How Do Historical Care Rituals Shape Modern Regimens for Textured Hair?
Historical care rituals, born from survival and cultural expression, deeply shape modern textured hair regimens, honoring an unbroken heritage of ancestral wisdom.

Why Did Textured Hair Become a Marker of Oppression after Colonial Contact?
Textured hair became an oppression marker when colonial powers weaponized its unique biology to justify racial hierarchies, diminishing its rich heritage.

Can Historical Oiling Practices Inform Modern Hair Care Regimens for Textured Hair?
Historical oiling practices offer timeless heritage knowledge for modern textured hair care routines.

Can Communal Hair Practices from the past Strengthen Today’s Textured Hair Routines?
Communal hair practices from the past offer deep historical wisdom and shared rituals that profoundly strengthen today’s textured hair routines, anchoring them in heritage.

What Oils Benefit Textured Hair?
Ancestral oils like shea butter, castor, baobab, and marula deeply benefit textured hair, rooted in centuries of Black care heritage.

How Does Traditional Oiling Safeguard Textured Hair?
Traditional oiling safeguards textured hair by deeply nourishing strands, minimizing friction, and sealing moisture, a practice rooted in ancestral wisdom and cultural resilience.

How Did Ancient Oiling Rituals Connect to Community Heritage?
Ancient oiling rituals connected deeply to community heritage, preserving textured hair health and affirming collective identity.

How Did Ancient Cultural Practices Define Hair’s Identity and Care?
Ancient cultural practices rooted textured hair identity and care in communal rituals and natural remedies.
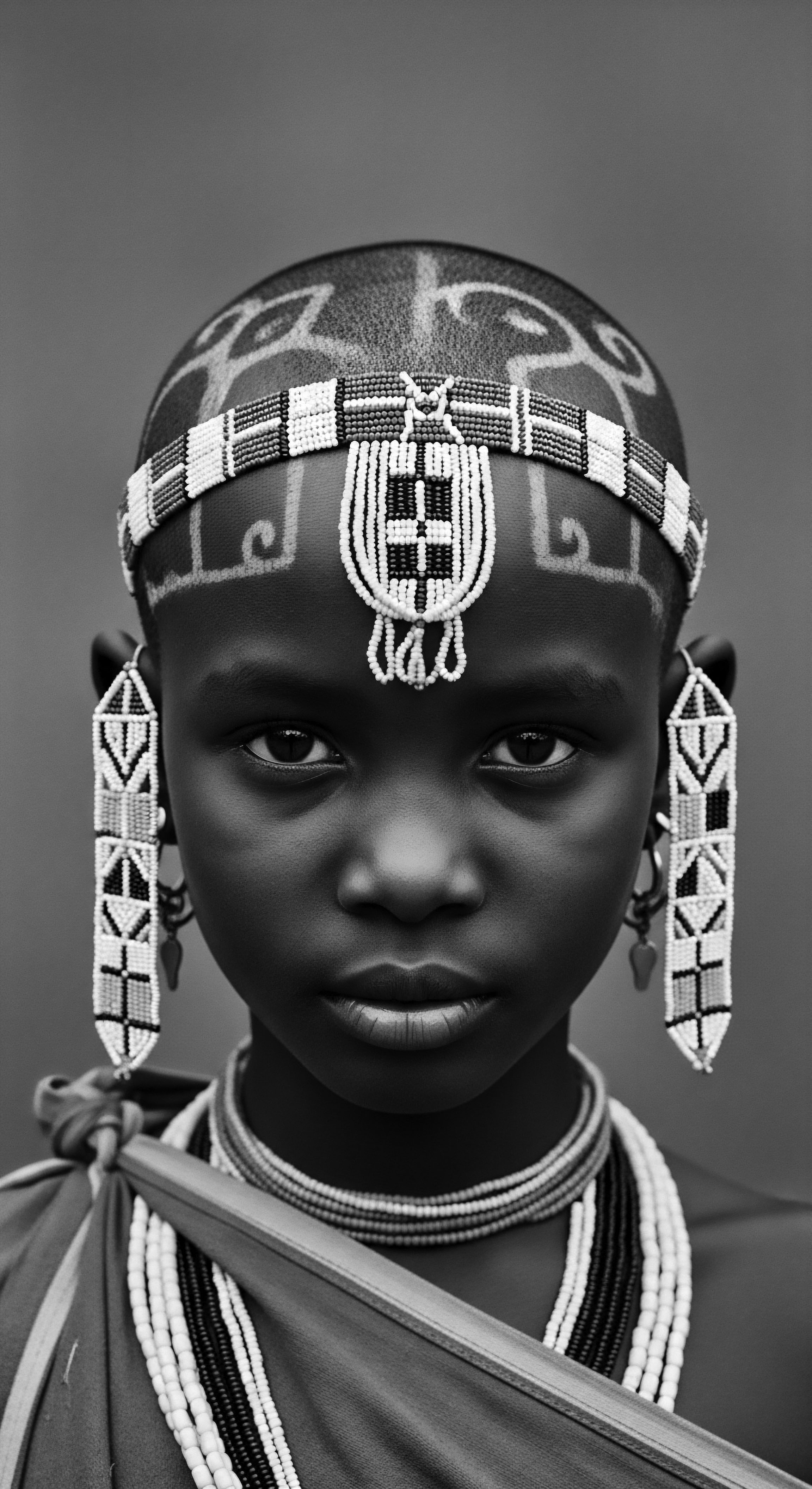

Can Celebrating Traditional Hair Practices Challenge Modern Discrimination?
Celebrating hair practices challenges modern discrimination by affirming cultural identity and ancestral connection.

Textured Hair Consultation
Meaning ❉ A Textured Hair Consultation is a culturally informed, scientifically grounded dialogue assessing hair's unique traits and historical context for optimal health and identity.

What Ancient Plant-Based Ingredients Fortified Textured Hair?
Ancient plant-based ingredients fortified textured hair by hydrating, lubricating, and strengthening strands, building upon a deep ancestral wisdom of natural care.
What Is the Cultural Significance of Textured Hair in Modern Times?
Textured hair signifies deep cultural heritage, linking individuals to ancestral practices and collective identity.

What Ancestral Hair Practices Influenced Modern Textured Hair Cleansing?
Ancestral hair cleansing practices, rooted in natural ingredients and holistic care, laid the groundwork for modern textured hair hygiene and heritage.

Did Ancestral Hair Care Rituals Influence Modern Practices for Textured Hair?
Ancestral hair rituals deeply inform modern textured hair care, preserving a heritage of protection, communal significance, and natural ingredient wisdom.

In What Ways Do Traditional Rituals Influence Textured Hair Care Today?
Traditional rituals offer profound historical wisdom, influencing modern textured hair care through ancestral practices, ingredient use, and cultural identity.

Can Ancient Plant Oils Truly Benefit Modern Textured Hair?
Ancient plant oils offer profound benefits for textured hair, rooted in deep ancestral care and historical practices.
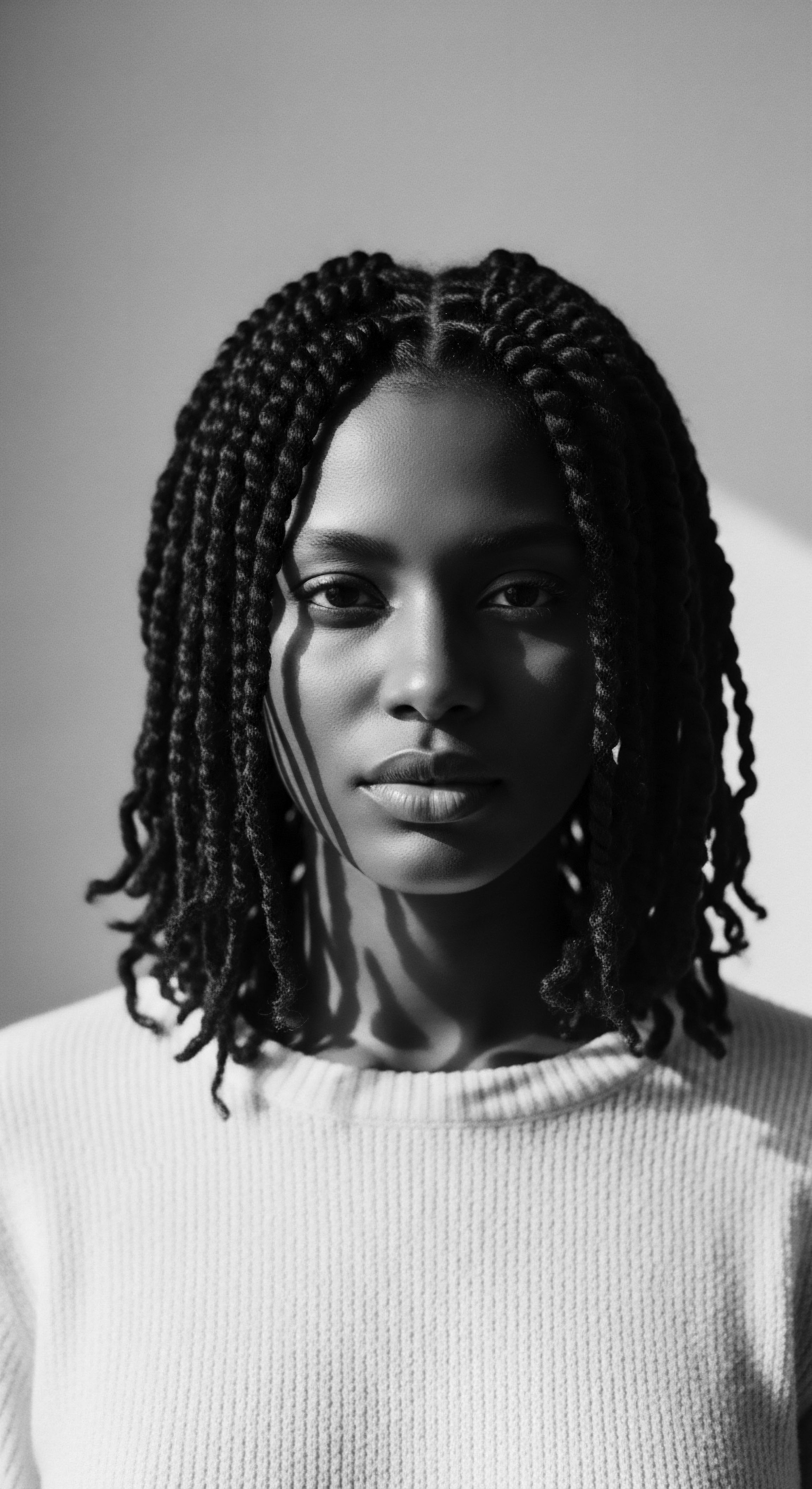

Why Did Textured Hair Become a Marker of Social Standing?
Textured hair’s social standing reflects a complex heritage, shifting from ancestral pride to colonial oppression and modern reclamation.
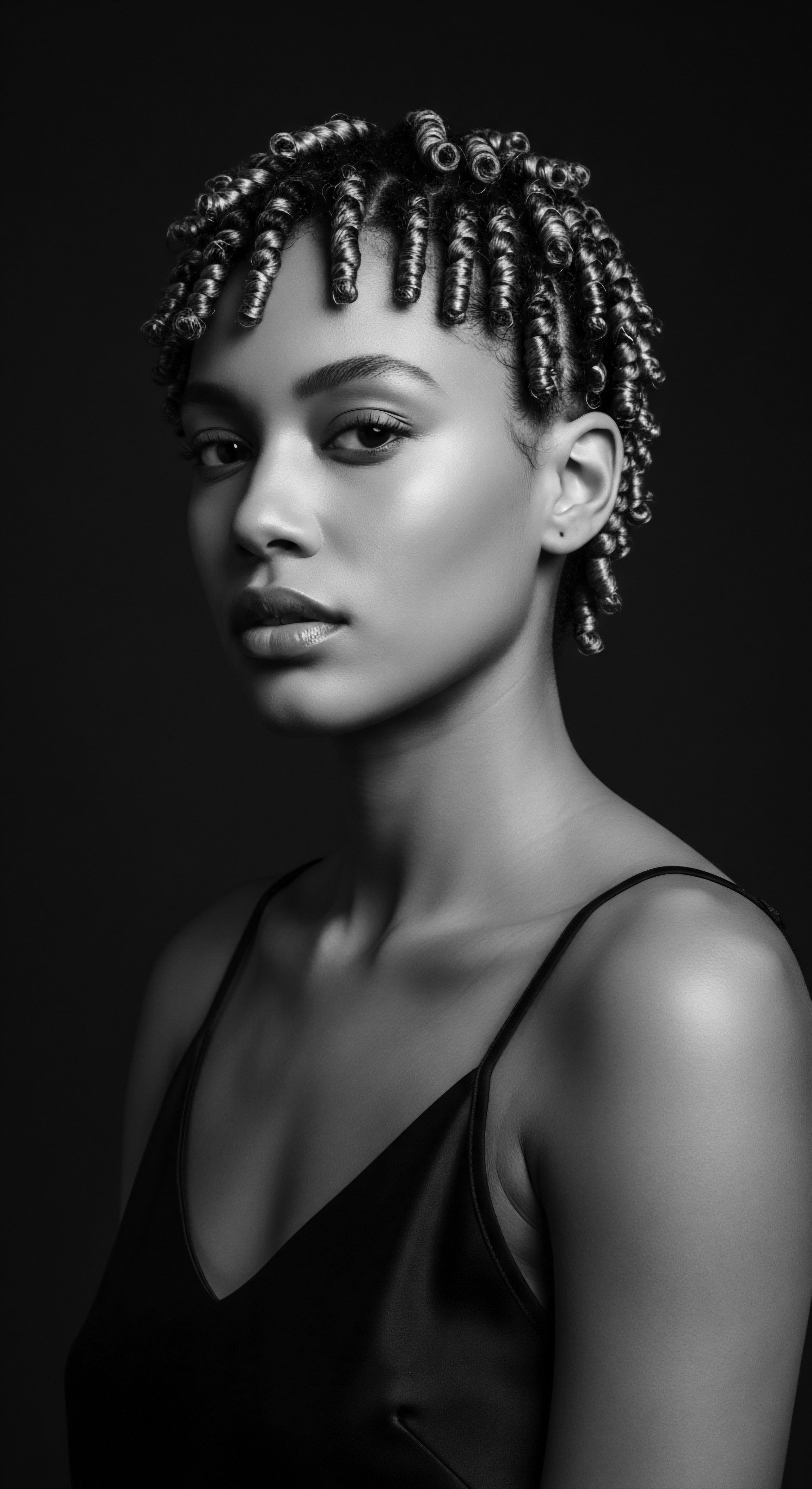

Can Historical Textured Hair Practices Validate Modern Science?
Historical textured hair practices, deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom, offer compelling validation for many principles of modern hair science.

In What Ways Do Ancient Hair Practices Align with Modern Hair Science for Textured Strands?
Ancient hair practices for textured strands align with modern science through intuitive care, protective styling, and natural ingredient use, all rooted in deep heritage.

What Traditional African Ingredients Protect Hair?
Traditional African ingredients protect textured hair by nourishing strands and guarding against damage, rooted in centuries of communal heritage.

What Cultural Significance Do Hair Oiling Practices Hold for Textured Hair Communities?
Hair oiling for textured hair is a living cultural practice embodying ancestral wisdom, identity, and resilience.

Hair Identity Centuries
Meaning ❉ Hair Identity Centuries defines the enduring cultural, historical, and biological significance of hair, particularly textured hair, across generations.
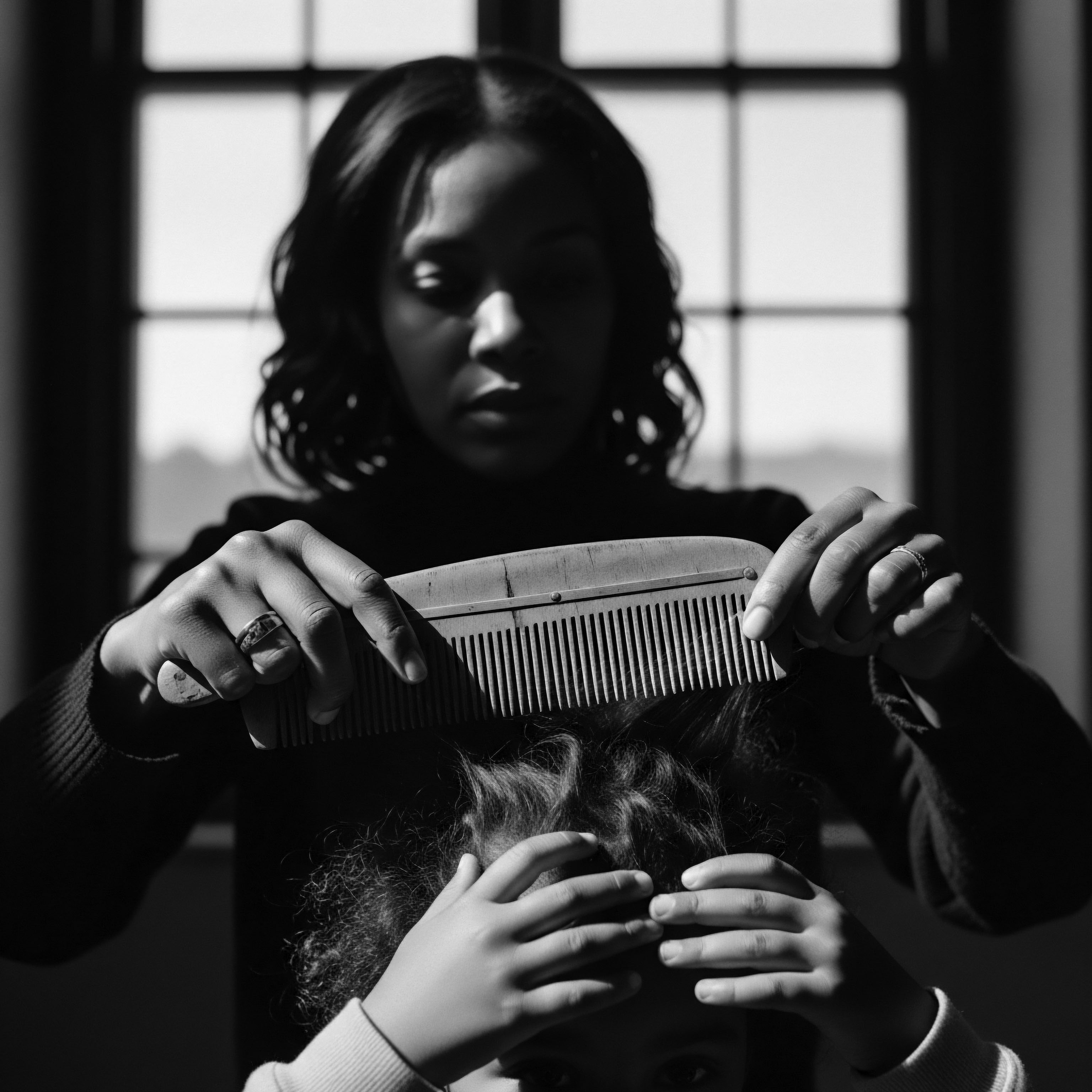

What Ancestral Ingredients Continue to Benefit Modern Textured Hair?
Ancestral ingredients like shea butter and specific oils, historically rooted in Black hair traditions, continue to nourish and protect modern textured hair.
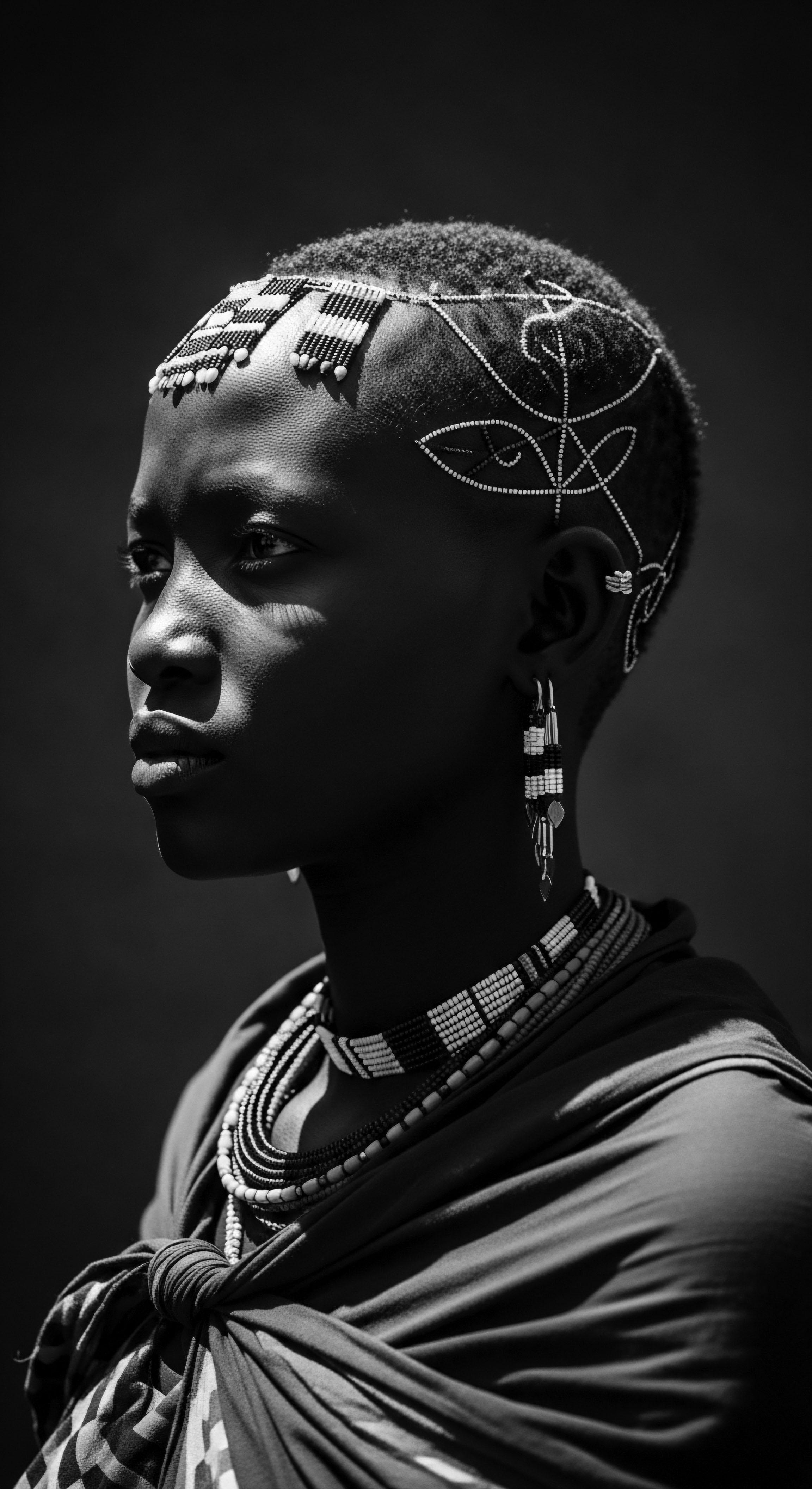

Can Ancient Botanical Care Enhance Modern Textured Hair Regimens?
Ancient botanical care offers powerful, heritage-rooted enhancements for modern textured hair regimens, valuing moisture and protection.
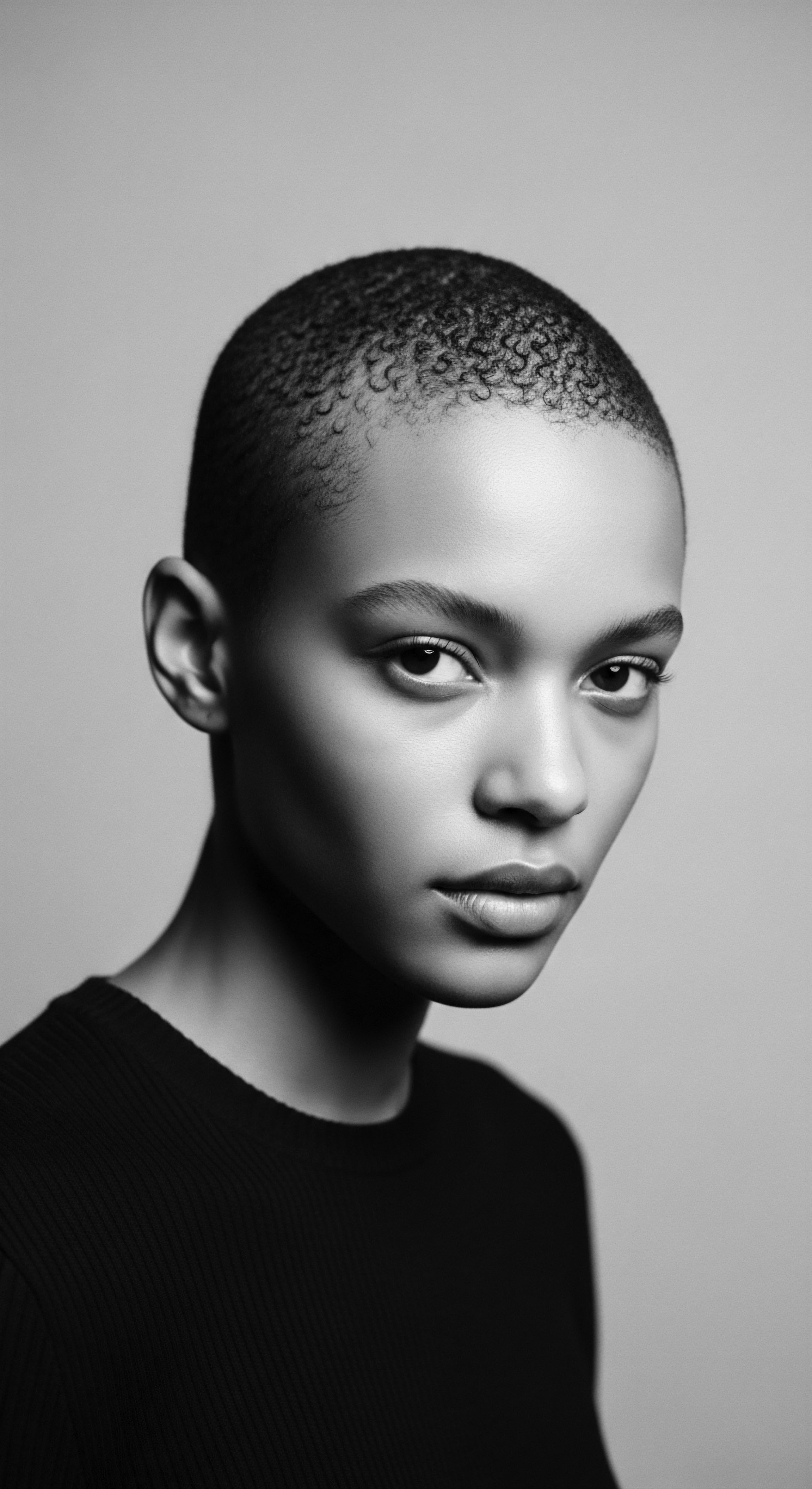

In What Ways Did Pre-Colonial African Societies View Hair as a Marker of Heritage?
Pre-colonial African societies viewed hair as a powerful heritage marker, communicating identity, social rank, and spiritual connection.
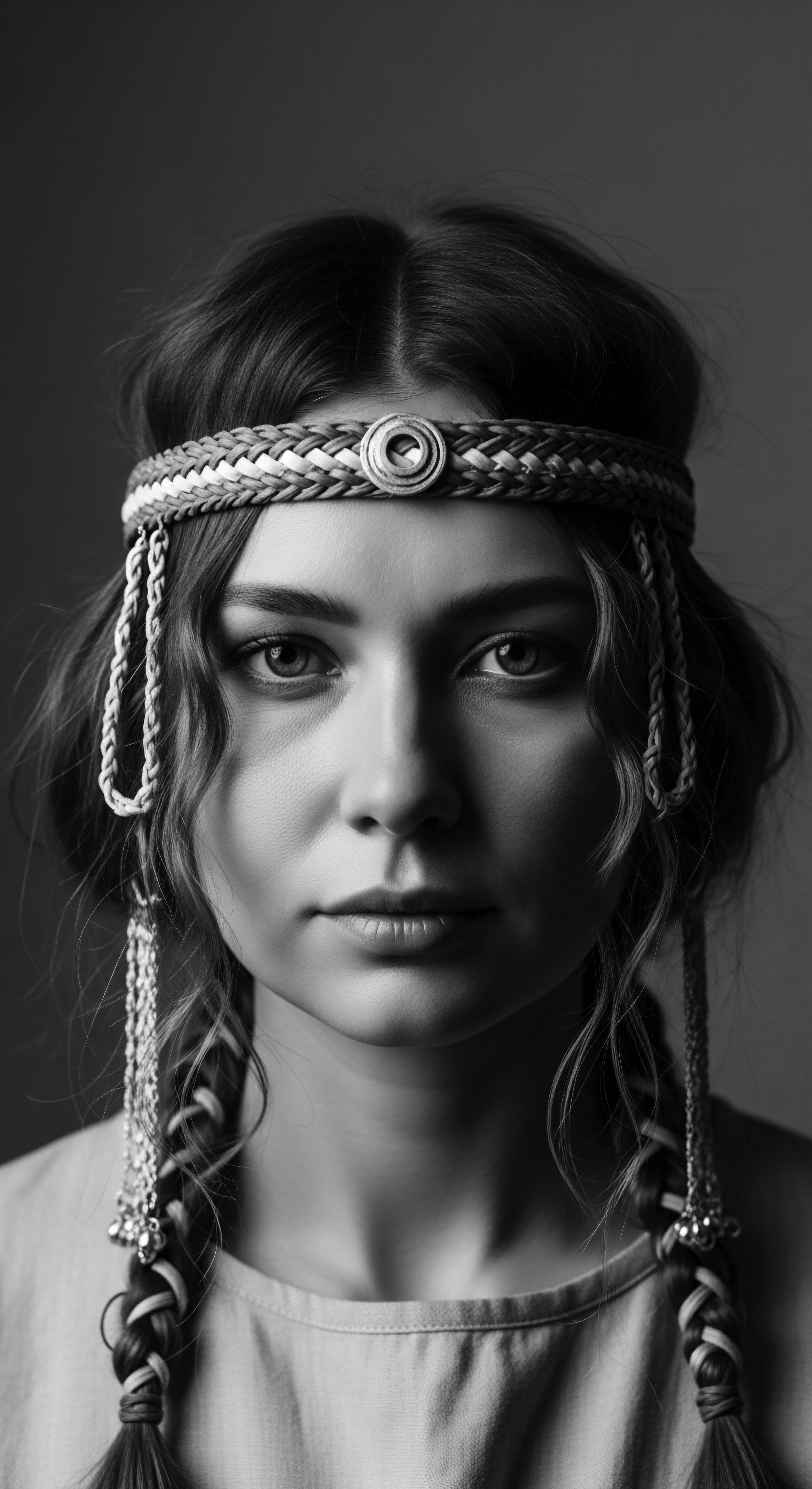

Mixed Hair Biology
Meaning ❉ Mixed Hair Biology describes the confluence of varied hair textures stemming from diverse genetic and ancestral inheritances, especially in mixed-race individuals.

What Ancestral Hair Rituals Connect to Community Identity?
Ancestral hair rituals are profound expressions of community identity, embodying historical wisdom, resilience, and cultural continuity for textured hair heritage.

Can Traditional Care Rituals Inform Today’s Textured Hair Regimens for Better Health?
Traditional care rituals offer profound heritage-infused insights for today's textured hair health, prioritizing natural methods and community wisdom.
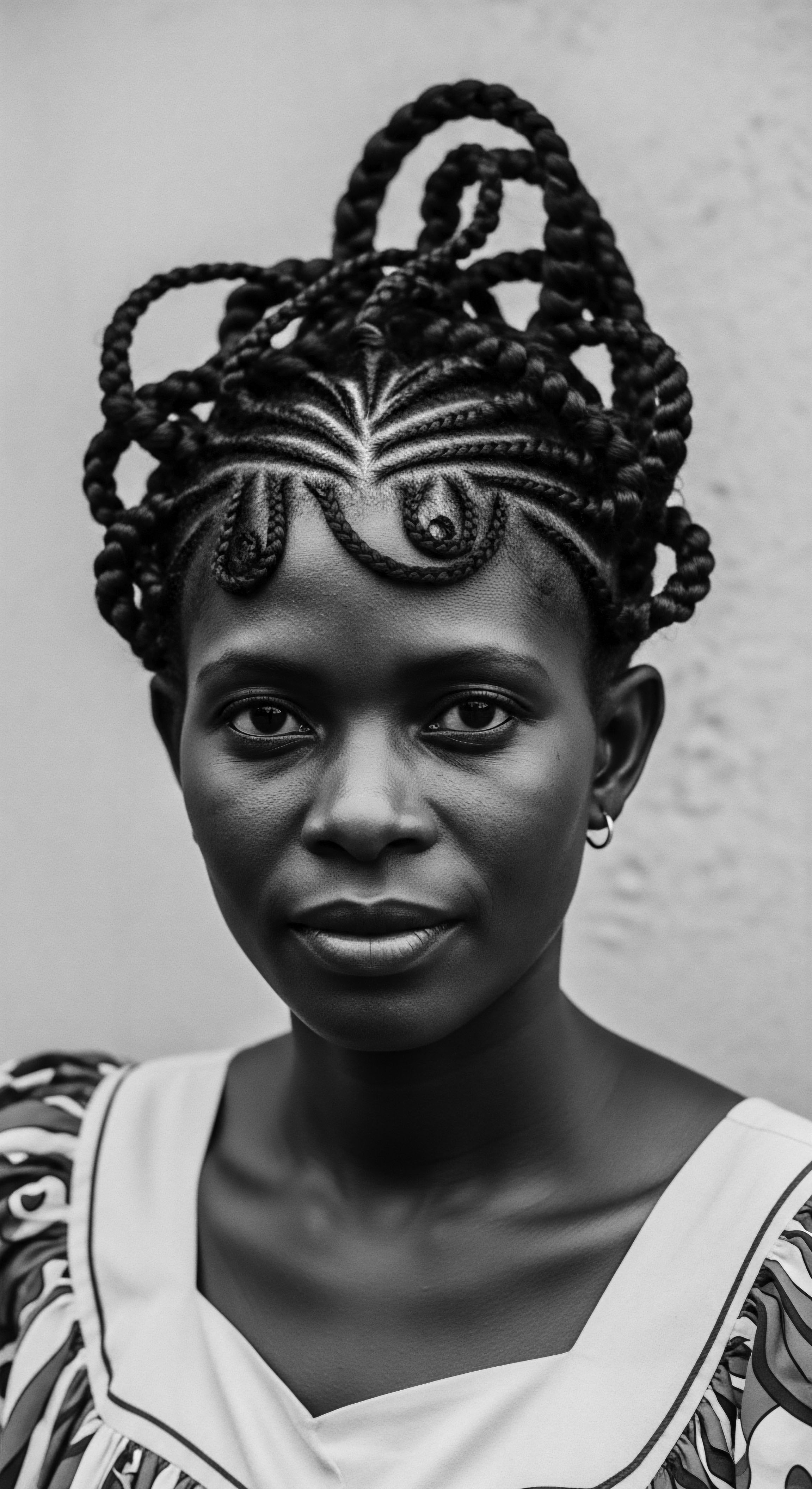

How Did Ancient Botanicals Protect Textured Hair at Night?
Ancient botanicals protected textured hair nightly through oils and protective styles, preserving moisture and honor, a deep thread of heritage.

