How Do Historical Styling Practices Connect with Hair Biology?
Historical styling practices deeply connect with hair biology through ancestral wisdom preserving health and cultural heritage.

In What Ways Did Hair Oiling Symbolize Resistance during Historical Periods?
Hair oiling symbolized resistance by preserving identity and heritage in textured hair through ancestral care and defiance against suppression.

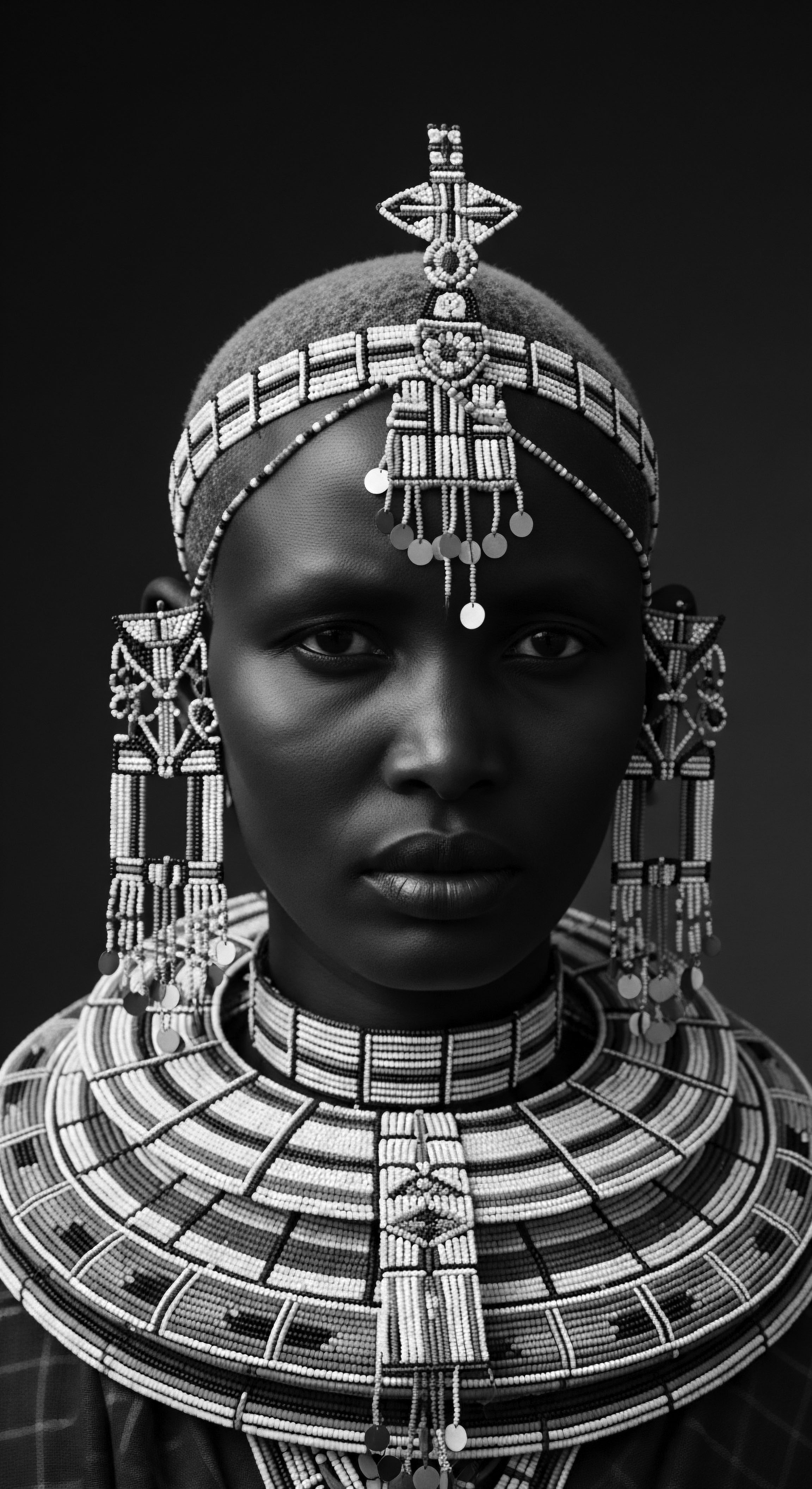
What Historical Patterns in Cornrows Communicated Liberation Messages?
Cornrows served as secret maps and vital communication during slavery, a profound expression of textured hair heritage and liberation.

Rastafari Hair Heritage
Meaning ❉ Rastafari Hair Heritage defines dreadlocks as a sacred emblem of identity, cultural resistance, and spiritual connection to ancestral wisdom.

Indigenous Filipinos
Meaning ❉ The Indigenous Filipinos represent a diverse collective whose hair heritage embodies ancestral wisdom, cultural identity, and profound ecological connection.

What Historical Hair Care Traditions Involved Oiling?
Historical oiling rituals for textured hair preserved vitality, embodied cultural connection, and upheld identity across generations.
What Roles Did Hair Play during Enslavement for Identity?
Hair during enslavement became a silent testament to identity and resistance, embedding ancestral heritage within each textured strand.

What Role Did Hair Play in Enslaved Communities?
Hair served as a potent symbol of identity, communication, and resilience within enslaved communities, connecting them to their textured hair heritage.

What Historical Examples Show Hair as a Hidden Language of Freedom?
Textured hair historically served as a covert medium for communication and resistance, embodying the resilience of Black heritage.

How Did Historical Combs Become Symbols of Black Identity and Resistance?
Historical combs became symbols of Black identity and resistance by embodying ancestral wisdom, communal care, and defiant self-affirmation.

How Have Textured Hairstyles Served as Cultural Resistance through History?
Textured hairstyles have historically served as a powerful declaration of identity, cultural continuity, and defiance against oppression, deeply rooted in ancestral heritage.

How Did Head Coverings Become Symbols of Resistance?
Head coverings transformed into symbols of resistance through defiant cultural reclamation of textured hair heritage against oppression.
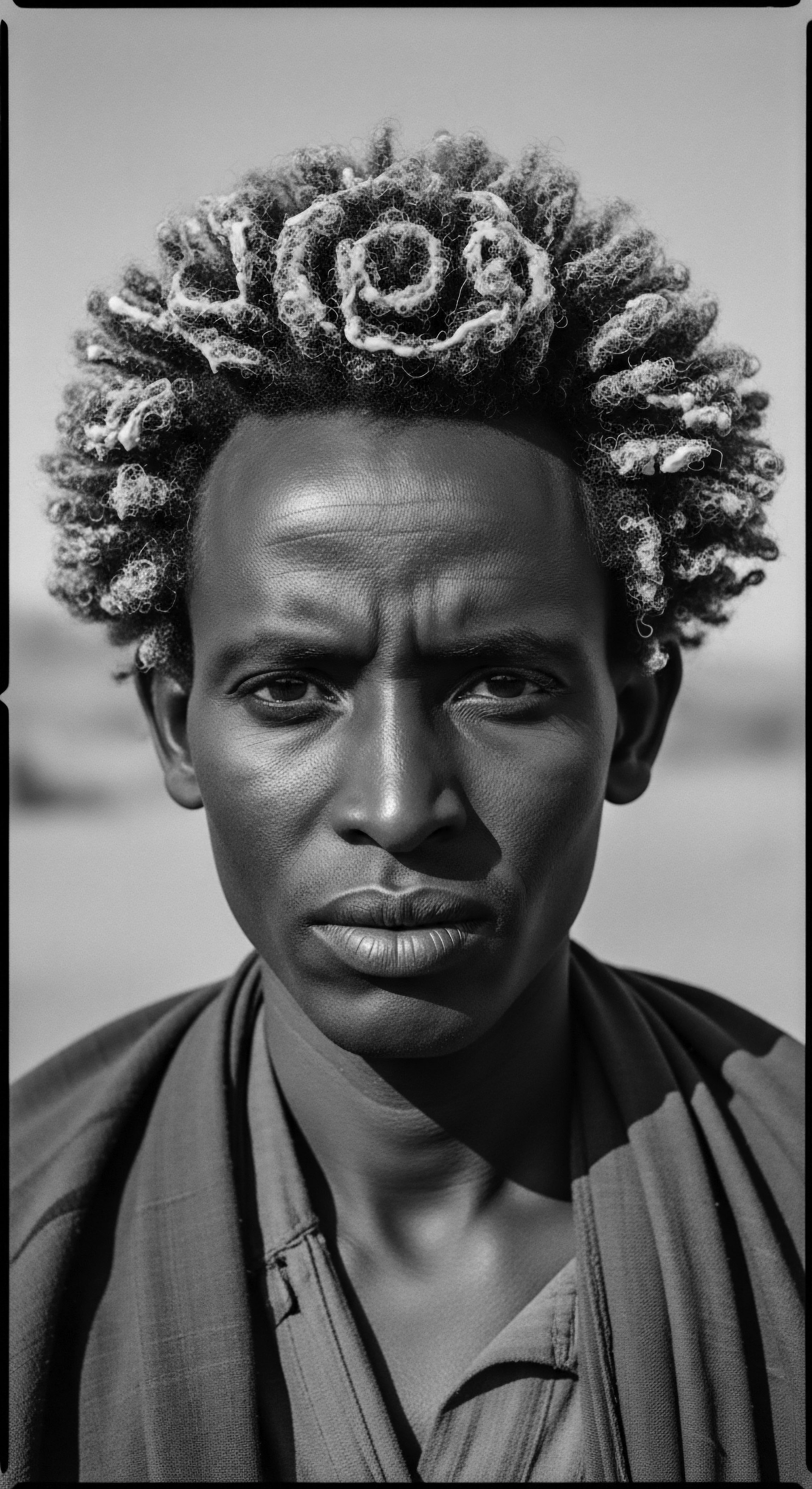

How Did Historical Resistance Movements Influence Textured Hair Practices?
Historical resistance movements fundamentally shaped textured hair practices, transforming them into powerful symbols of cultural identity and heritage.
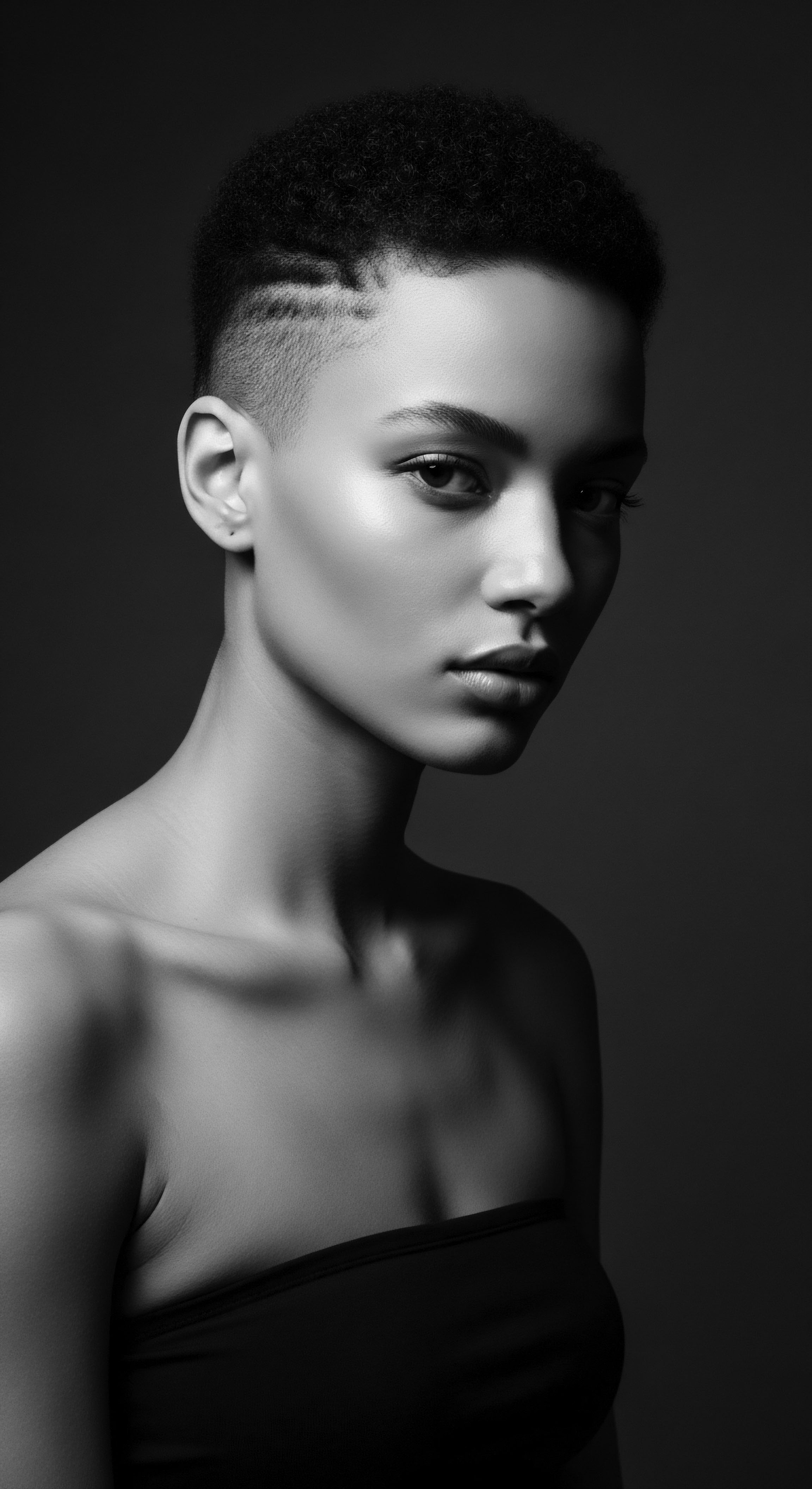

Ofo Authority
Meaning ❉ Ofo Authority is the inherent ancestral wisdom and self-governing power of textured hair, deeply rooted in its biological resilience and cultural significance.

Zamia Integrifolia
Meaning ❉ Zamia integrifolia is an ancient cycad whose heritage symbolizes resilience and ancestral knowledge, profoundly connecting to textured hair experiences.

How Did Early Colonial Laws Impact Textured Hair Heritage?
Early colonial laws sought to suppress textured hair heritage, yet sparked powerful acts of cultural resistance and identity reclamation.

Aymara Heritage
Meaning ❉ Aymara Heritage embodies the enduring cultural practices and resilient identity of the Andean people, profoundly shaped by their hair traditions and ancestral wisdom.

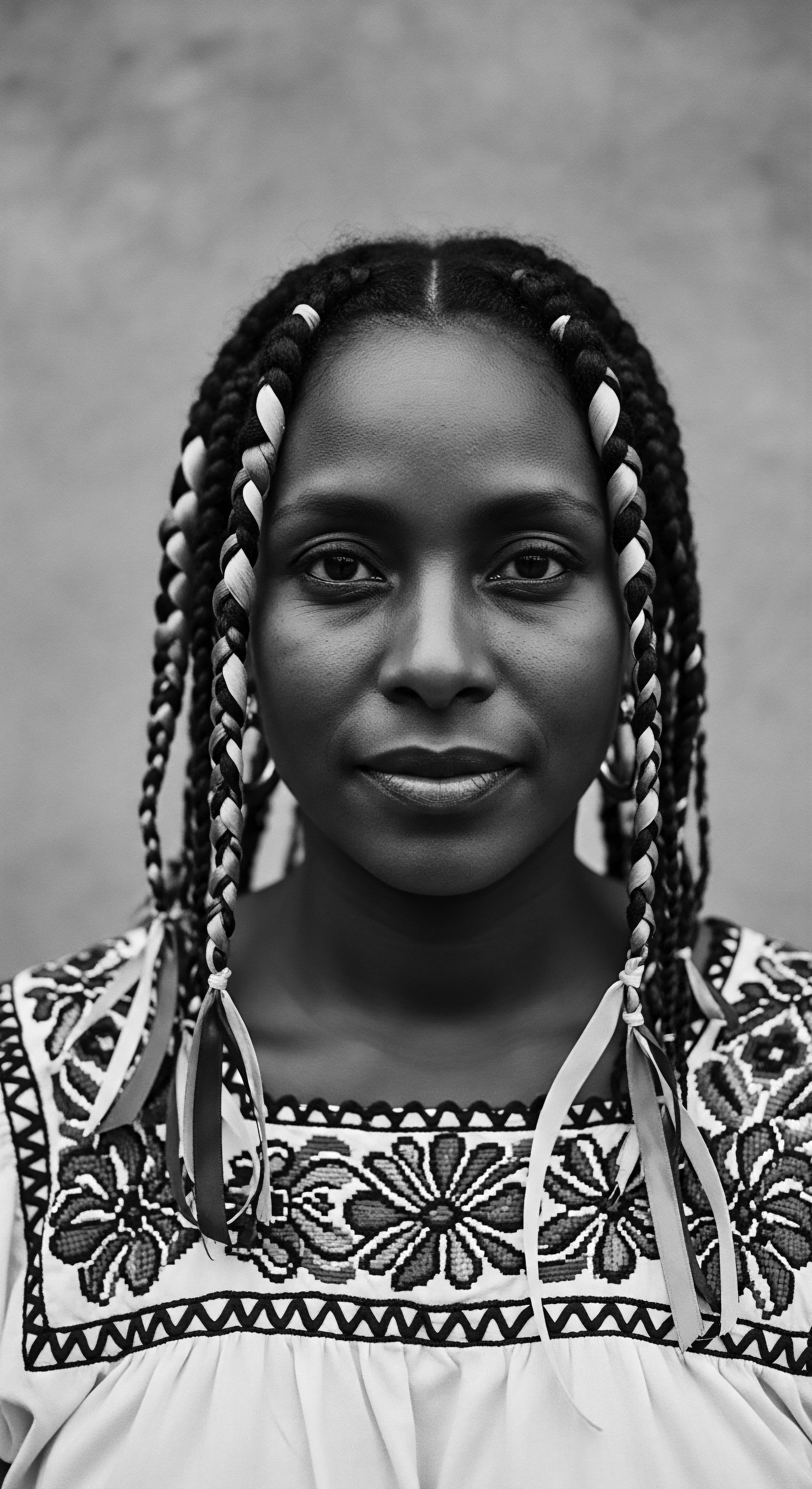
How Is Textured Hair a Symbol of Identity and Resistance?
Textured hair serves as a profound symbol of identity and resistance, rooted in rich ancestral heritage and sustained through centuries of cultural affirmation.

Mouride Hair Traditions
Meaning ❉ Mouride Hair Traditions define the spiritual and cultural hair practices of the Baye Fall, signifying devotion, humility, and cultural identity.

Can Historical Hair Care Practices Influence Modern Scientific Understanding of Textured Hair?
Historical hair care practices offer crucial insights into textured hair biology, enriching modern scientific understanding through ancestral wisdom.

What Is the Historical Significance of Headwraps for Black Women’s Heritage?
Headwraps for Black women symbolize heritage, resilience, and identity, rooted in ancestral practices for textured hair.
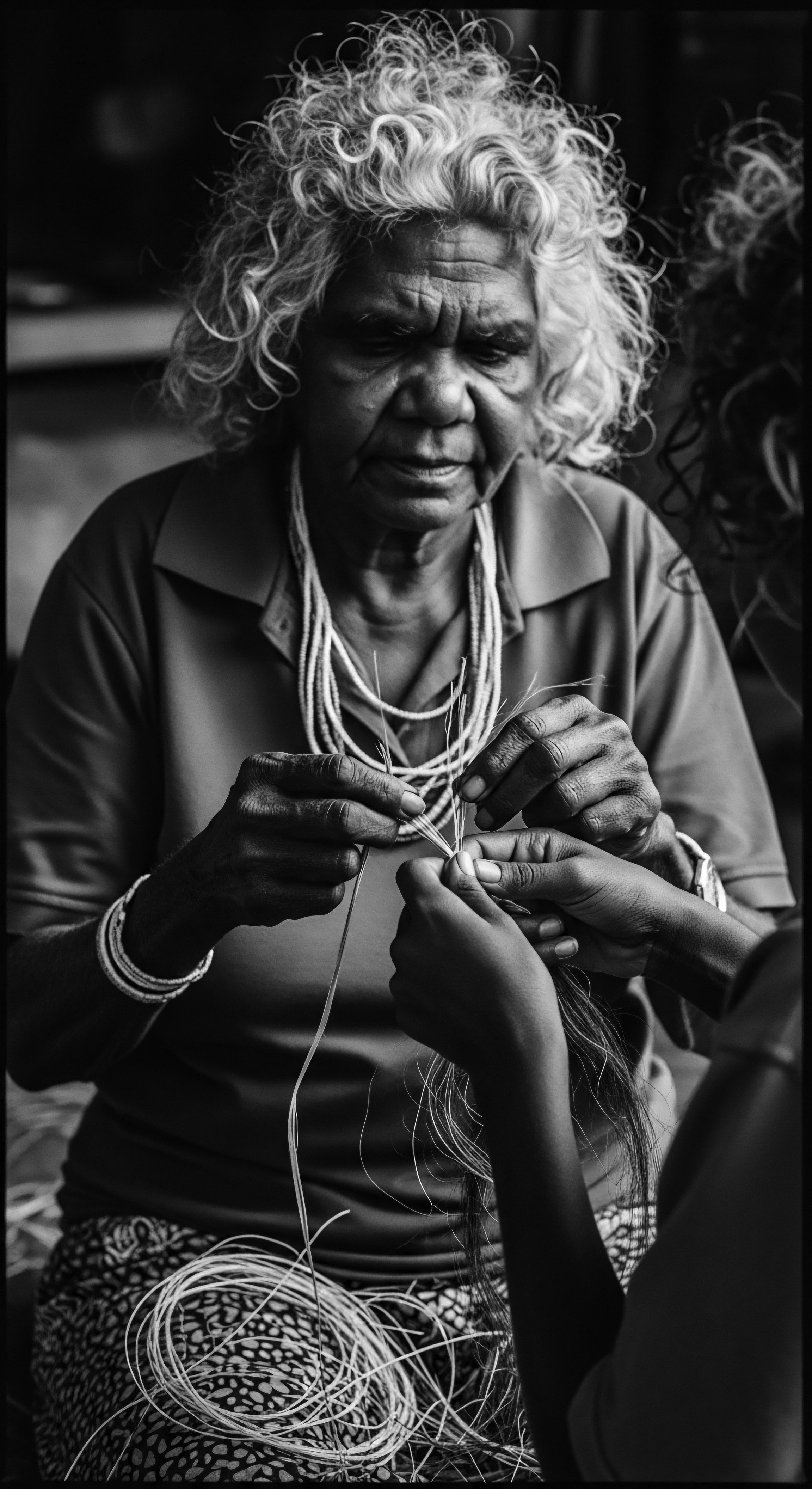

How Do Headwraps Symbolize Resistance in Textured Hair History?
Headwraps symbolize resistance through ancestral continuity, cultural affirmation, and creative defiance of oppressive laws, deeply rooted in textured hair heritage.

Andalusian Hair History
Meaning ❉ Andalusian Hair History describes the rich legacy of hair practices and cultural expressions from medieval Islamic Iberia.

Mapuche Hair Care
Meaning ❉ Mapuche Hair Care represents an indigenous system of hair maintenance rooted in ancestral wisdom, natural elements, and deep cultural identity.

Aeta Heritage
Meaning ❉ Aeta Heritage refers to the enduring cultural and historical legacy of the Philippines' indigenous Aeta people, profoundly marked by their distinct coiled hair and ancestral wisdom.

Resistance Hairstyle
Meaning ❉ The Resistance Hairstyle transforms hair into a powerful declaration of cultural heritage and autonomy, defying oppressive beauty norms through ancestral practices.

Afro-Bolivian Heritage
Meaning ❉ Afro-Bolivian heritage encompasses the historical, cultural, and lived experiences of people of African descent in Bolivia, deeply rooted in ancestral practices and identity.

Aymara Hair Practices
Meaning ❉ Aymara Hair Practices embody cultural identity and spiritual connection through long, braided styles in Andean indigenous communities.

Vodou Cultural Significance
Meaning ❉ Vodou Cultural Significance represents a spiritual and historical framework, deeply intertwined with the heritage and identity expressed through textured hair in the African diaspora.

