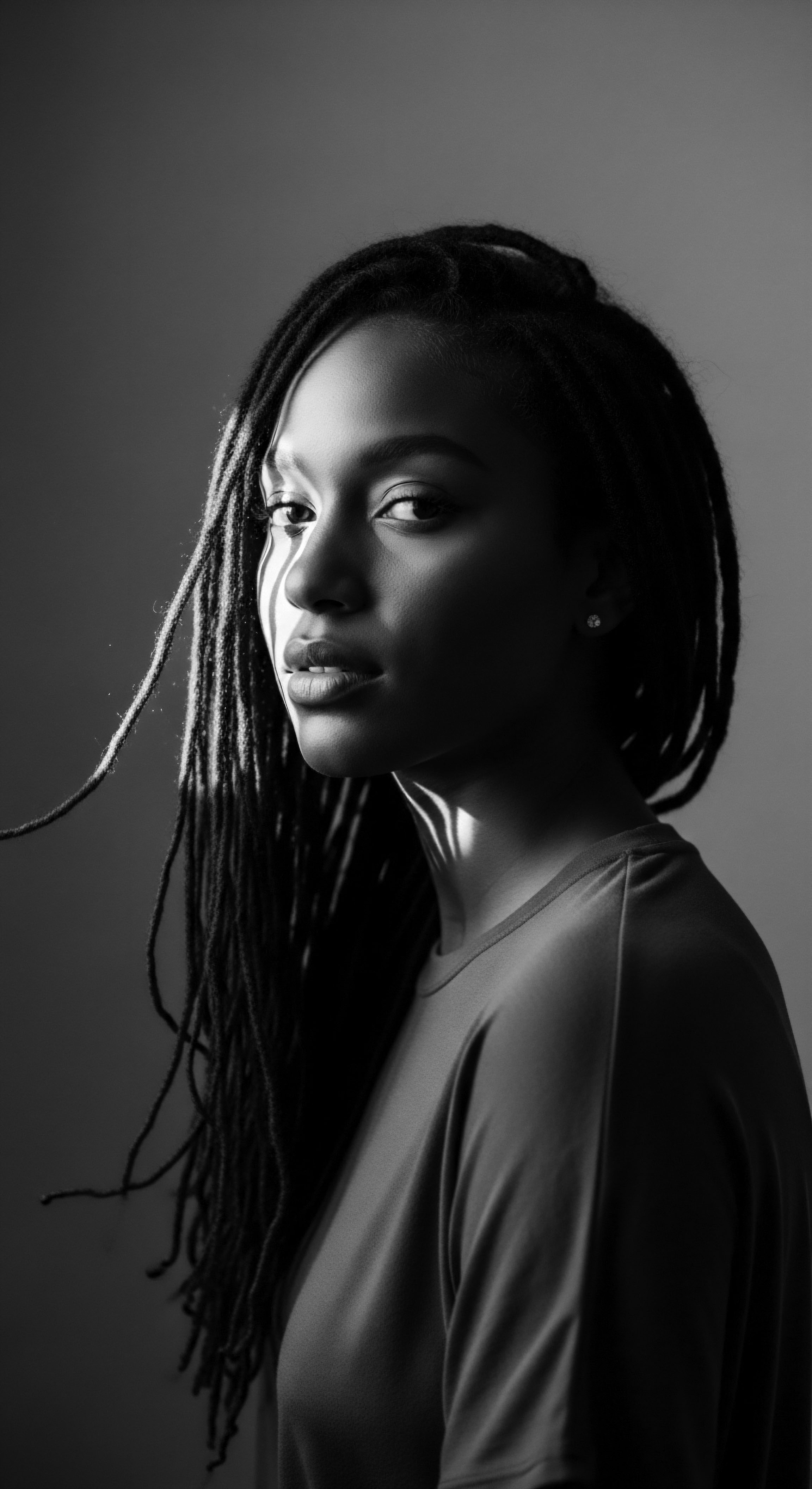

What Cultural Significance Does Hair Oiling Hold within Black Hair Heritage?
Hair oiling honors Black hair heritage, deeply connecting ancestral wisdom with textured hair's resilience and vitality.
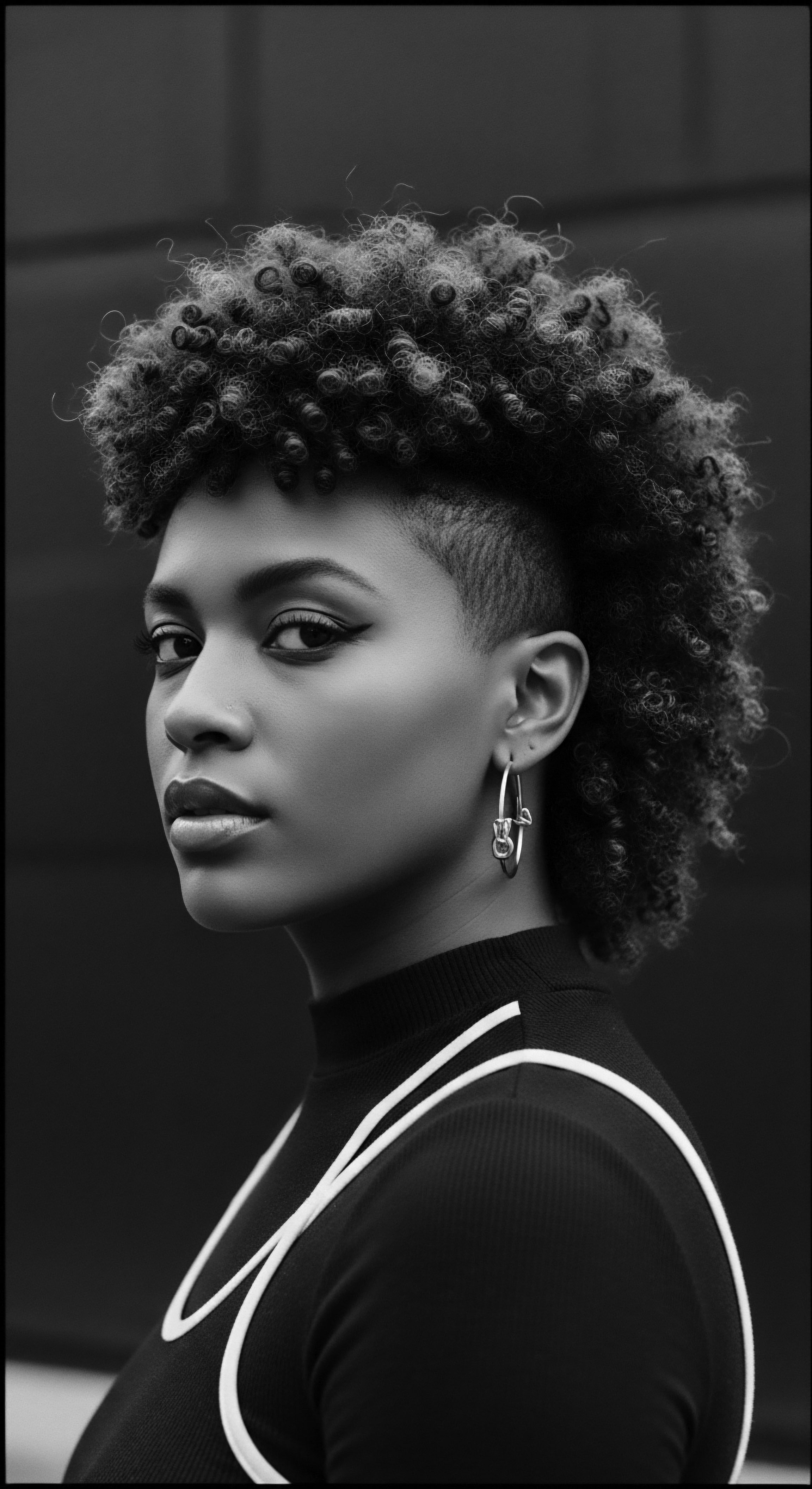

What Challenges to Scalp Health Have Textured Hair Communities Faced Throughout History?
Textured hair communities have faced historical scalp health challenges stemming from forced assimilation, harmful chemical processes, and limited scientific understanding, which ancestral wisdom and modern insights are working to overcome.
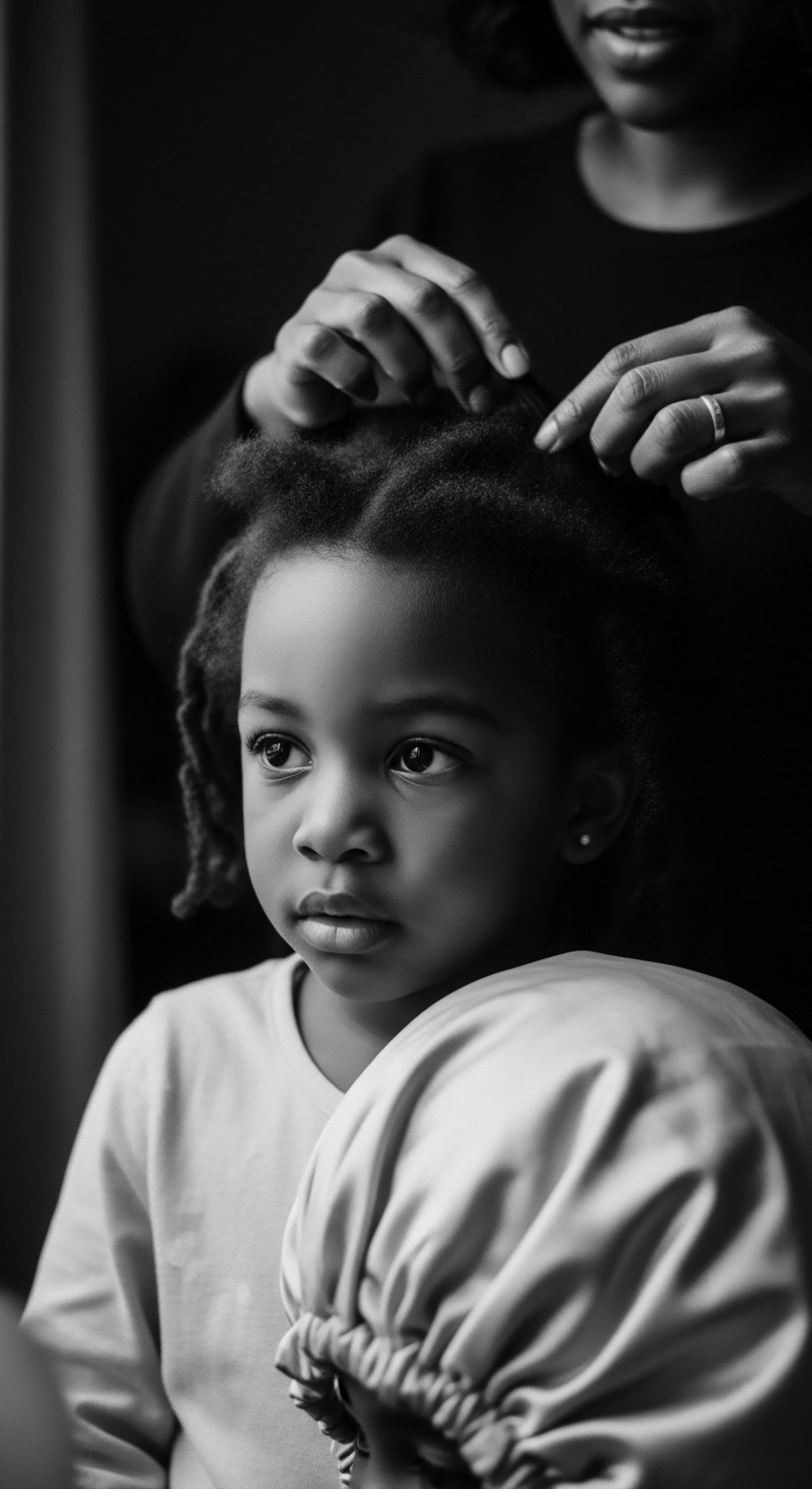

What Ancestral Practices Influence Modern Textured Hair Care with Plant Oils?
Ancestral plant oils influence modern textured hair care by providing a heritage of botanical knowledge, specific applications, and a profound connection to cultural identity.

How Did Hair Care Practices in the African Diaspora Adapt to Preserve Heritage?
African diaspora hair care adapted by preserving ancestral styles and ingredients, transforming them into symbols of resilience and identity.

In What Ways Did Ancient Wisdom Inform the Use of Natural Ingredients for Textured Hair?
Ancient wisdom for textured hair centered on natural ingredients and holistic care, a testament to enduring heritage.

Hair Bio-Cultural Adaptation
Meaning ❉ Hair Bio-Cultural Adaptation explains how hair’s biology and cultural practices co-evolved, reflecting heritage and environmental responses, especially for textured hair.

Heritage Remedies
Meaning ❉ Heritage Remedies are ancestral practices and ingredients for textured hair care, embodying cultural wisdom and historical resilience.

What Historical Care Rituals Shaped Textured Hair?
Historical care rituals for textured hair, rooted in ancestral wisdom, prioritized natural ingredients and protective styling to preserve cultural identity.

How Did Ancient Oils Shape Hair Care Heritage?
Ancient oils nurtured textured hair, serving as ancestral moisture sealants and cultural symbols across heritage traditions.

What Historical Knowledge Shapes Textured Hair Cleansing Practices?
Historical knowledge grounded in African and diaspora traditions profoundly shapes textured hair cleansing, blending ancestral wisdom with resilient adaptations.

What Historical Oils Were Significant in Textured Hair Heritage?
Ancestral oils like shea butter, coconut, castor, and palm deeply nourished textured hair, offering protection and cultural meaning.

How Does Cultural Heritage Influence Modern Textured Hair Oiling?
Cultural heritage profoundly shapes modern textured hair oiling through ancestral wisdom on natural ingredients and community care rituals.

How Did Historical Tools Differ for Caring for Textured Hair?
Historical textured hair tools differed profoundly, evolving from ancestral natural implements for care and cultural expression to later adaptations influenced by systemic oppression.

