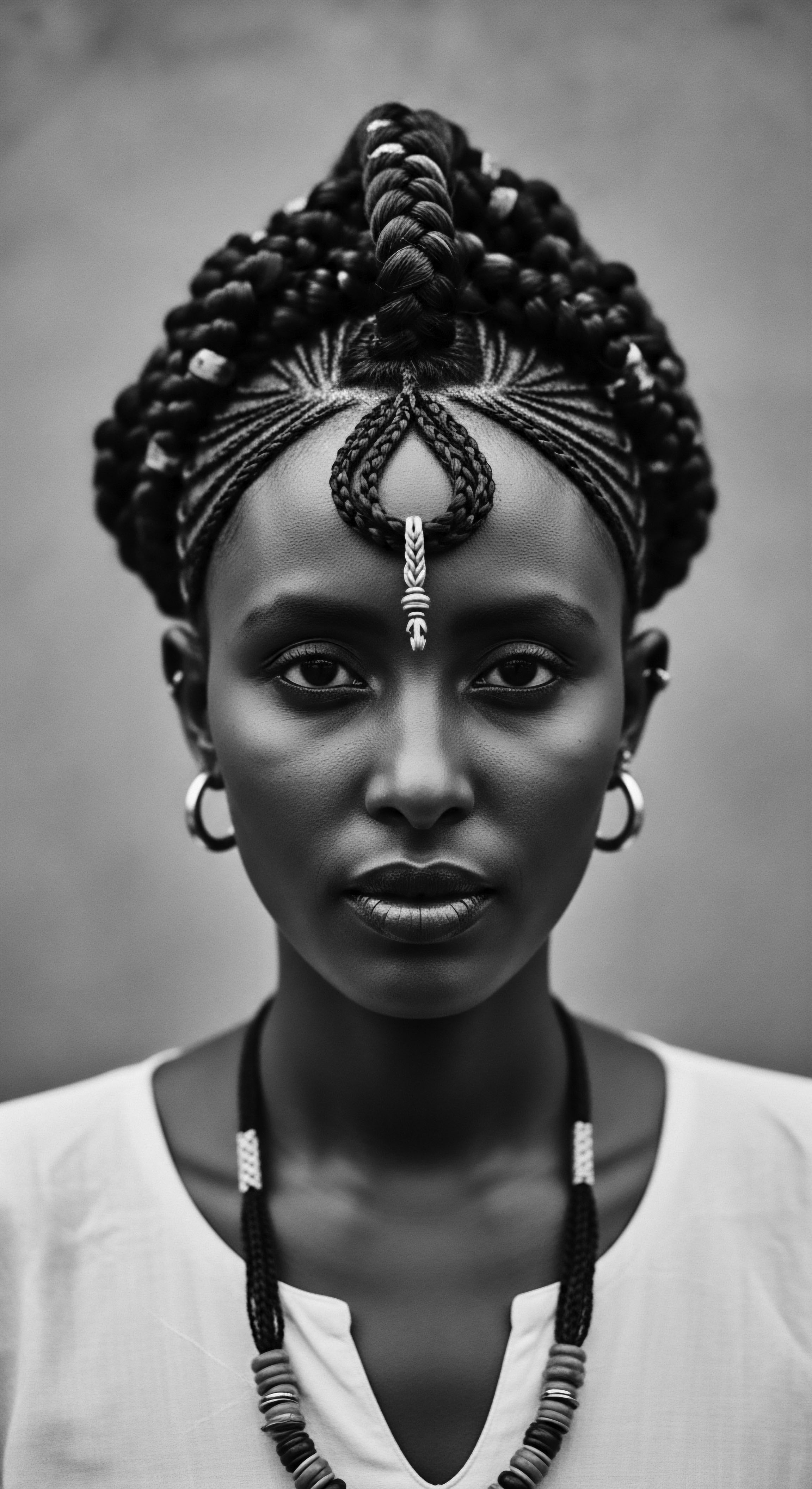

Apartheid Hair History
Meaning ❉ The Apartheid Hair History details how hair, especially textured hair, was weaponized for racial classification and control in South Africa.

Turkana Traditional Beauty
Meaning ❉ Turkana Traditional Beauty is a cultural system of self-adornment, primarily through textured hair, reflecting identity, social status, and ancestral wisdom.
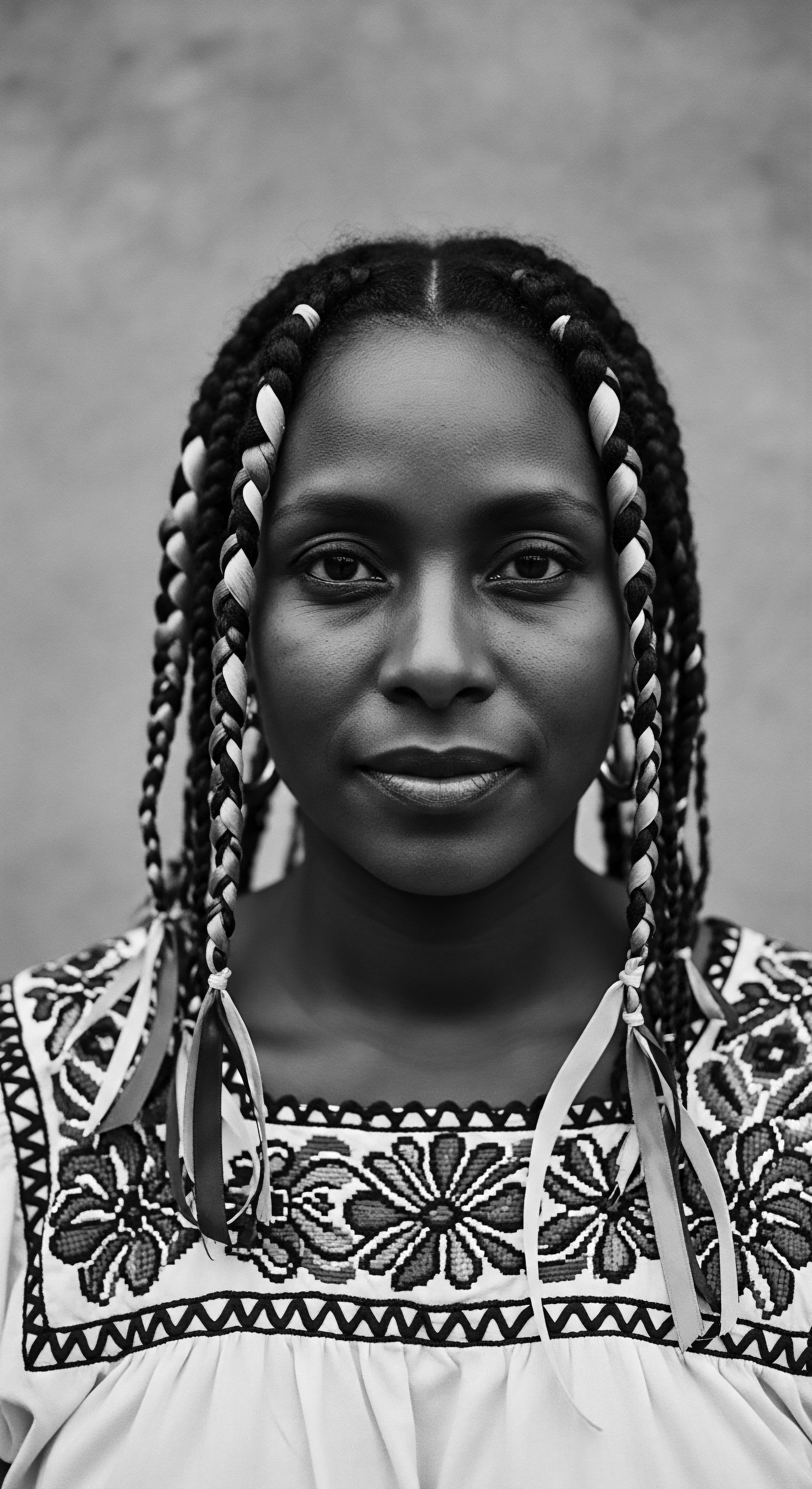

Somali Beauty
Meaning ❉ Somali Beauty defines an aesthetic valuing distinctive ancestral features and traditional hair care, deeply rooted in cultural heritage and identity.

Portable Beauty Rituals
Meaning ❉ Portable Beauty Rituals are adaptable, transportable hair and self-care practices deeply rooted in textured hair heritage, preserving cultural identity across generations.
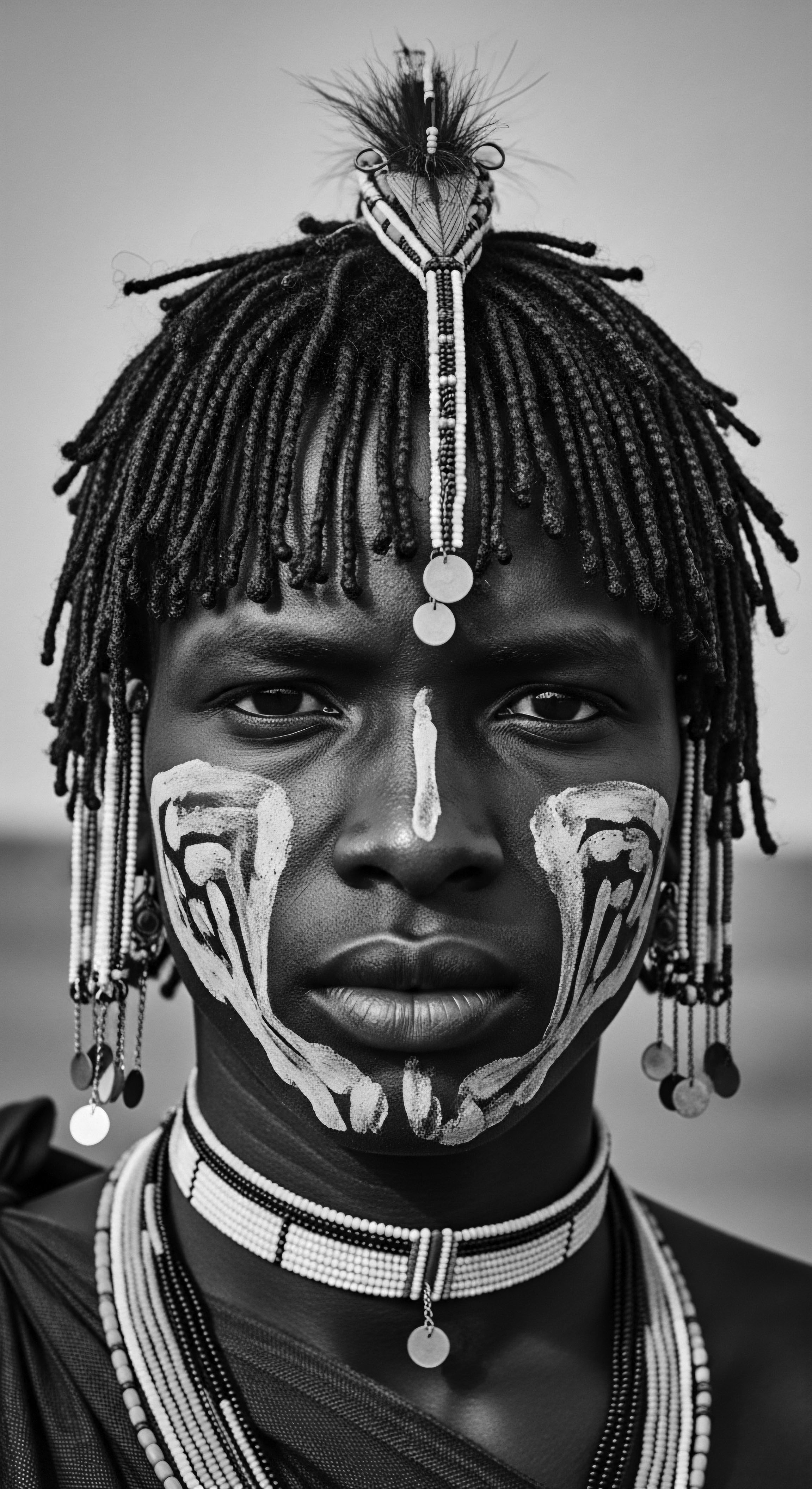

Ndebele Hair
Meaning ❉ Ndebele Hair signifies a rich cultural expression of identity, status, and heritage through elaborate adornments and traditional care rituals.
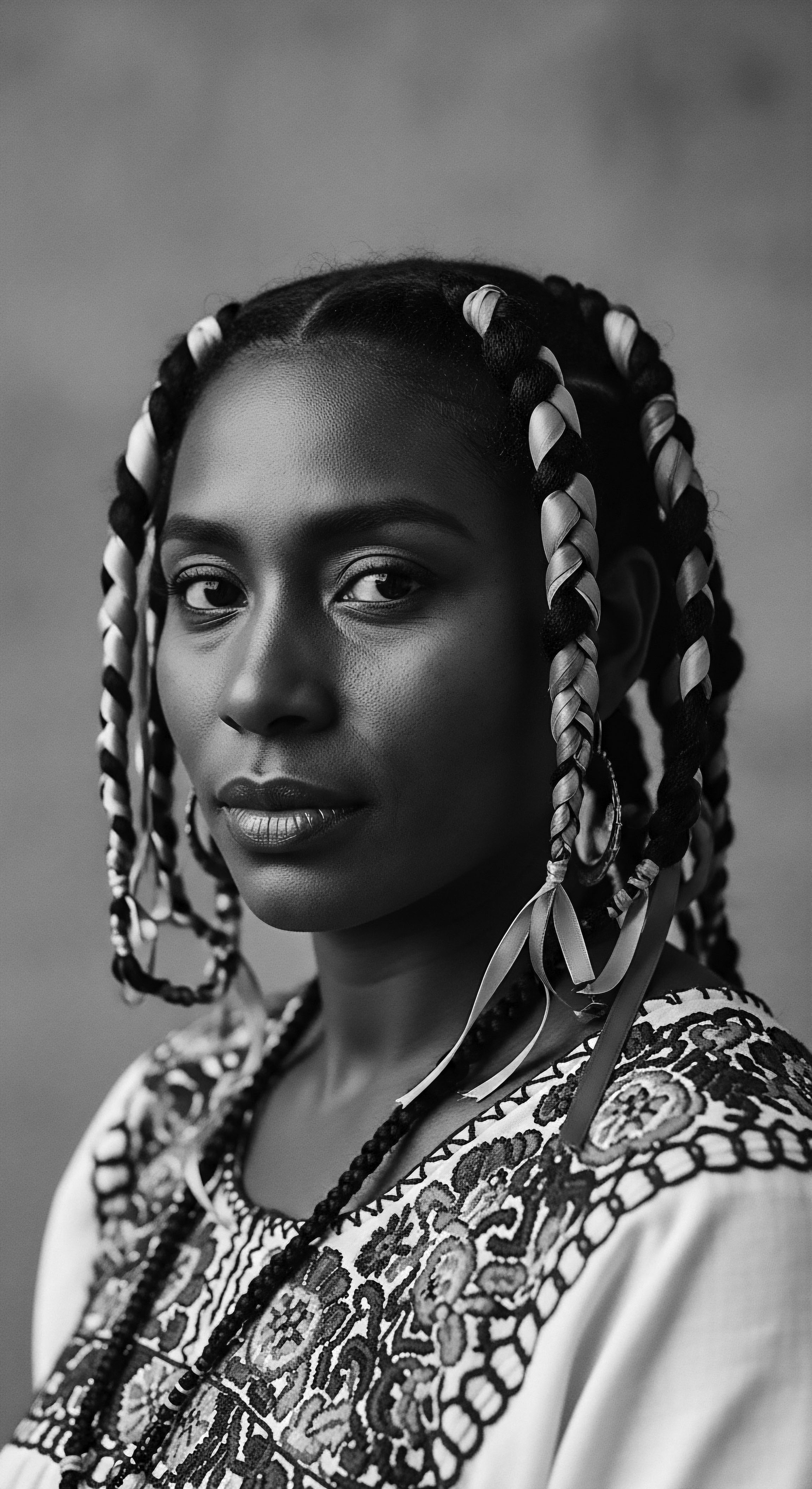

Anti-Colonial Hair
Meaning ❉ Anti-Colonial Hair signifies practices and styles that resist colonial beauty standards, honoring textured hair's ancestral and cultural significance.

Anti-Miscegenation Laws
Meaning ❉ Historical laws criminalizing interracial marriage and relationships, deeply impacting racial identity and textured hair heritage.

How Did Ancient African Traditions Protect Textured Hair?
Ancient African traditions protected textured hair through protective styles, natural ingredients, and communal rituals, preserving its heritage and health.
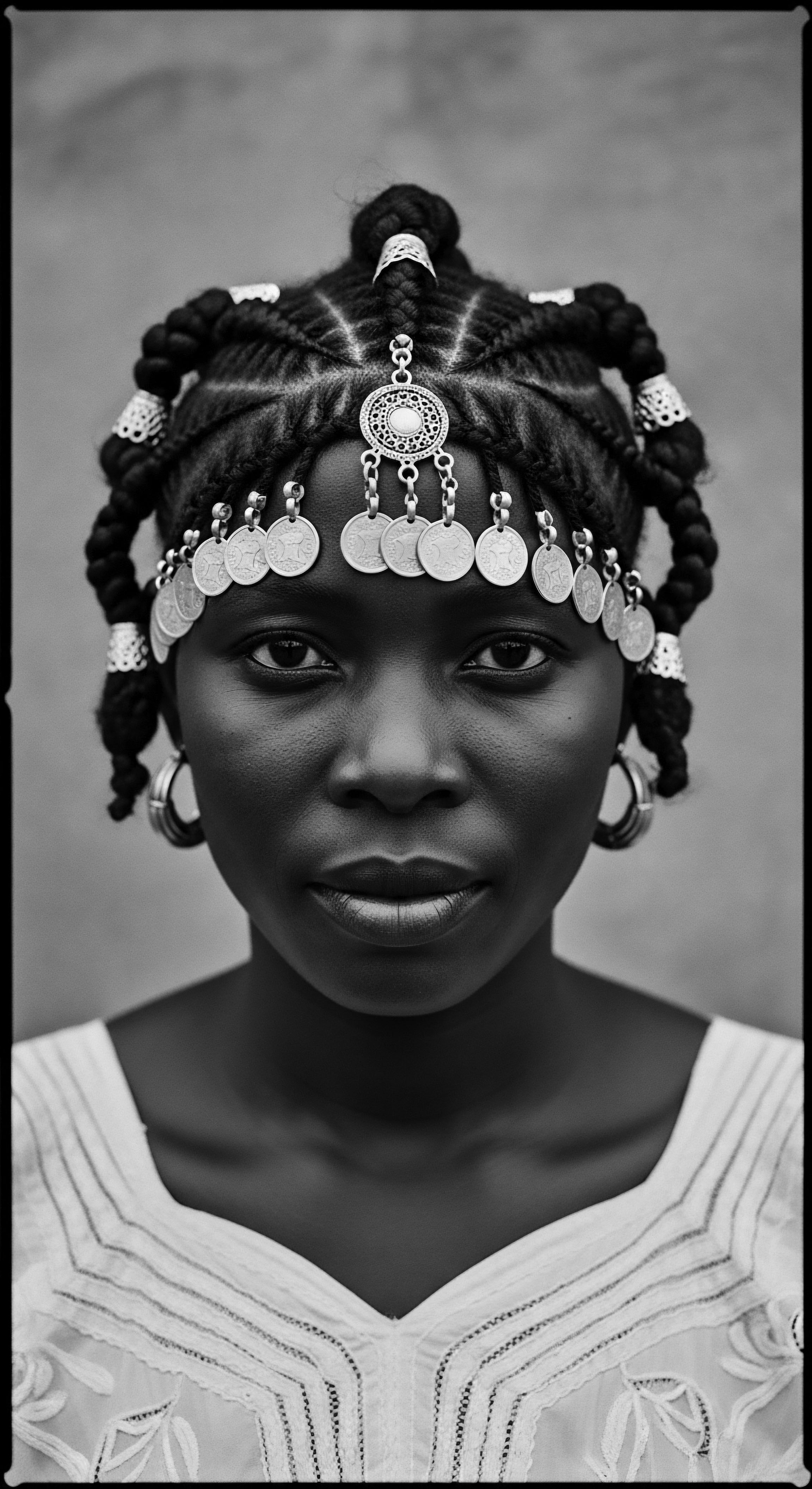

What Specific Textured Hairstyles Conveyed Coded Messages of Freedom?
Textured hairstyles, particularly cornrows, Afros, and dreadlocks, conveyed coded messages of freedom, resistance, and cultural pride deeply rooted in heritage.

Colonial Mexico
Meaning ❉ Colonial Mexico profoundly shaped textured hair heritage through racial classification, sumptuary laws, and enduring acts of cultural resistance.

Legal Precedents
Meaning ❉ Legal Precedents are past legal decisions guiding future rulings, profoundly shaping the historical and ongoing experiences of textured hair heritage.

What Is the Cultural Significance of Hair Bonnets in Heritage?
Hair bonnets hold deep cultural significance as a heritage practice for protecting textured hair, preserving styles, and affirming identity.
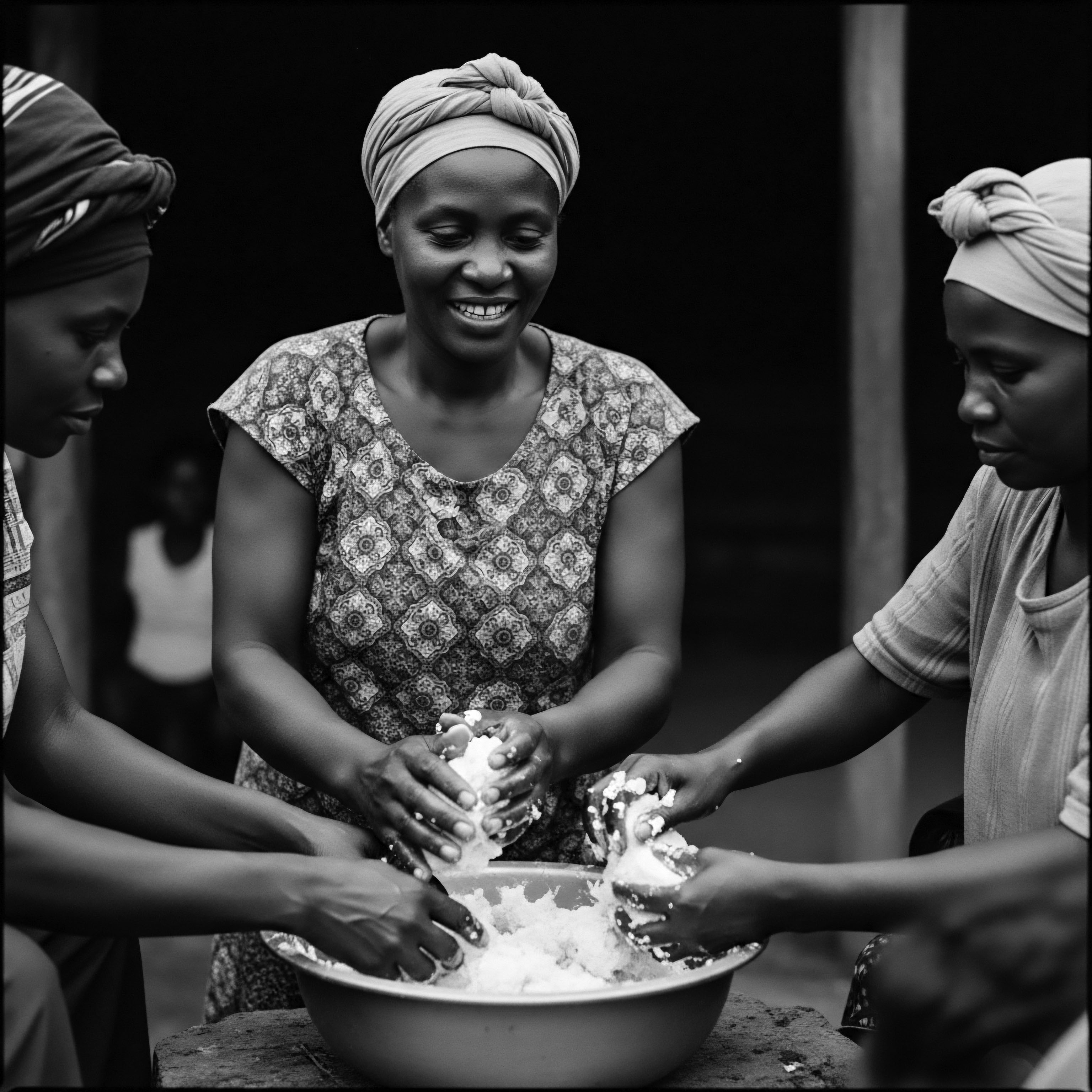
What Is the Cultural Meaning of Hair Cleansing in African Heritage?
Hair cleansing in African heritage signifies spiritual connection, communal bonding, and a profound assertion of identity and ancestral pride.

Va Fealoa’i
Meaning ❉ Va Fealoa'i signifies the profound, interwoven relationship between textured hair's biology and its enduring legacy of ancestral care and cultural identity.

What Ancestral Practices Preserved Textured Hair Identity?
Ancestral practices preserved textured hair identity through cultural symbolism, natural ingredients, and communal care, rooted deeply in heritage.
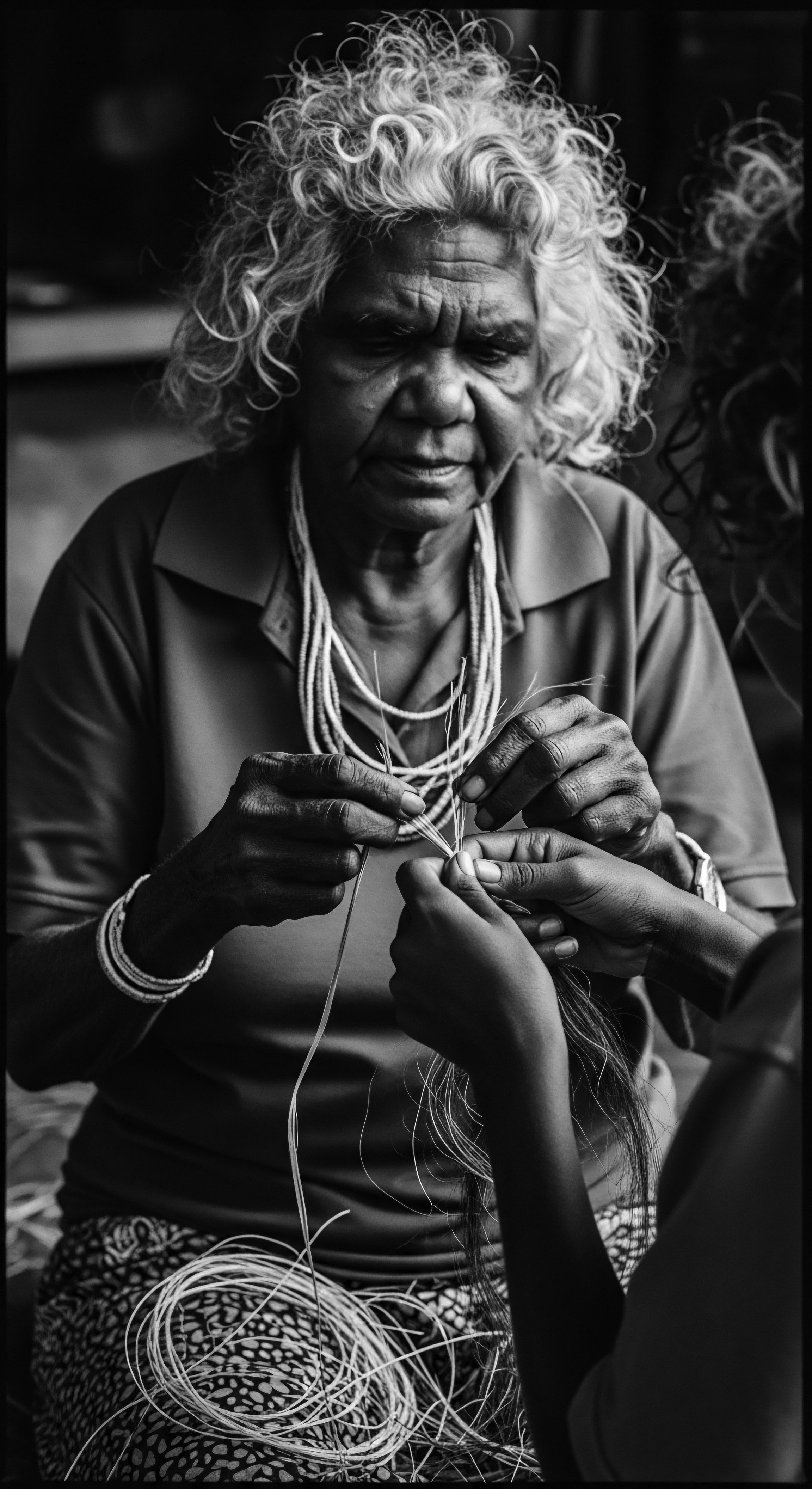

Identity Businesses
Meaning ❉ Identity Businesses are commercial entities deeply intertwined with and actively perpetuating the cultural significance and heritage of textured hair.
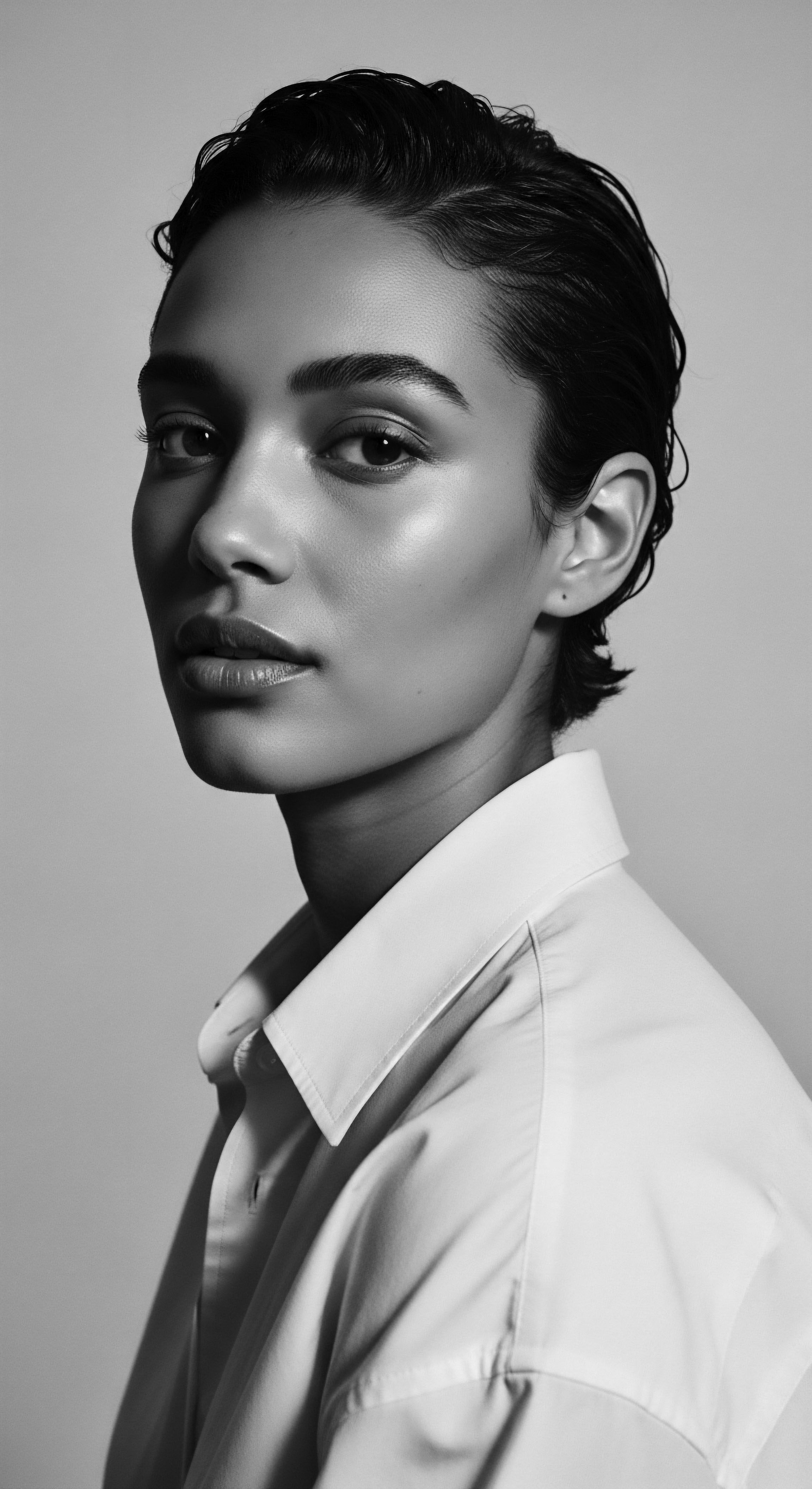

Afro-Brazilian Autonomy
Meaning ❉ Afro-Brazilian Autonomy signifies the self-determination of Afro-Brazilian communities and individuals, powerfully expressed through textured hair heritage.

Willie Morrow
Meaning ❉ The Willie Morrow represents a profound legacy of innovation and cultural affirmation in textured hair, rooted in tools and philosophies for self-acceptance.

Cultural Resilience Hair
Meaning ❉ Cultural Resilience Hair defines the enduring power of textured hair as a symbol of identity, heritage, and resistance within Black and mixed-race communities.
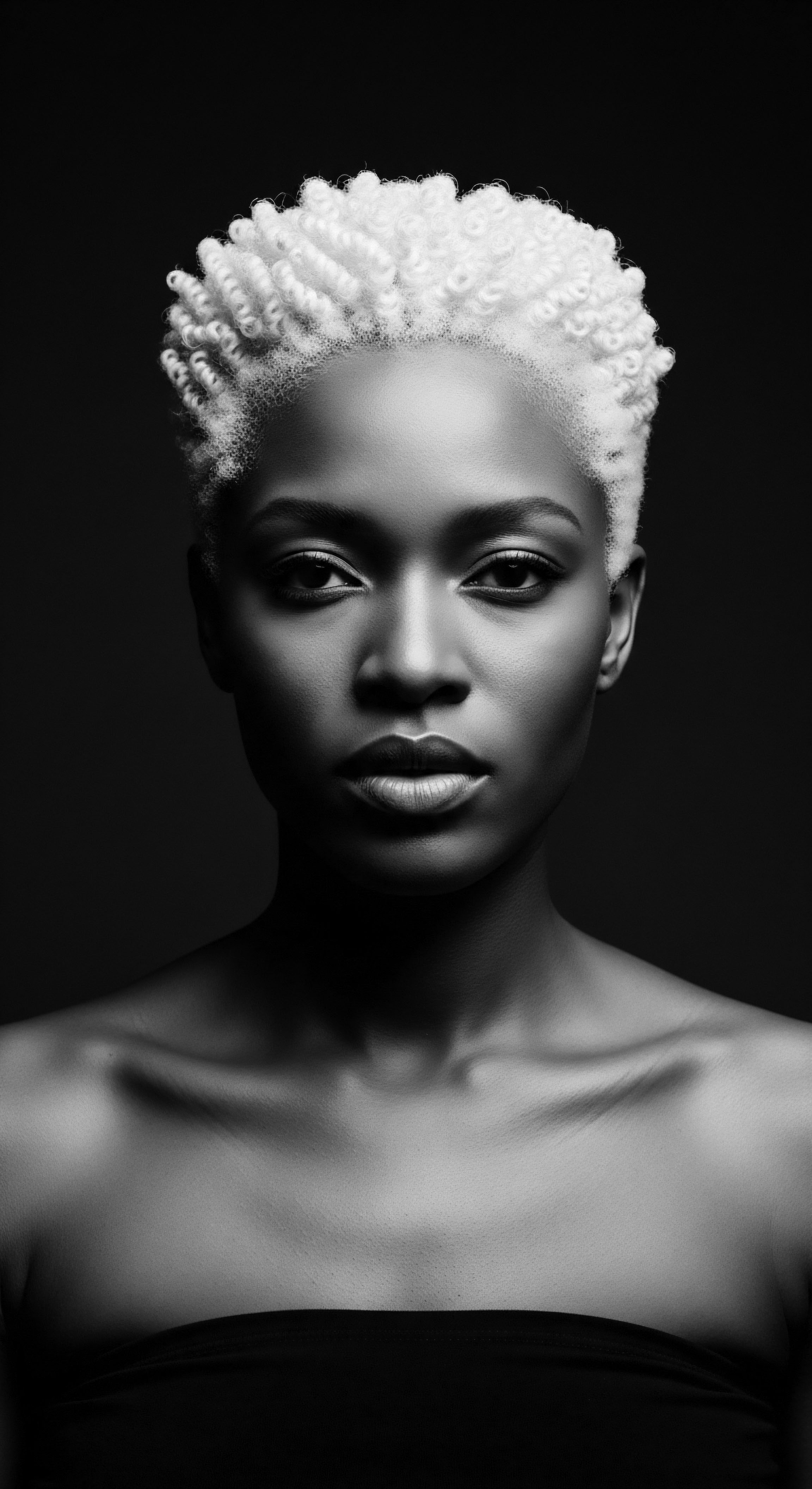

Quilombola Communities
Meaning ❉ Quilombola Communities are groups of Brazilians of African descent who have preserved their cultural heritage and identity, often through the significance of textured hair.
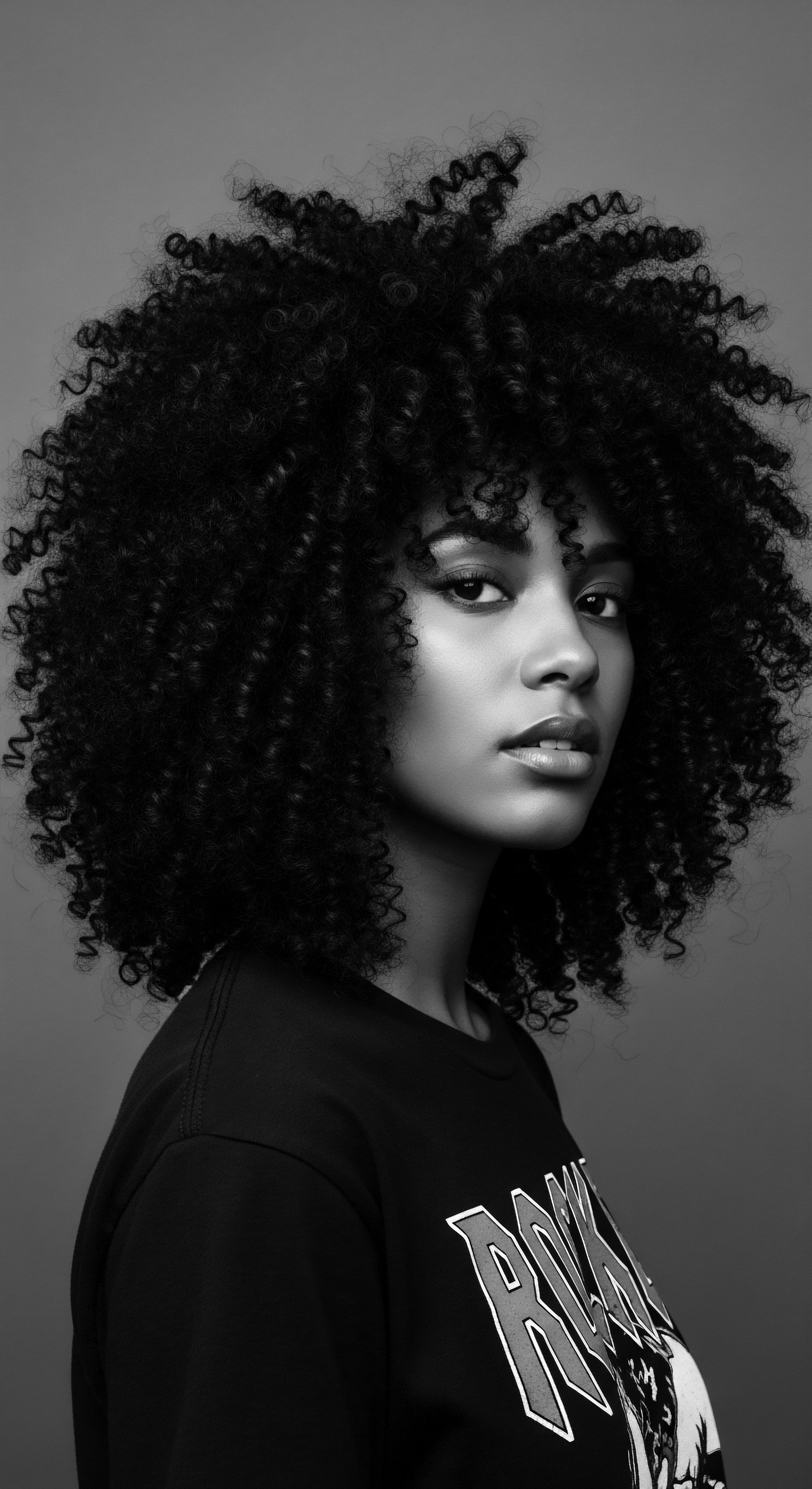

Quilombola History
Meaning ❉ Quilombola History defines the enduring legacy of self-liberated communities in Brazil, deeply intertwined with the heritage of textured hair and ancestral cultural preservation.

How Did Headwraps Become Symbols of Black Hair Heritage and Resistance?
Headwraps became symbols of Black hair heritage and resistance through their protective, cultural, and defiant uses across centuries.

What Is the Tignon Law’s Heritage?
The Tignon Law's heritage is a story of Black women transforming oppression into a vibrant expression of textured hair identity and cultural pride.

Brazilian Identity
Meaning ❉ Brazilian Identity is a dynamic cultural concept profoundly shaped by historical racial hierarchies and the enduring heritage of textured hair.

New Orleans Tignons
Meaning ❉ The New Orleans Tignon is a head covering mandated by colonial law, transformed by Black women into a vibrant symbol of cultural resistance and beauty.

Can Modern Science Validate Traditional Textured Hair Care Methods?
Modern science increasingly validates traditional textured hair care methods by affirming their efficacy and alignment with hair biology, honoring a rich ancestral heritage.

Holistic Black Wellness
Meaning ❉ Holistic Black Wellness is a comprehensive approach to well-being for Black individuals, integrating physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual health through the lens of textured hair heritage and ancestral practices.

Owambo Hair
Meaning ❉ Owambo Hair defines the distinctive hair traditions, care rituals, and cultural significance rooted in the ancestral practices of the Owambo people.

Orixá Plants
Meaning ❉ Orixá Plants are sacred botanicals, imbued with spiritual energy, central to Afro-diasporic traditions for holistic well-being and textured hair care.

