Can Modern Science Validate Ancient African Hair Care Practices for Textured Hair?
Modern science often validates ancient African hair care practices, confirming their efficacy and deep connection to textured hair heritage.

What Traditional Methods Supported Textured Hair Biology?
Traditional methods supported textured hair biology through natural ingredients, protective styles, and communal rituals, all rooted in cultural heritage.

Hair Protection Methods
Meaning ❉ Hair Protection Methods are practices and styles that shield textured hair from damage, reduce manipulation, and preserve its cultural and historical meaning.
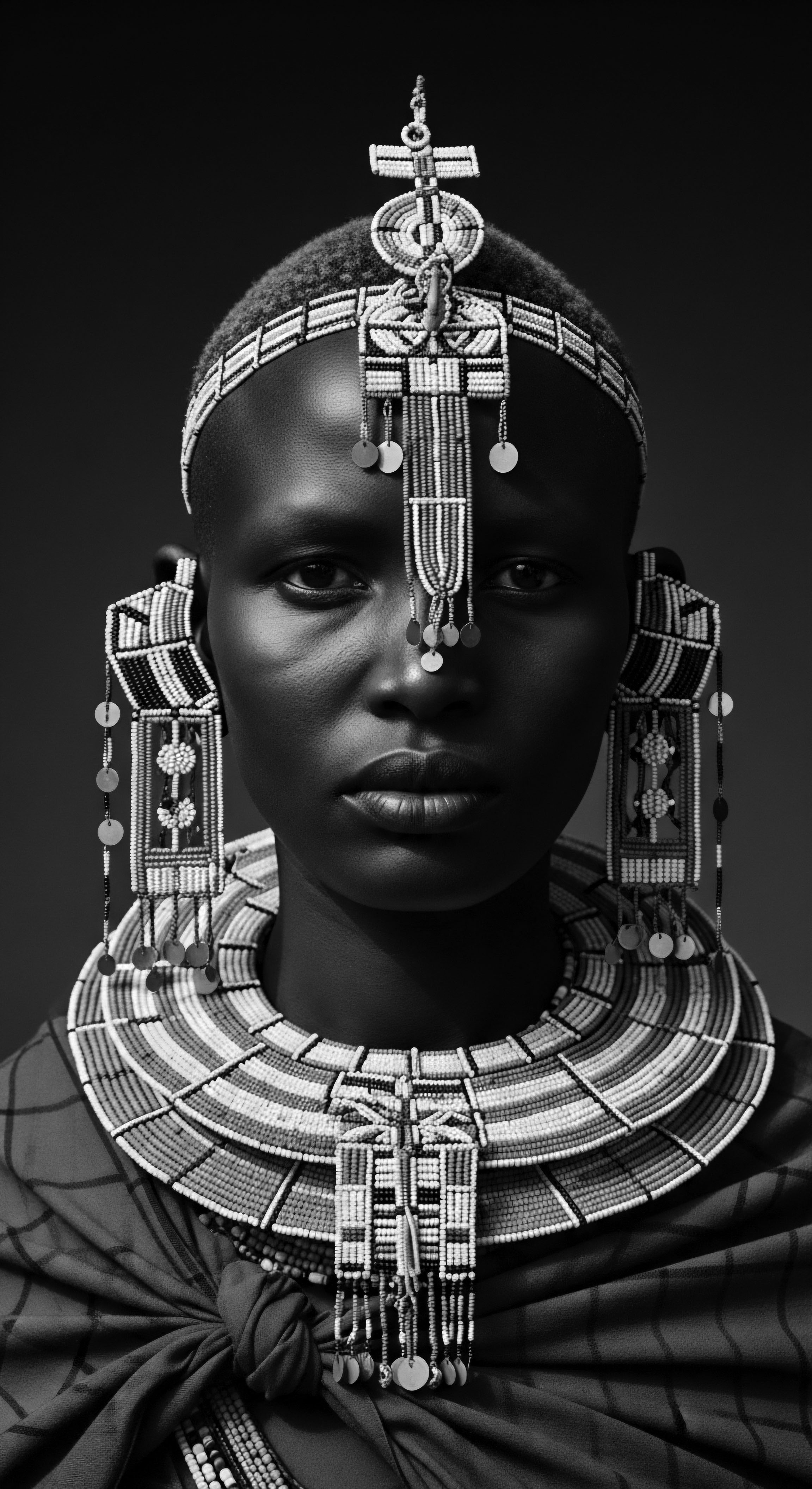

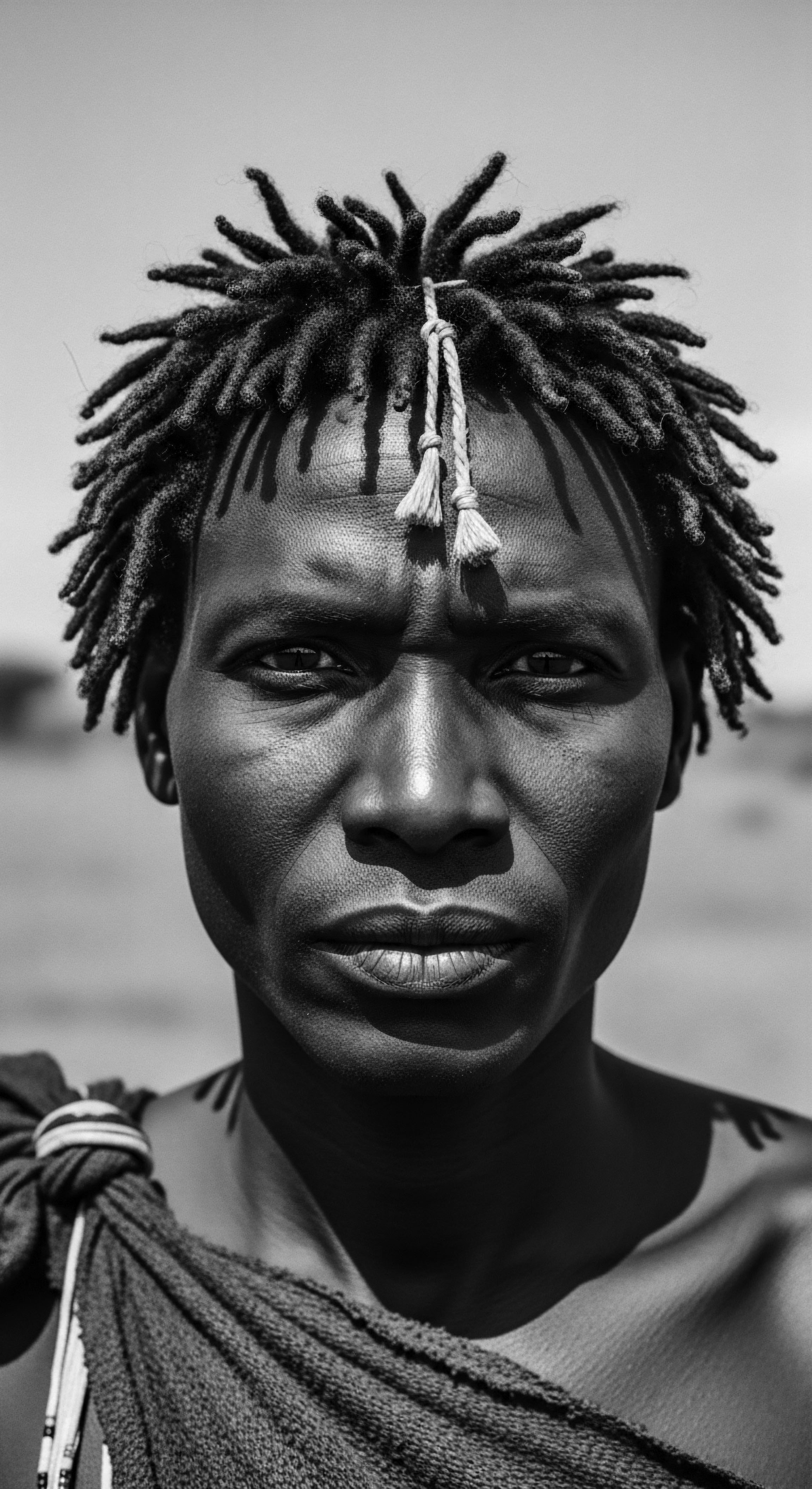
Ovahimba Hair Rituals
Meaning ❉ The Ovahimba Hair Rituals are ancestral practices of care and adornment, using Otjize paste to signify identity and cultural resilience.

How Did Ancestral Practices Influence Modern Textured Hair Care?
Ancestral practices shaped modern textured hair care by providing foundational knowledge of hair biology, protective styling, and holistic well-being, deeply rooted in heritage.

Textured Hair Polynesia
Meaning ❉ Textured Hair Polynesia encompasses the diverse hair textures of Pacific Islanders, their ancestral care practices, and profound cultural significance.

How Did Historical Hair Care Methods Influence Modern Textured Hair Products?
Historical hair care methods, deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom, profoundly influence modern textured hair products by providing foundational ingredients and care philosophies that honor its unique heritage.

Afro-Textured Heritage
Meaning ❉ Afro-Textured Heritage signifies the deep cultural, historical, and biological significance of tightly coiled hair in Black and mixed-race communities.

How Did Ancient Cultures Protect Textured Hair from Damage?
Ancient cultures protected textured hair through natural oils, protective styles, and nighttime coverings, deeply rooted in heritage and community wisdom.

Hair Culture History
Meaning ❉ Hair Culture History examines the deep significance of hair as a cultural marker, identity symbol, and ancestral legacy, especially for textured hair.

Can Ancient Hair Oiling Rituals Offer Lessons for Modern Textured Hair Care?
Ancient hair oiling rituals offer profound lessons for modern textured hair care, connecting ancestral wisdom with contemporary needs.

Kalahari Botanicals
Meaning ❉ Kalahari Botanicals refers to desert-adapted plants, particularly Kalahari Melon, and their historical use in traditional hair care and wellness by indigenous Southern African communities.

Can Science Explain the Cultural Significance of Oiling Textured Hair?
Science validates the cultural significance of oiling textured hair by illuminating its ancestral roots in protection, communal bonding, and identity.

Saharan Hair Care
Meaning ❉ Saharan Hair Care is a legacy of traditional practices from Africa's arid regions, honoring textured hair through indigenous wisdom and communal rituals.

In What Ways Did Hair Practices Symbolize Identity in African Heritage?
African hair practices symbolized identity through lineage, social standing, spiritual connection, and resistance against oppression.

What Historical Examples Show the Resilience of Textured Hair Heritage?
Textured hair heritage demonstrates resilience through ancient cultural symbolism, resistance during oppression, and contemporary movements for identity and acceptance.

Cultural Hair Vitality
Meaning ❉ Cultural Hair Vitality is the profound connection between textured hair and ancestral heritage, embodying identity, history, and community resilience.

What Traditional Ingredients Benefited Textured Hair’s Moisture Needs?
Ancestral wisdom leveraged natural oils and butters, like shea and coconut, to deeply hydrate textured hair, honoring its unique heritage.

How Do Ancient Hair Practices Protect Textured Hair?
Ancient hair practices protected textured hair through ancestral protective styles, natural botanical ingredients, and communal care rituals, preserving its heritage.

Hair Discrimination Jamaica
Meaning ❉ Hair discrimination in Jamaica is the prejudicial treatment of individuals based on their natural textured hair and traditional styles, rooted in colonial legacies.

Which Traditional African Oils Offer Specific Benefits for Textured Hair Health?
Traditional African oils offer textured hair profound moisture, strength, and protection, reflecting a deep ancestral heritage of care and resilience.

How Does Contemporary Science Affirm the Wisdom of Traditional Textured Hair Cleansing?
Contemporary science affirms traditional textured hair cleansing by revealing the biological efficacy and scalp health benefits of ancestral ingredients and practices.

What Ancestral Practices Continue to Inform Modern Textured Hair Care?
Ancestral practices deeply inform modern textured hair care, connecting contemporary routines to a rich heritage of resilience and wisdom.

Can Historical Hair Practices Inform Modern Textured Hair Identity?
Historical hair practices provide a profound blueprint for modern textured hair identity, grounding it in a rich heritage of self-expression and cultural resilience.

What Historical Evidence Supports the Efficacy of Traditional Textured Hair Practices?
Historical evidence confirms traditional textured hair practices, deeply rooted in African heritage, effectively maintained hair health and conveyed cultural identity for millennia.

What Ancient African Ingredients Are Still Used for Textured Hair Care?
Ancient African ingredients like shea butter, chebe powder, argan oil, and baobab oil are still used for textured hair care, honoring ancestral wisdom.
Inherited Hair Practices
Meaning ❉ Inherited Hair Practices are intergenerational care methods and cultural understandings of hair, deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom and the biological essence of textured hair.
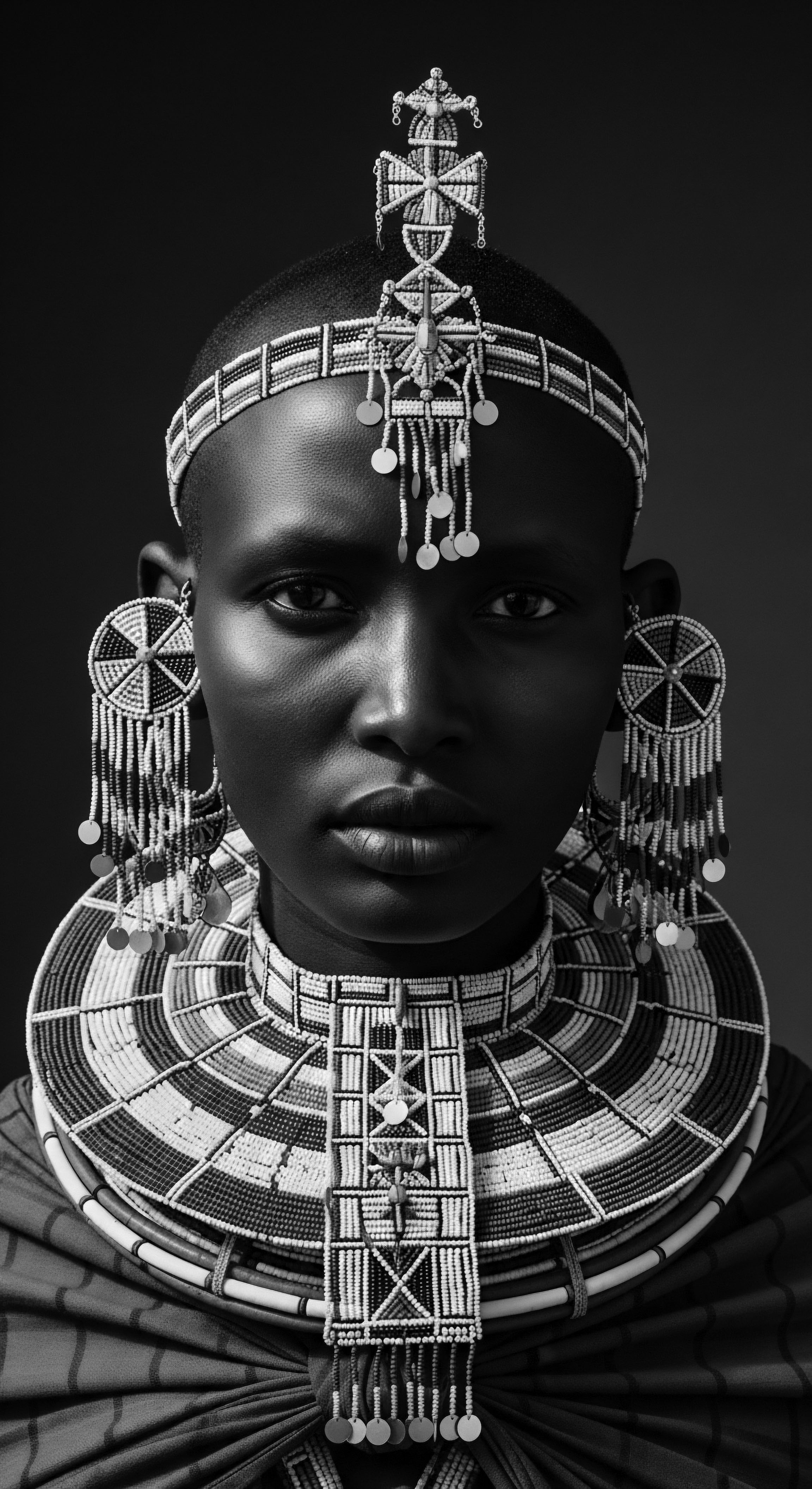

Ancestral Hair Identity
Meaning ❉ Ancestral Hair Identity is the inherent connection between textured hair and its deep historical, cultural, and biological legacies.

How Did Ancient Cultures Manage Textured Hair?
Ancient cultures managed textured hair through natural ingredients, protective styles, and rituals reflecting deep heritage and communal identity.

