What Historical Plant Pigments Were Used for Textured Hair in Africa?
Historical plant pigments used for textured hair in Africa encompassed natural dyes and protective pastes for color, care, and cultural identity.

How Did Shea Butter Support Textured Hair in Ancient Africa?
Shea butter provided ancient African textured hair with vital moisture, protection, and softness, a heritage passed through generations.
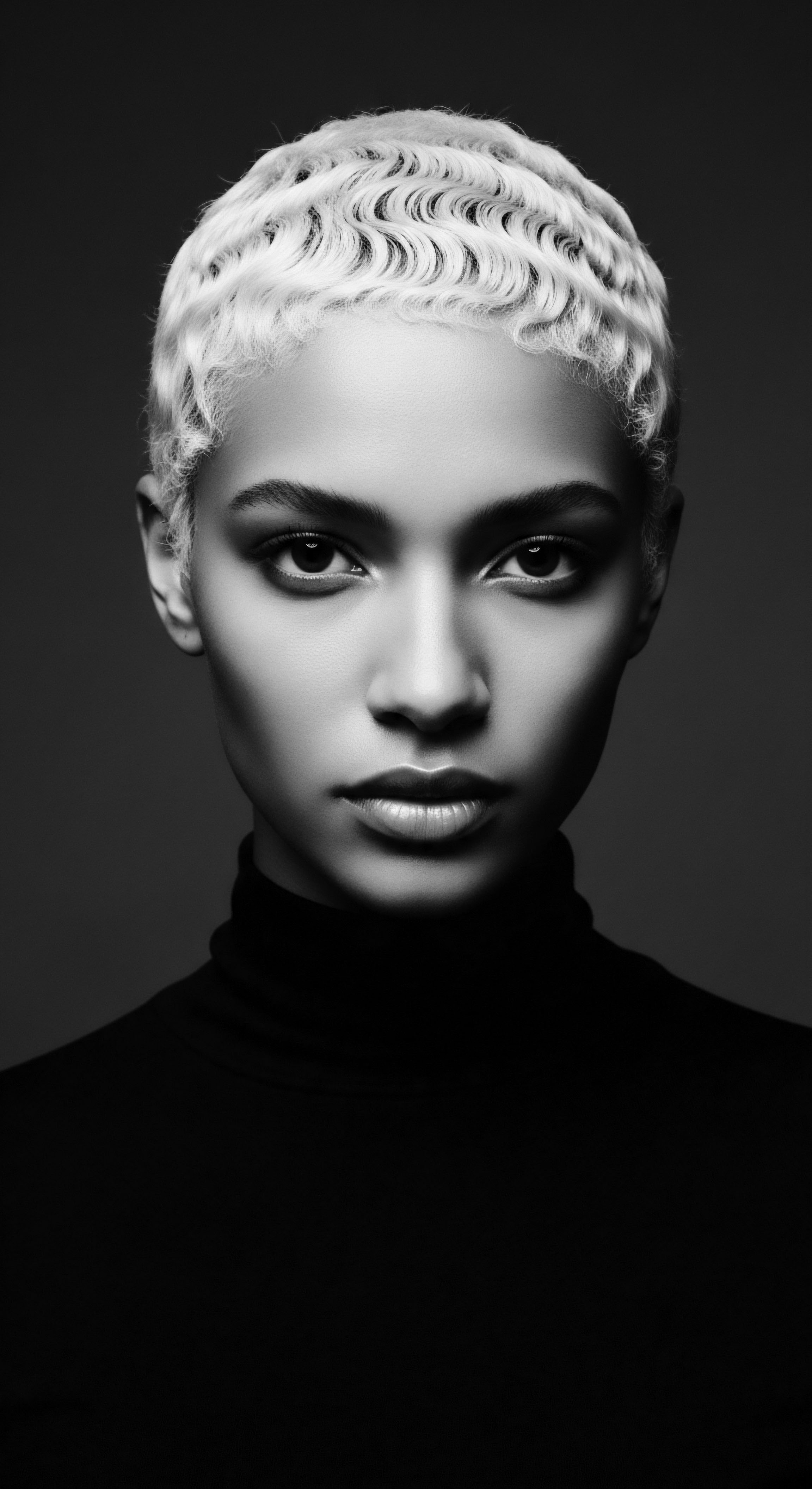

How Do Ancestral Hair Care Practices from North Africa Connect with Modern Textured Hair Regimens?
Ancestral North African hair care practices offer timeless insights into moisturizing and safeguarding textured hair, enriching contemporary regimens.
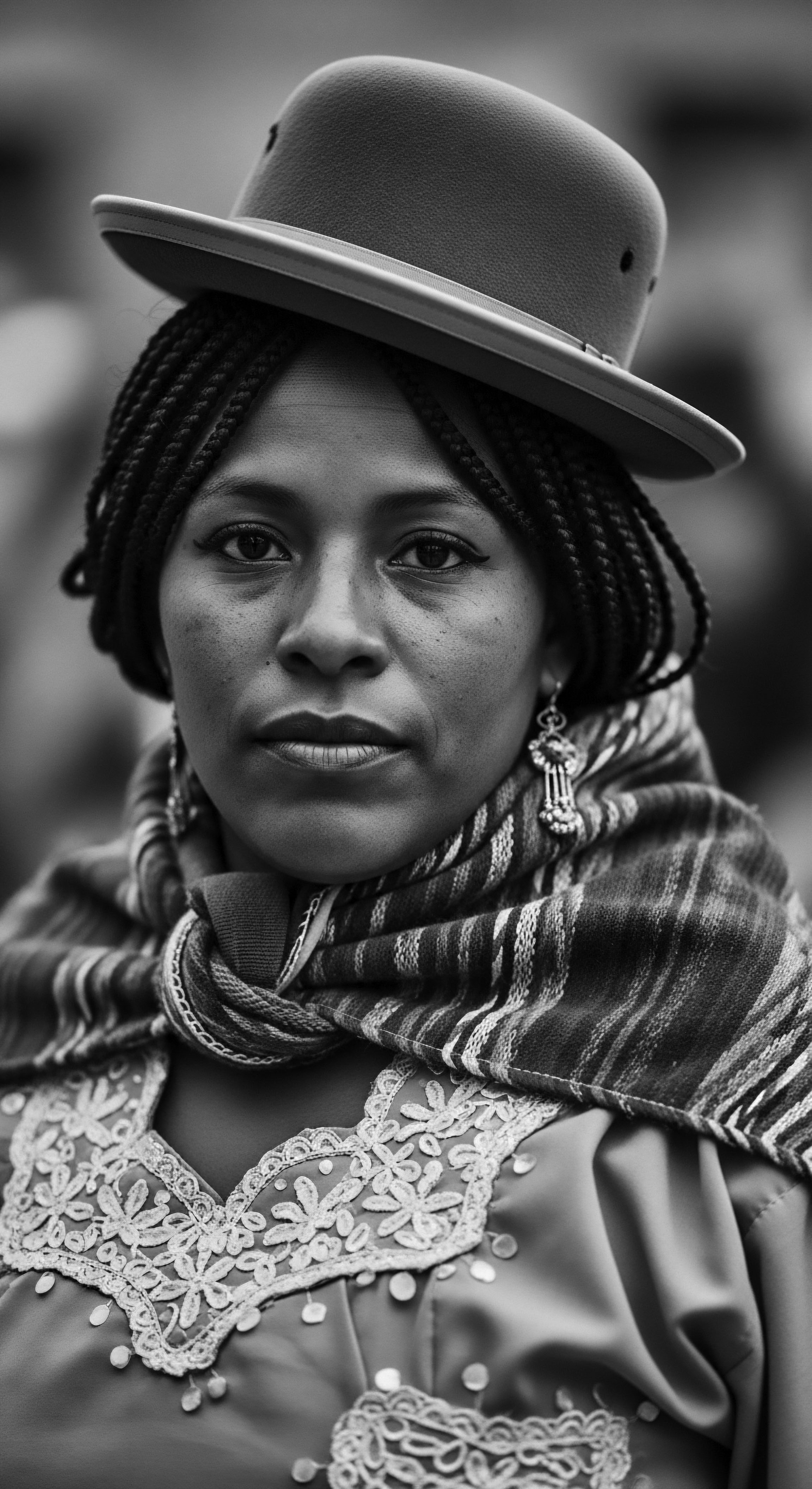

Hair Status Africa
Meaning ❉ Hair Status Africa is the profound, ancestral, and living interpretation of textured hair as a symbol of identity, cultural heritage, and resilience for African peoples.

In What Ways Did Hair Practices Strengthen Communal Bonds in Pre-Colonial Africa?
Pre-colonial African hair practices deeply fortified communal bonds by serving as visual markers of identity, facilitating intergenerational wisdom transfer during shared styling, and enabling collective expressions of empathy and celebration.
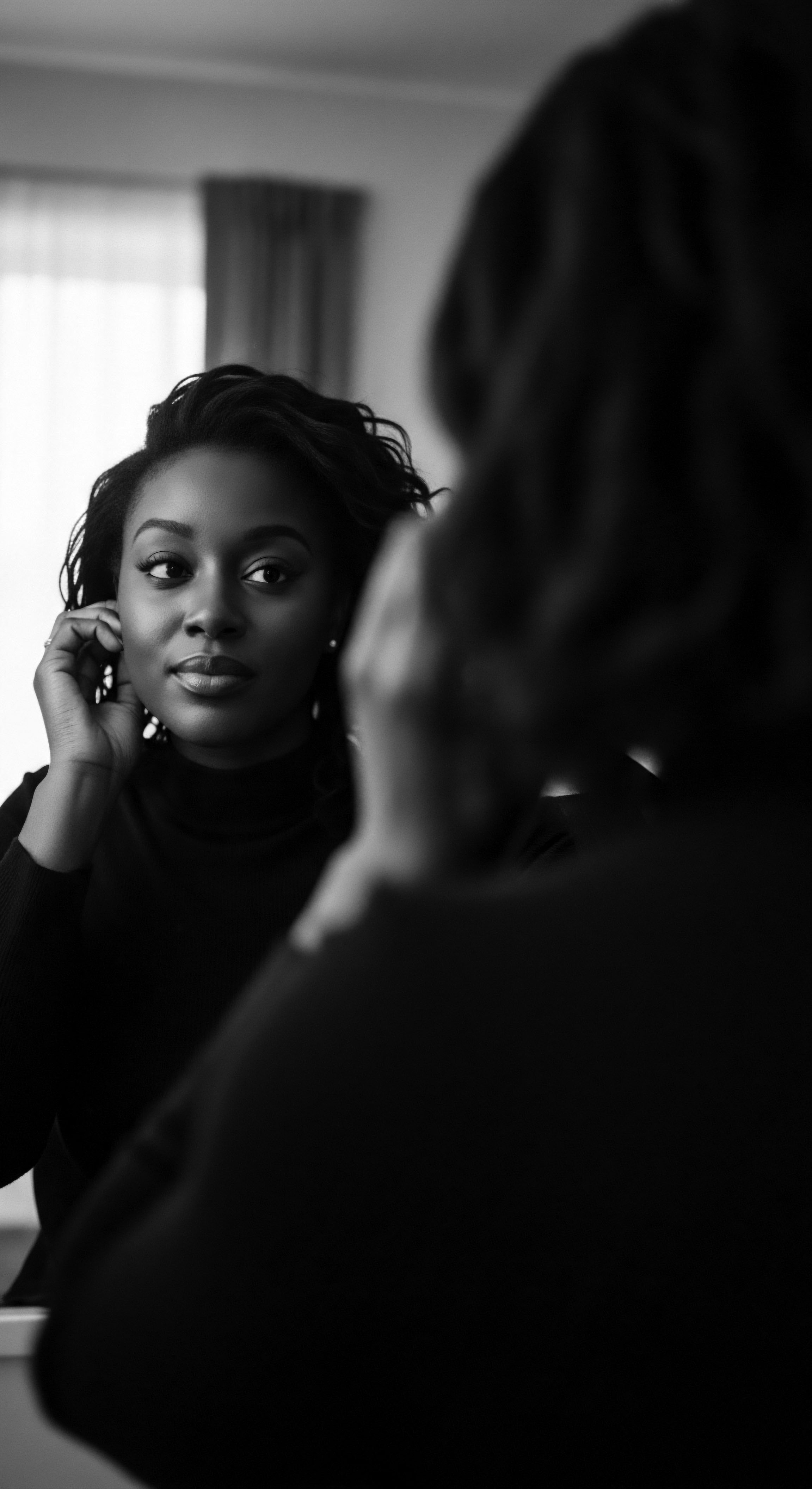

How Did Protective Styling Evolve from Ancient Africa to Diasporic Communities?
Protective styling from ancient Africa to the diaspora reveals a heritage of ingenious care, cultural identity, and resilient self-affirmation for textured hair.

What Oils Were Traditionally Used on Textured Hair in Africa?
Traditional African oils like shea butter, argan, baobab, and castor nourished textured hair, embodying ancestral heritage through protective care.

Did Ancient Cultures Use Clay beyond North Africa for Textured Hair?
Ancient cultures beyond North Africa used diverse clays for textured hair cleansing, styling, and symbolic adornment, reflecting a global ancestral wisdom.

Wigs Africa
Meaning ❉ Wigs Africa represents the culturally rich continuum of hair adornment, signifying identity and resilience within African and diasapora communities.

Can Ancient Hair Care Practices from Africa Truly Improve Modern Textured Hair Wellness?
Ancient African hair care deeply informs modern textured hair wellness through its heritage of holistic, natural, and protective practices.

What Ancestral Practices Shaped Textured Hair Conditioning in North Africa?
North African ancestral practices conditioned textured hair using natural oils, mineral clays, and herbal infusions, deeply rooted in cultural heritage.

How Does Fonio Benefit Textured Hair?
Fonio, an ancient grain, provides essential amino acids and minerals, bolstering textured hair strength and resilience, honoring ancestral wellness.

What Historical Examples Show Clay Use for Textured Hair in Africa?
Historical examples from Africa show clay use for textured hair across cultures for cleansing, styling, protection, and identity expression.

What Were the Cultural Significances of Textured Hair Ingredients in Africa?
African textured hair ingredients hold ancestral stories of community, status, and wellness deeply rooted in cultural heritage.

What Ancestral Ingredients Shielded Textured Hair in Ancient Africa?
Ancestral African ingredients, primarily plant-derived butters, oils, and clays, shielded textured hair through natural emollients and protective barriers.

What Historical Role Does Fonio Hold in African Heritage?
Fonio, as an ancestral staple in Africa, supported holistic well-being and nourished textured hair from within, solidifying its role in heritage.

Can Modern Science Explain Traditional Textured Hair Cleansing Methods from Africa?
Modern science confirms the remarkable efficacy of traditional African hair cleansing methods, rooted in a deep, inherited understanding of natural chemistry and textured hair heritage.

What Historical Cleansing Agents Were Used for Textured Hair in West Africa?
West Africa’s historical cleansing agents for textured hair centered on plant ashes, saponin-rich flora, and mineral clays, deeply rooted in heritage.

What Ancient Practices Safeguarded Textured Hair in Africa?
Ancient African practices safeguarded textured hair through indigenous plant oils, protective styling, and communal care, rooted in a deep heritage of ancestral wisdom.
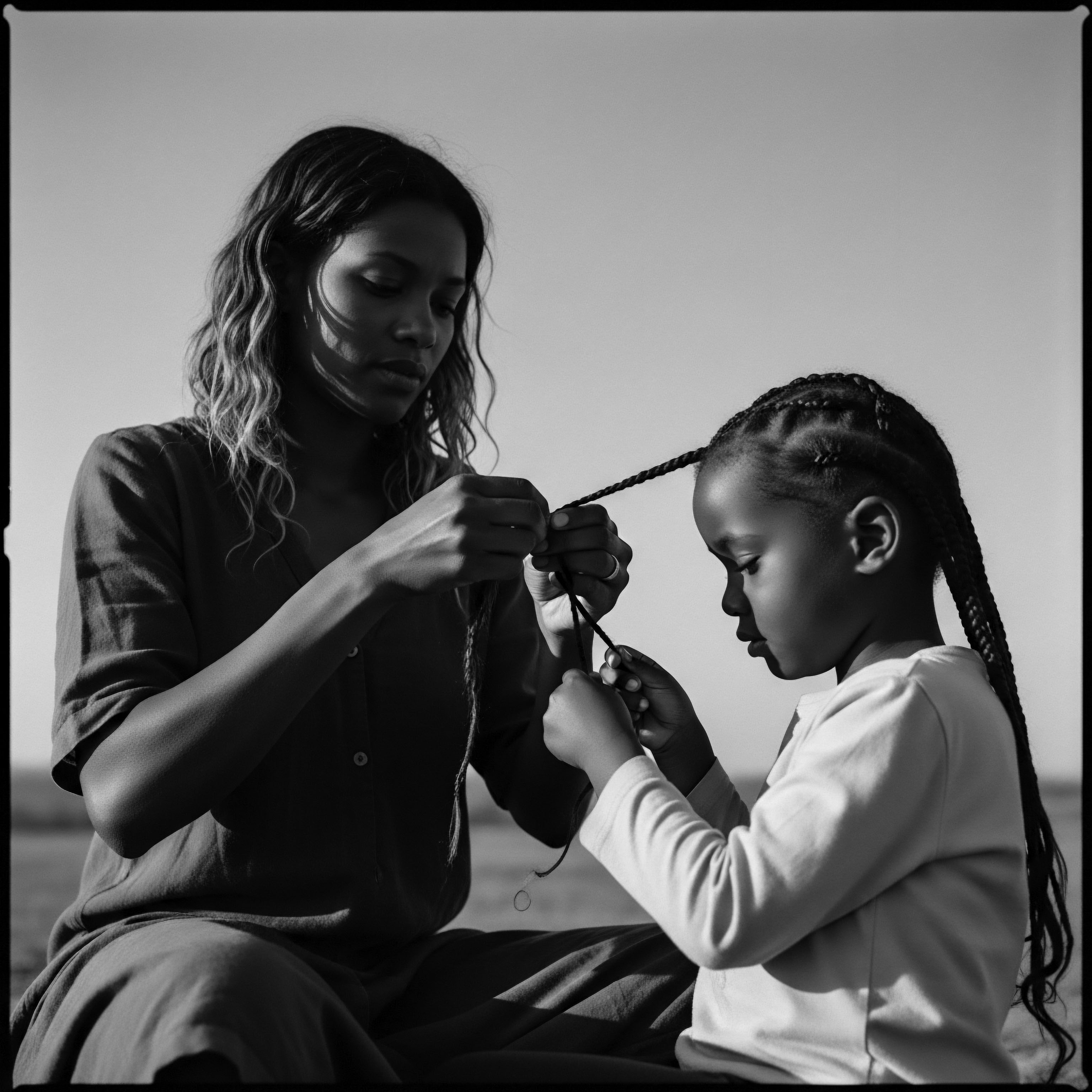

What Is the Ancestral Significance of Oiling Textured Hair in Africa?
Oiling textured hair in Africa is an ancestral practice deeply rooted in cultural identity, community bonds, and a profound understanding of hair's needs.
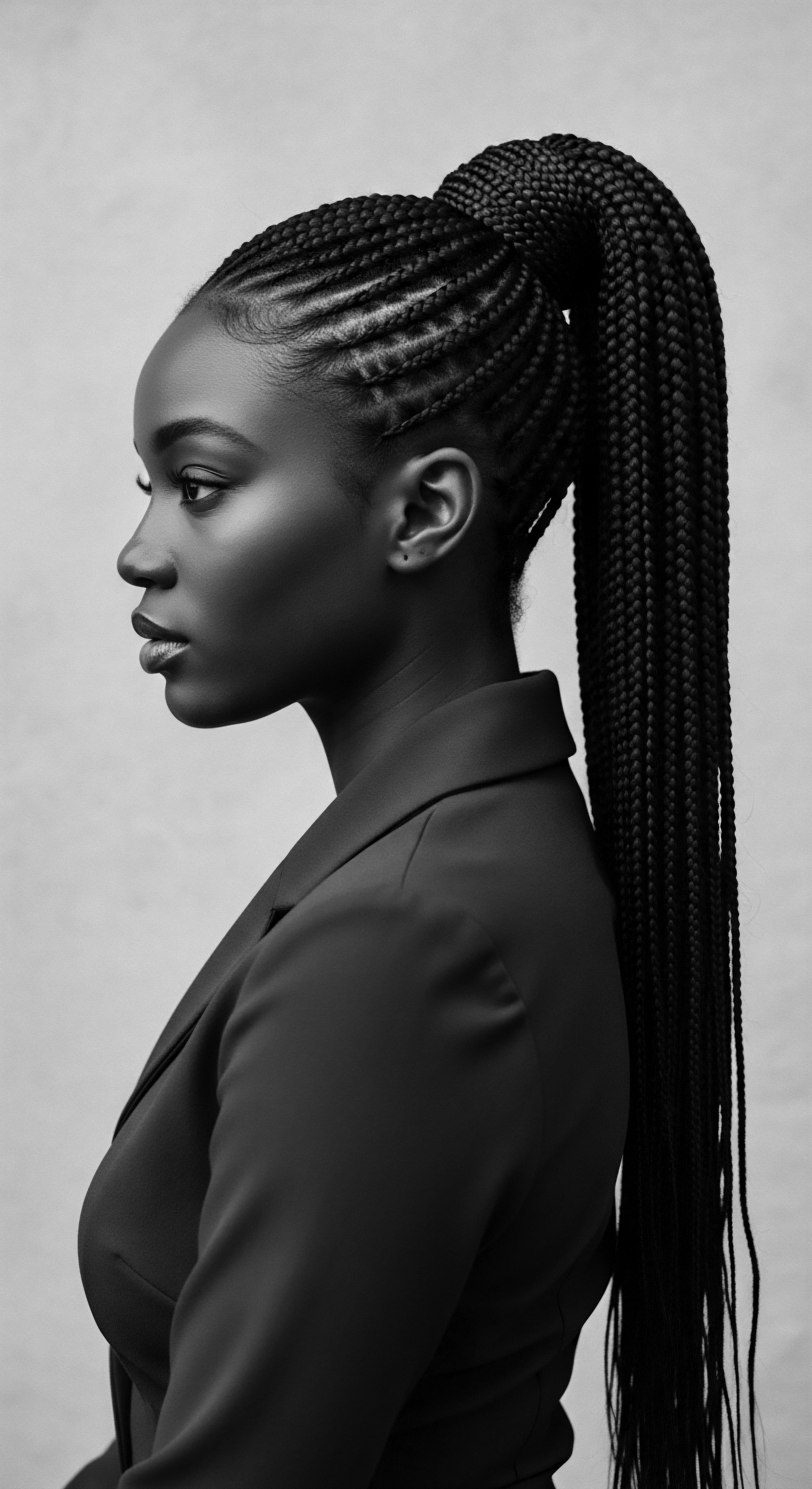

How Is Fonio’s Resilience Mirrored in Textured Hair Heritage and Community Empowerment?
Fonio’s growth in arid lands mirrors textured hair’s survival, both symbols of heritage and community fortitude.

Fonio Cultural Significance
Meaning ❉ Fonio Cultural Significance encapsulates the deep reverence for this ancient grain, bridging ancestral wisdom, holistic wellbeing, and textured hair vitality.

Which Oils Traditionally Protected Textured Hair in West Africa?
West African communities traditionally protected textured hair with oils like shea butter and palm oil, using them in daily rituals for moisture and resilience.

Fonio Hair Wellness
Meaning ❉ Fonio Hair Wellness deeply connects textured hair vitality to the heritage of West African fonio grain and ancestral nourishing practices.

Fonio Hair Benefits
Meaning ❉ Fonio Hair Benefits define how consuming this ancient West African grain supports hair health through its unique nutritional compounds and ancestral wisdom.

West African Fonio
Meaning ❉ West African Fonio is an ancient, resilient grain, profoundly significant to African heritage, nourishing both communities and hair vitality for millennia.
Fonio West Africa
Meaning ❉ Fonio West Africa is an ancient, gluten-free grain, foundational to West African heritage and a silent contributor to holistic health and hair vitality.
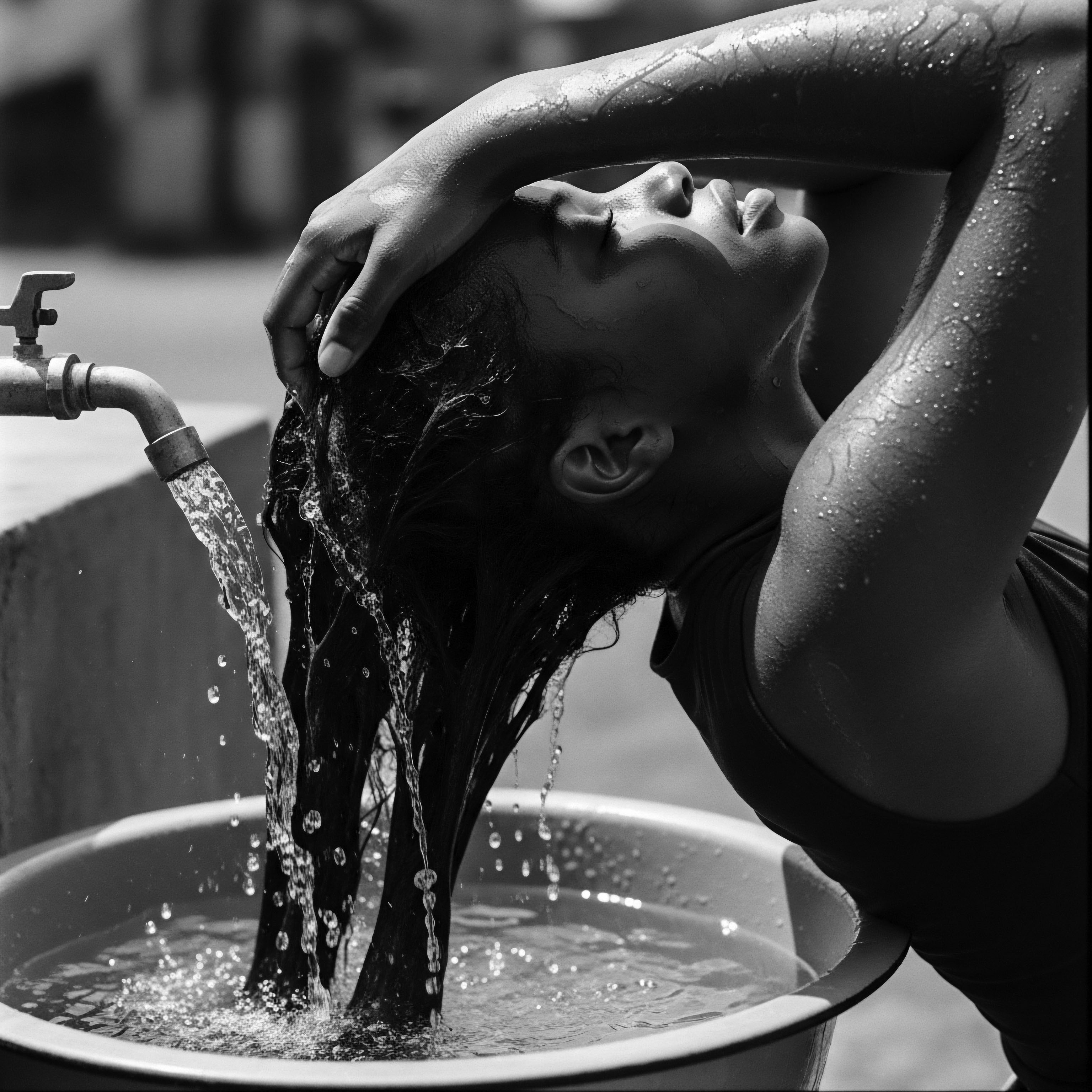

What Historical Natural Ingredients from Africa Benefit Textured Hair Today?
Historical African ingredients like shea butter and Chebe powder continue to nourish textured hair, honoring deep ancestral practices.

Digitaria Exilis
Meaning ❉ Digitaria Exilis, or fonio, is an ancient West African grain symbolizing resilience, ancestral wisdom, and cultural heritage.

