
Can Traditional Hair Practices Offer Solutions for Modern Textured Hair Challenges?
Traditional hair practices offer robust solutions for modern textured hair challenges, deeply rooted in ancestral heritage and cultural wisdom.
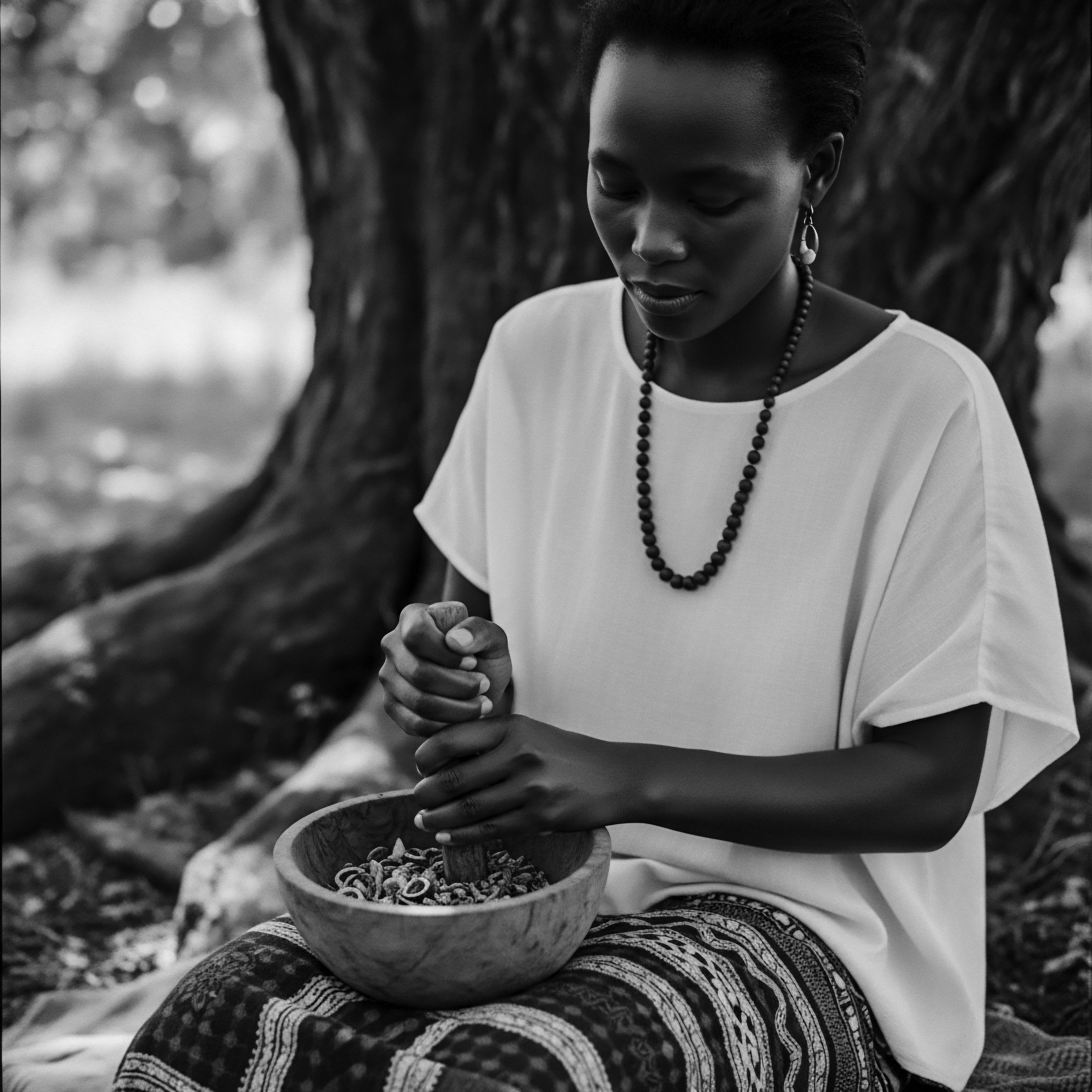

What Historical Hair Care Practices Protected Textured Strands?
Historical hair care protected textured strands through protective styling, natural ingredients, and mindful rituals deeply rooted in heritage.

Scalp Health History
Meaning ❉ The Scalp Health History is a profound delineation of the ancestral, cultural, and scientific journey of scalp care, especially for textured hair.

Textured Hair Safeguarding
Meaning ❉ Textured Hair Safeguarding is the holistic preservation of textured hair's health, structure, and cultural significance, honoring its ancestral roots.

Indigenous Braiding
Meaning ❉ Indigenous Braiding is the ancient, culturally rich practice of interlacing hair, a profound expression of heritage, identity, and protective care for textured hair.

How Did Ancient Styling Practices Influence Modern Textured Hair Care?
Ancient styling practices inform modern textured hair care by providing foundational wisdom on protection, natural ingredients, and holistic hair preservation rooted in heritage.

How Do Braids Protect Textured Hair?
Braids protect textured hair by reducing manipulation and environmental exposure, a practice deeply rooted in ancestral heritage for hair health and cultural identity.

In What Ways Do Historical Hair Care Traditions Continue to Shape Contemporary Beauty for Textured Strands?
Historical hair care traditions profoundly shape contemporary beauty for textured strands by preserving ancestral wisdom, styling techniques, and cultural resilience.

Cultural Hair Value
Meaning ❉ Cultural Hair Value is the profound, inherited significance hair holds as a repository of identity, heritage, and communal wisdom.

In What Ways Did Hair Care Become a Communal Heritage?
Hair care became a communal heritage through shared ancestral knowledge, intergenerational rituals, and collective affirmation of identity.

What Historical Tools Shaped Textured Hair Care Practices?
Historical tools for textured hair care, from ancient combs to the Afro pick, are extensions of ancestral wisdom, shaping identity and community.

Polynesian Hair Traditions
Meaning ❉ Polynesian Hair Traditions define hair as a sacred repository of spiritual power and cultural identity, guiding ancient and modern care practices.

Social Hierarchies
Meaning ❉ Social hierarchies are structured arrangements of power and prestige, often influenced by hair's cultural meaning and historical perceptions.

Zanj Rebellion Hair
Meaning ❉ Zanj Rebellion Hair conceptually designates the enduring spirit of textured hair heritage and identity, symbolizing resilience against historical oppression.

What Historical Hair Tools Connect to Textured Hair Heritage?
Historical hair tools like ancient wide-toothed combs, styling pins, and improvised picks connected textured hair to ancestral care and identity.

How Did Ancestral Communities Protect Textured Hair from Sun?
Ancestral communities protected textured hair from sun using natural oils, strategic coverings, and intricate styles, all rooted in deep heritage.

What Ancient African Ingredients Shape Contemporary Textured Hair Care?
Ancient African ingredients like shea butter, argan oil, and chebe powder deeply moisturize and strengthen textured hair, directly linking contemporary care to ancestral heritage.

What Ancestral Oils Nurtured Textured Hair Heritage?
Ancestral oils like shea butter, palm, and castor oil nourished textured hair, embodying cultural heritage and resilience across generations.

Ethnobotany Namibia
Meaning ❉ Ethnobotany Namibia is the study of ancestral plant knowledge and its cultural significance for textured hair, particularly among indigenous communities like the Himba.

What Traditional Ingredients Nourish Textured Hair across Generations?
Traditional ingredients like shea butter and amla nourish textured hair across generations, preserving a heritage of self-care and cultural identity.
Epistemicide
Meaning ❉ Epistemicide describes the systematic suppression of a group's knowledge systems, particularly ancestral textured hair practices and cultural wisdom.

What Traditional African Practices for Textured Hair Hydration Continue to Hold Cultural Significance?
Traditional African practices hydrate textured hair using natural emollients, protective styling, and communal rituals that continue to honor a rich cultural heritage.
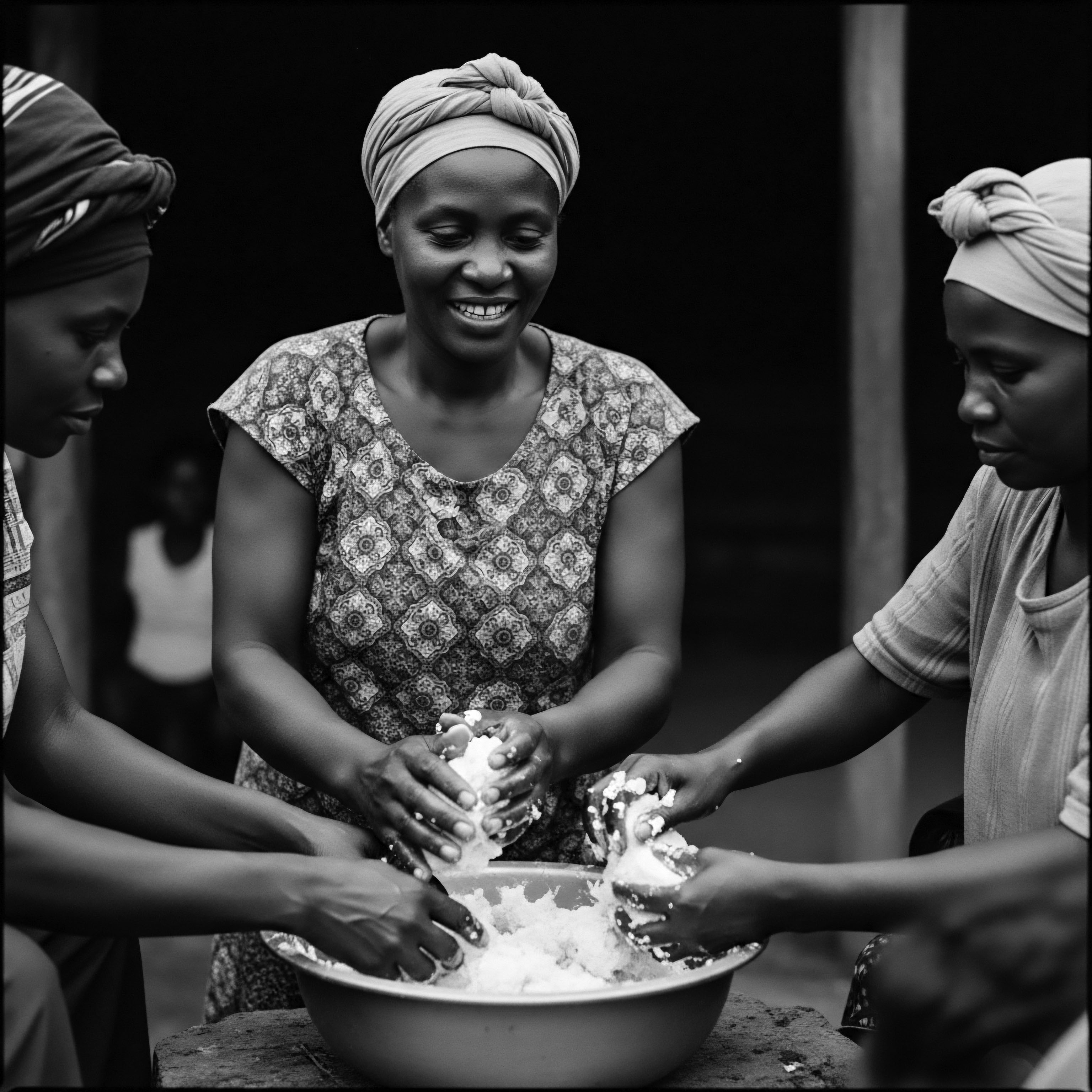

Marula Oil Heritage
Meaning ❉ Marula Oil Heritage defines the enduring cultural significance and traditional use of Marula oil in African textured hair care.

What Historical Hair Care Practices Fortify Textured Hair?
Historical hair care practices fortified textured hair through natural ingredients, protective styling, and holistic, community-rooted rituals that honored its unique biology.
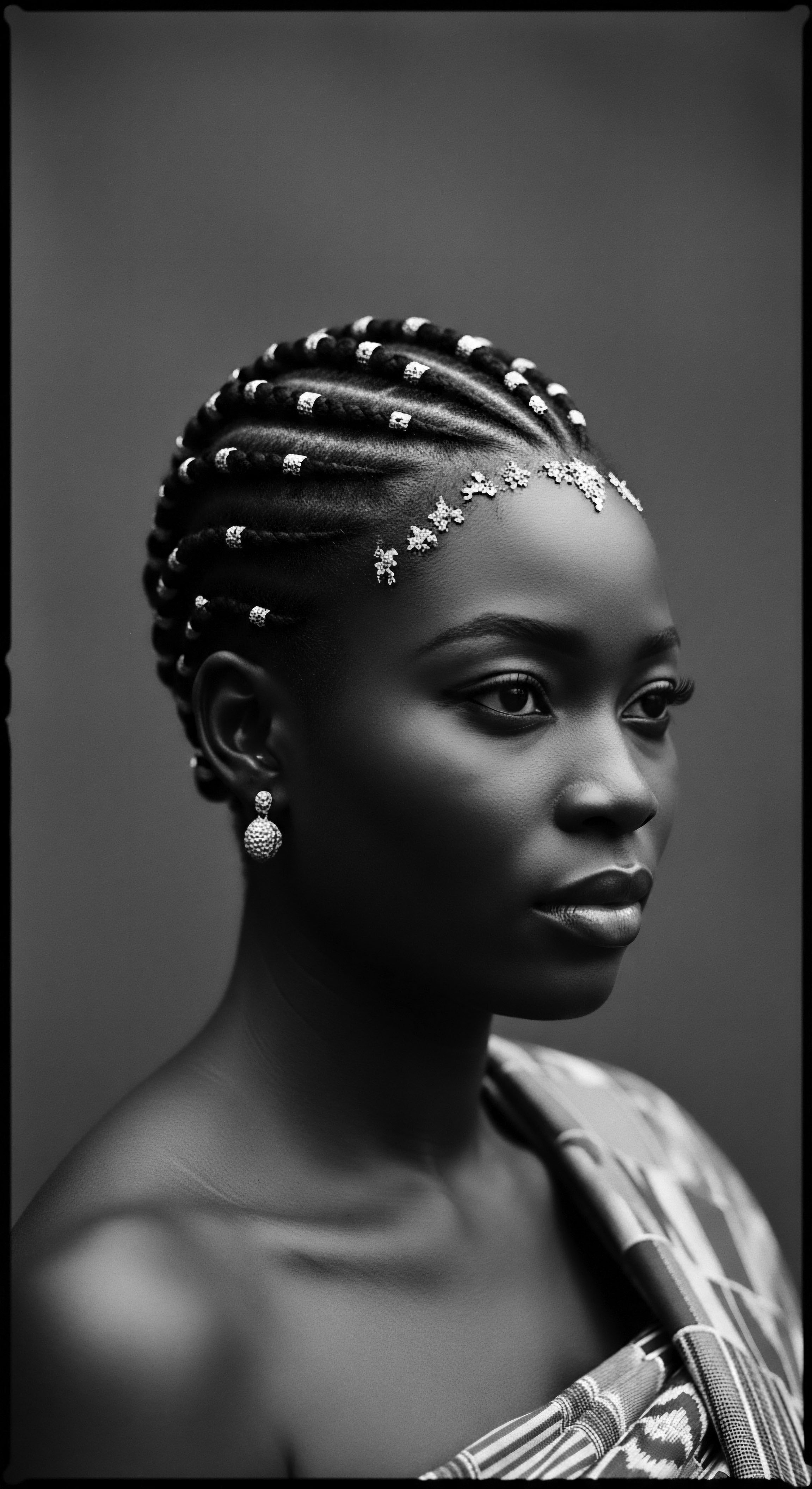

Ancient Hair Coverings
Meaning ❉ Ancient Hair Coverings represent more than mere fabric; they are profound symbols of identity, protection, and cultural resilience for textured hair across history.
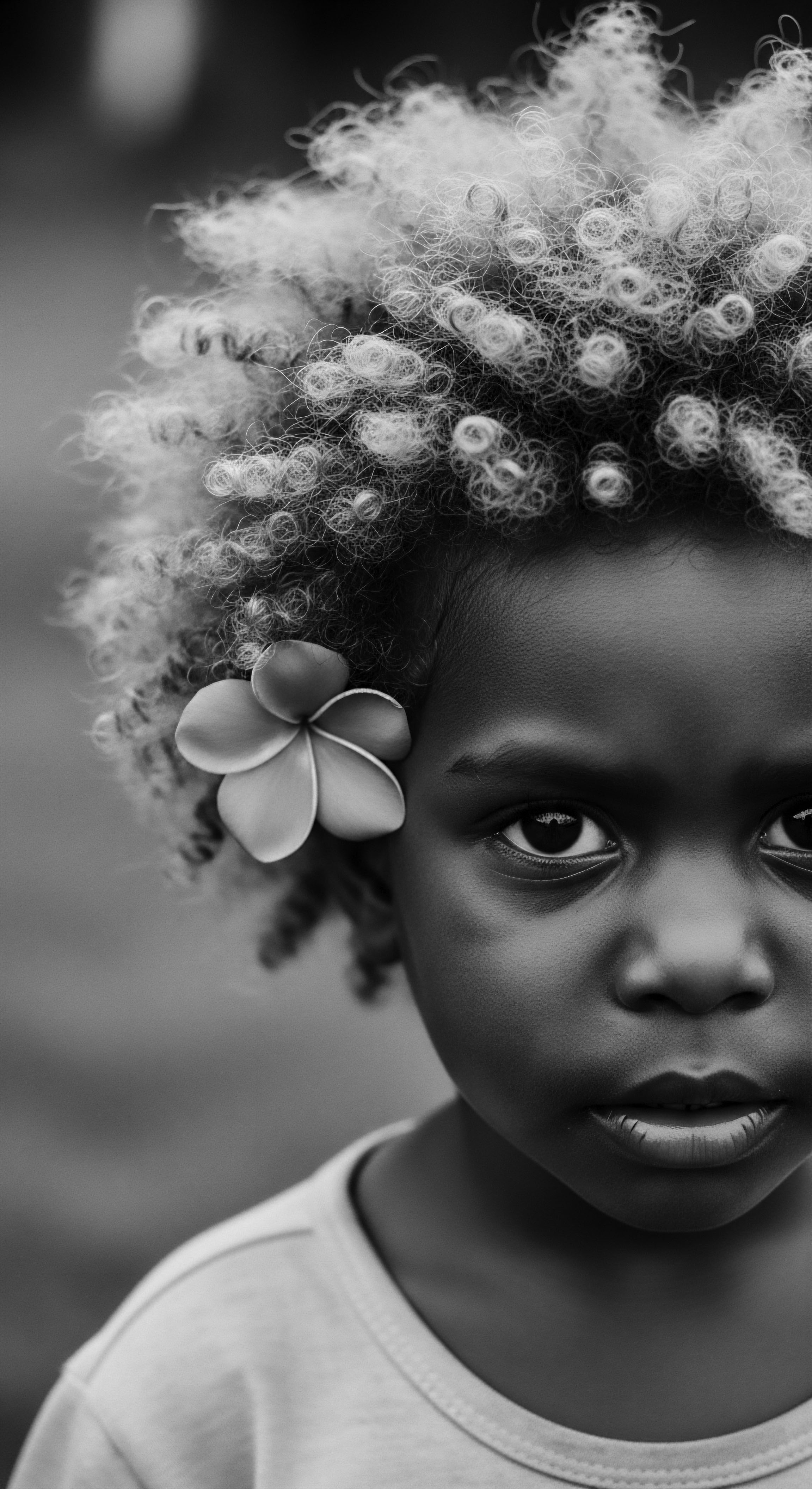

Traditional Beauty Wisdom
Meaning ❉ Traditional Beauty Wisdom is the inherited knowledge system for textured hair care, deeply rooted in ancestral practices, natural observation, and cultural significance.

Historical Hair Rituals
Meaning ❉ Historical Hair Rituals are culturally significant practices of hair care and styling, deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom and collective identity, particularly for textured hair.
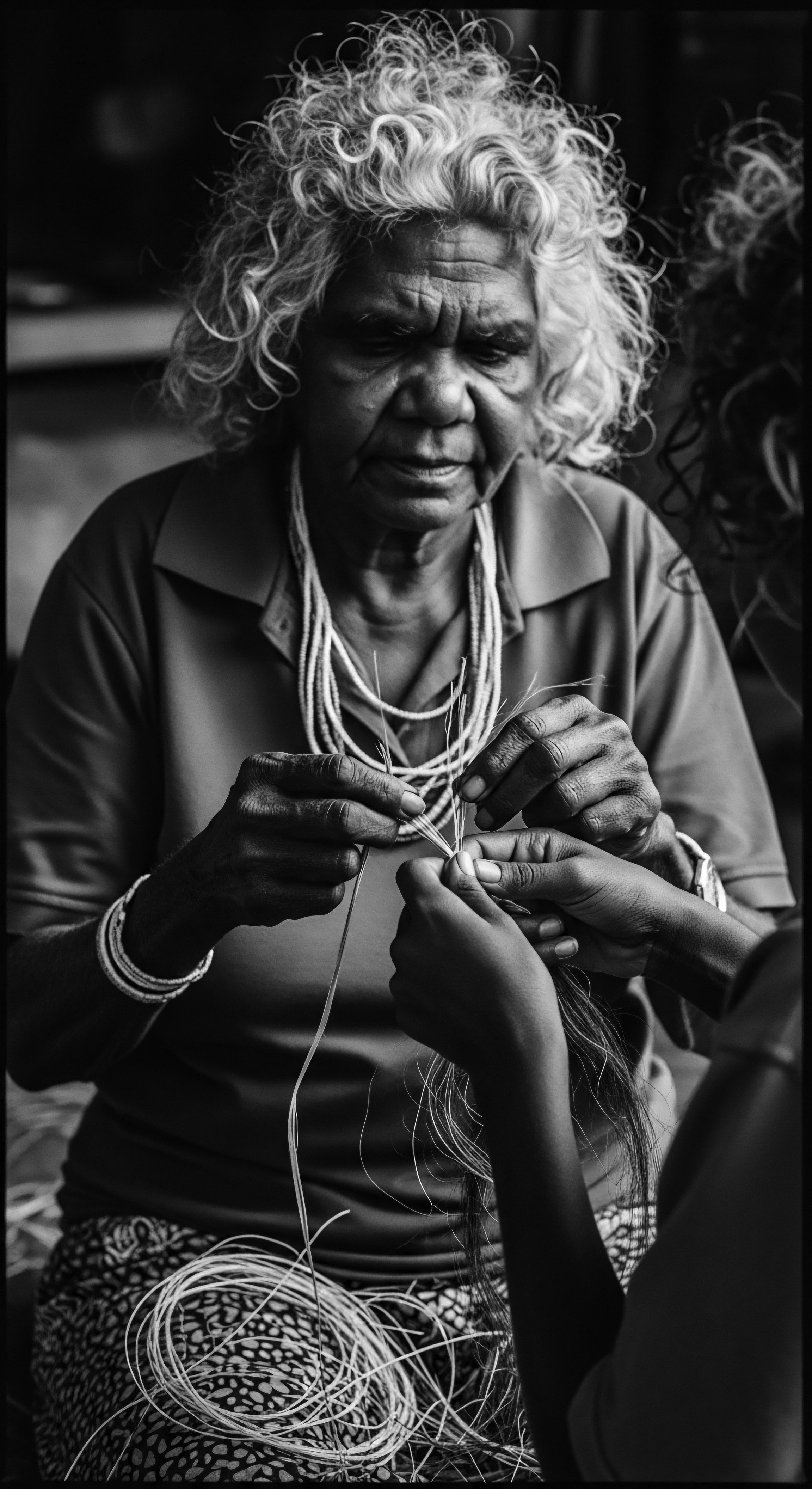

African Botanical Traditions
Meaning ❉ African Botanical Traditions refer to the ancestral wisdom of utilizing indigenous plants for holistic wellbeing, deeply focused on textured hair care and cultural identity.

How Did African Societies Honor Hair Heritage?
African societies honored textured hair heritage through spiritual reverence, social communication, and communal care rituals.

