
How Does Hair Connect People to Their Heritage?
Hair connects people to heritage through its physical structure, styling traditions, communal rituals, and its symbolic role in identity and resistance.
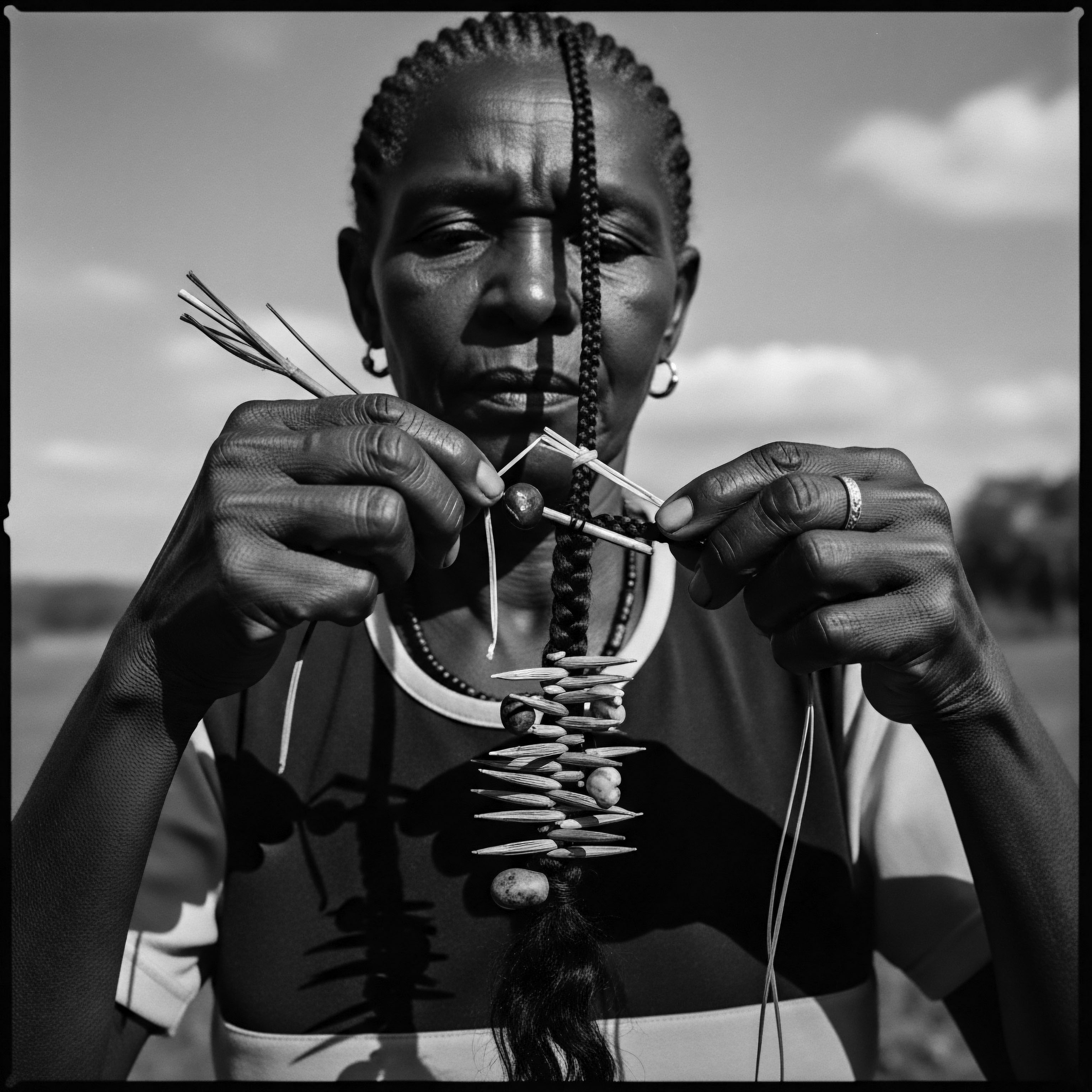

How Did Enslaved Communities Preserve Their Hair Heritage for Future Generations?
Enslaved communities preserved textured hair heritage through ingenious adaptations of ancestral practices and covert cultural acts.

In What Ways Did Enslaved Communities Preserve Hair Heritage Amidst Oppression?
Enslaved communities preserved hair heritage through secret styling, communal rituals, and the ingenious use of natural resources.

In What Ways Did Enslaved Women Preserve Cultural Heritage through Hair Care?
Enslaved women preserved heritage through hair care by adapting ancestral styling techniques, using natural ingredients, and transforming practices into acts of cultural and personal resilience.

In What Ways Did Enslaved Communities Maintain Their Hair Heritage against All Odds?
Enslaved communities maintained hair heritage through ingenious care, covert communication via styles, and shared rituals, affirming identity against deliberate erasure.

Did Ancient People Protect Textured Hair from Sun?
Ancient people often protected textured hair from the sun through a blend of natural oils, mineral pastes, and strategic styling.

How Did Ancient People Protect Textured Hair from Sun?
Ancestors shielded textured hair with natural oils, plant butters, and culturally significant head coverings, a testament to heritage and resilience.

How Did Enslaved Women Preserve Hair Heritage Using Cloth?
Enslaved women preserved hair heritage using cloth for protection, hygiene, and as a powerful, defiant expression of identity and cultural continuity.
How Did Enslaved West Africans Preserve Hair Heritage during Transatlantic Passage?
Enslaved West Africans preserved hair heritage through essential protective styles, covert communication via braids, and communal care in harrowing conditions.

In What Ways Did Enslaved Individuals Maintain Hair Heritage?
Enslaved individuals maintained hair heritage through resilient communal care, resourceful adaptation of materials, and ingenious use of styles for identity and coded communication.

First Light People
Meaning ❉ First Light People signifies the ancestral human lineage whose textured hair became a profound expression of identity, adaptation, and spiritual connection.

Enslaved Hair Rituals
Meaning ❉ Enslaved Hair Rituals denote the adaptive, symbolic hair care practices and communication systems maintained by enslaved Africans to preserve identity and cultural heritage.

In What Ways Did Enslaved Communities Preserve Hair Heritage through Rituals?
Enslaved communities preserved textured hair heritage through resilient rituals of communal care, covert communication in braids, and ingenious material adaptation.

In What Ways Did Enslaved Africans Preserve Their Hair Traditions and Heritage?
Enslaved Africans preserved hair traditions through covert styling as resistance, adapting ancestral ingredients, and communal care rituals.

How Did Enslaved People Preserve Their Hair Heritage?
Enslaved people preserved hair heritage through ingenious adaptations of ancestral practices, transforming care into acts of survival and cultural defiance.
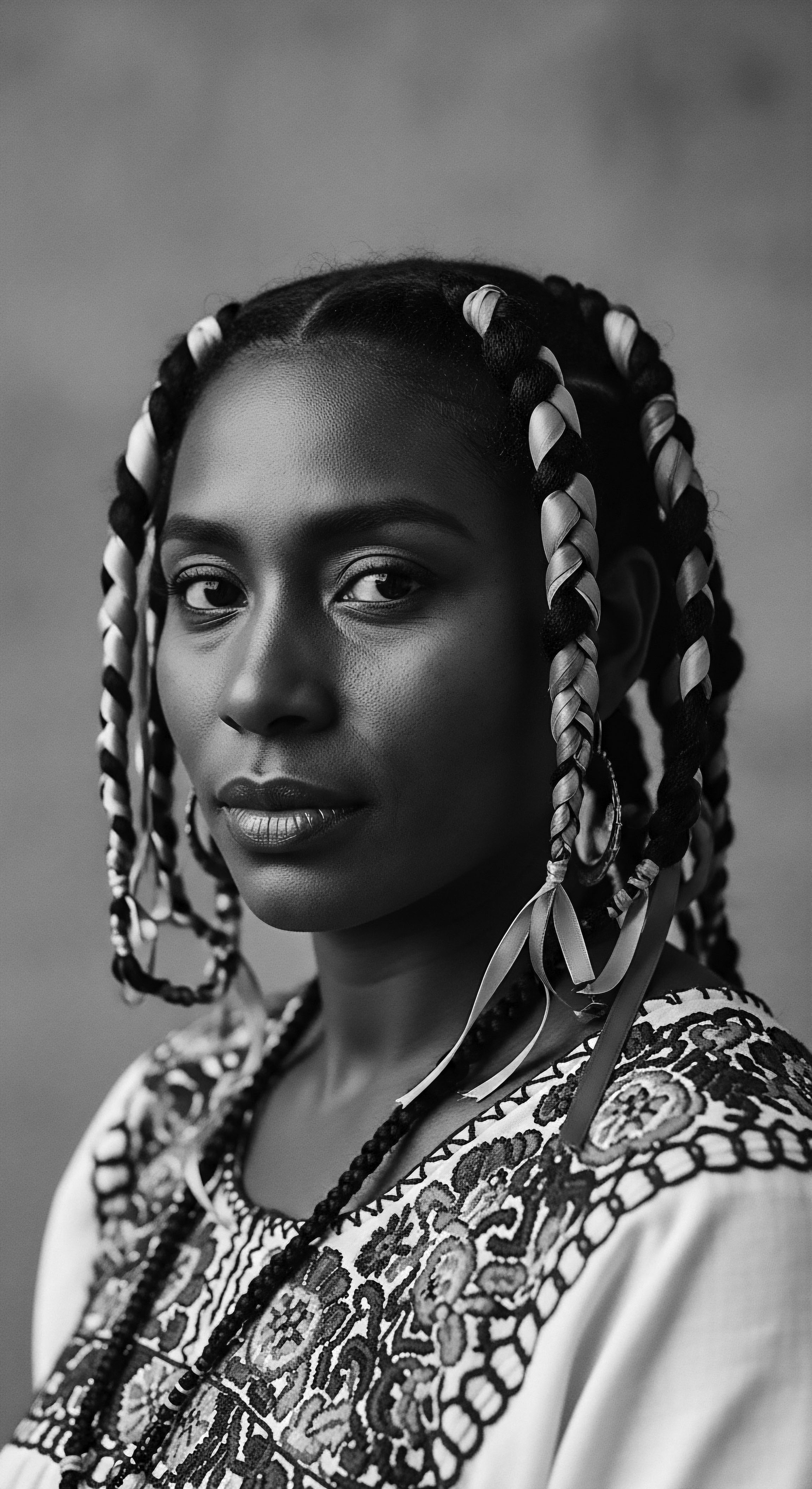

In What Ways Did Enslaved People Preserve Their Hair Heritage despite Oppression?
Enslaved people preserved hair heritage through secret styling, communal care, and coded messages within braids.
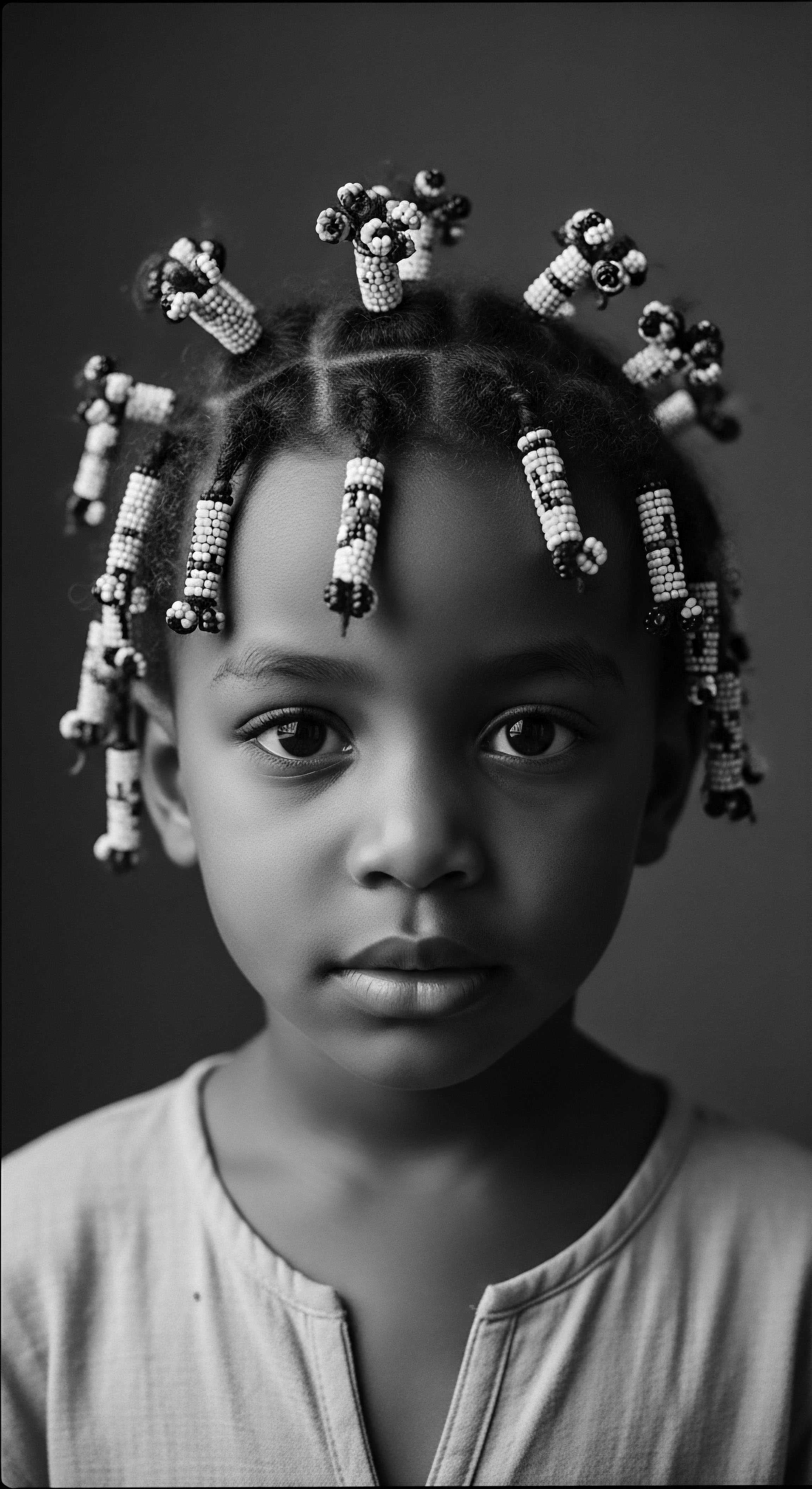

In What Ways Did Enslaved Africans Preserve Heritage through Hair?
Enslaved Africans preserved heritage through hair by transforming styling into coded communication, communal bonding, and a profound assertion of cultural identity.
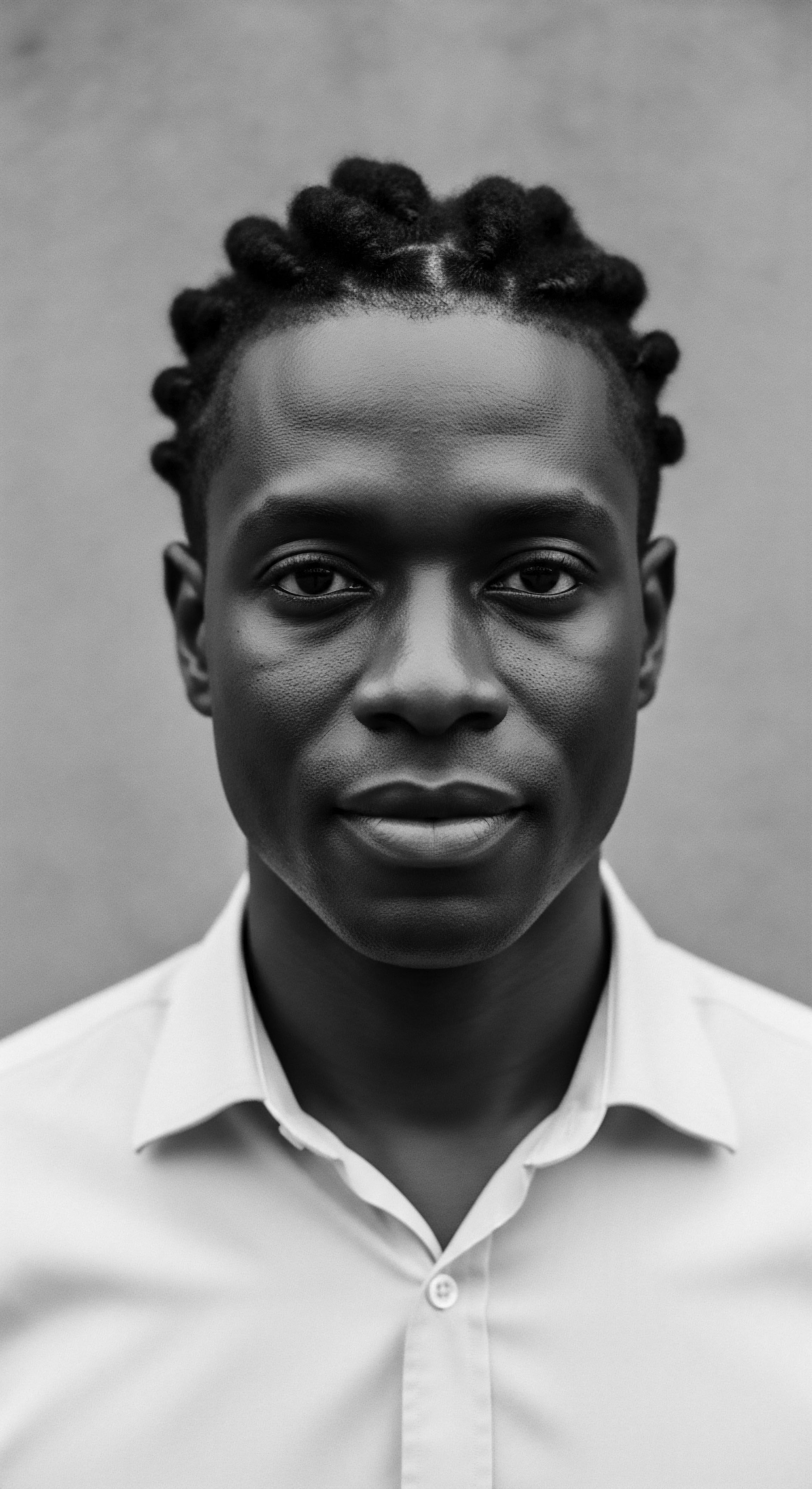

How Does the Himba People’s Hair Care Relate to Their Cultural Heritage?
Himba hair care, centered on otjize, embodies a living heritage of identity, status, and environmental adaptation for textured hair.

Which Traditional Scalp Care Techniques for Textured Hair Did Enslaved Africans Adapt?
Enslaved Africans adapted traditional scalp care with available resources, using techniques for hygiene, moisture, and covert communication, deeply preserving their hair heritage.

In What Ways Did Enslaved Communities Preserve Hair Heritage through Care Practices?
Enslaved communities preserved textured hair heritage through adaptive care practices, coded communication, and acts of profound cultural resistance.

Zo People Heritage
Meaning ❉ Zo People Heritage refers to the collective ancestral wisdom and cultural expressions deeply connected to textured hair across diverse communities.

Zo People History
Meaning ❉ A conceptual exploration of Zo People History as a metaphor for the enduring journey of textured hair identity and cultural resilience.

In What Ways Did Enslaved Communities Maintain Textured Hair Heritage?
Enslaved communities preserved hair heritage through ingenious adaptation, communal rituals, and hair's symbolic role as a core part of identity.

Fang People
Meaning ❉ The Fang People's hair heritage reveals a profound connection to ancestry, spiritual beliefs, and communal identity through intricate care and adornment.
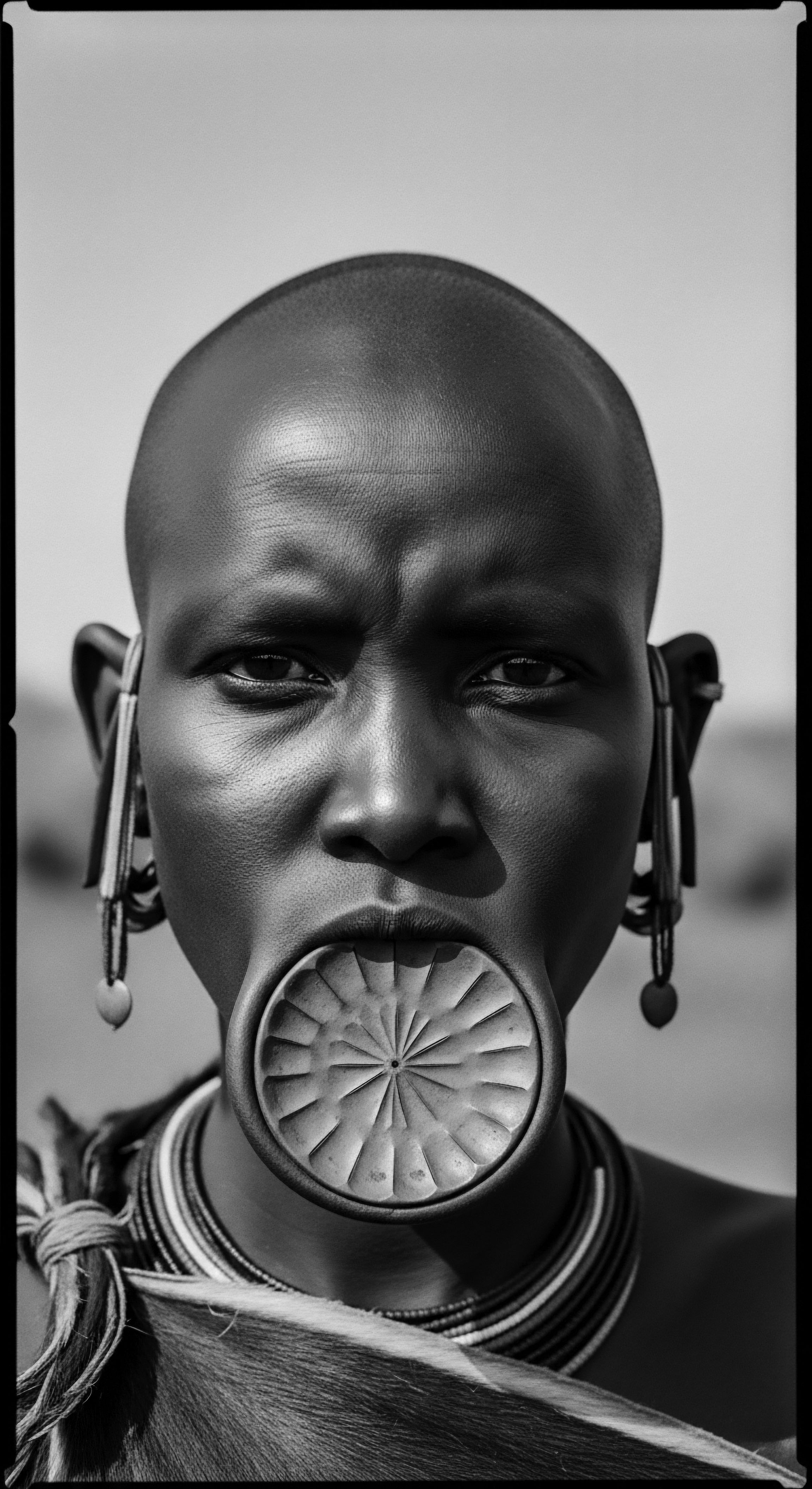

Why Do People Protect Textured Hair?
Protecting textured hair honors its unique structure, safeguards ancestral traditions, and expresses deep cultural identity and resilience.
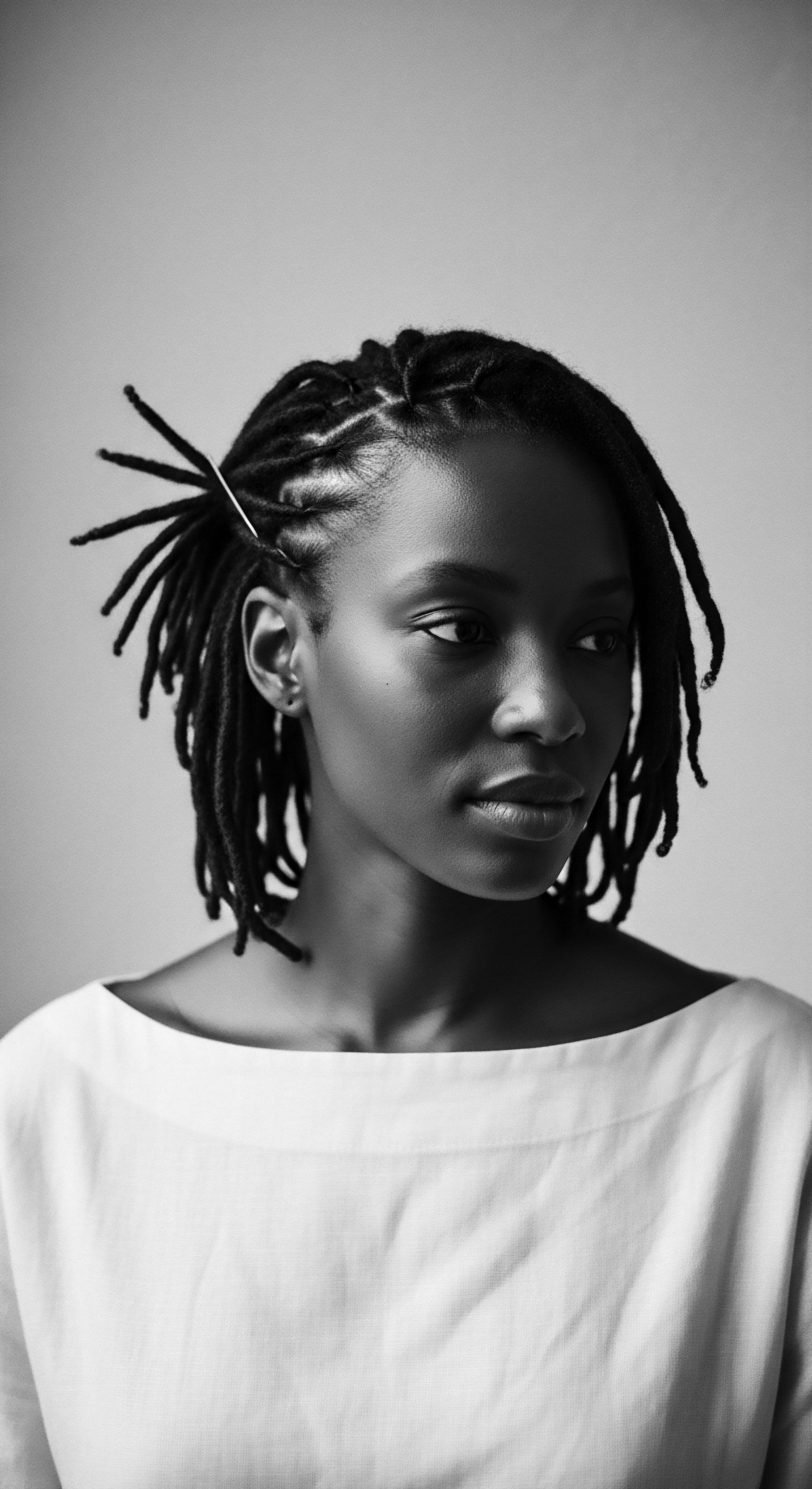

Senufo People
Meaning ❉ The Senufo people represent a rich West African culture where hair serves as a profound symbol of identity, life stages, and spiritual connection.

Dan People Hair
Meaning ❉ Dan People Hair defines the profound cultural, spiritual, and communal significance of hair practices within the Dan community and textured hair heritage.

Dan People Aesthetics
Meaning ❉ Dan People Aesthetics defines a cultural system where beauty, especially in textured hair, reflects spiritual connections, social status, and ancestral wisdom.

What Ingredients Did Ancient People Use for Hair Cleansing?
Ancient peoples cleansed hair with natural clays, saponin-rich plants, and mild oils, honoring textured hair's need for gentle care.

