
Anti-Colonial Resistance
Meaning ❉ Anti-Colonial Resistance signifies the active pushback against colonial rule, profoundly expressed through the enduring heritage and symbolic power of textured hair.

Black Seminole Identity
Meaning ❉ The Black Seminole Identity is a cultural fusion born of African and Indigenous resistance, profoundly expressed through textured hair heritage and traditions.

Rastafari Influence
Meaning ❉ The Rastafari Influence is a profound declaration of identity and a re-rooting in ancestral hair practices, challenging colonial beauty norms.

Hair Resistance Symbolism
Meaning ❉ Hair Resistance Symbolism denotes the profound cultural, historical, and personal declaration of identity through textured hair against systemic oppression.

In What Ways Did Historical Events Impact Textured Hair Care Traditions?
Historical events profoundly shaped textured hair care, transforming ancient identity markers into symbols of both oppression and powerful heritage resistance.
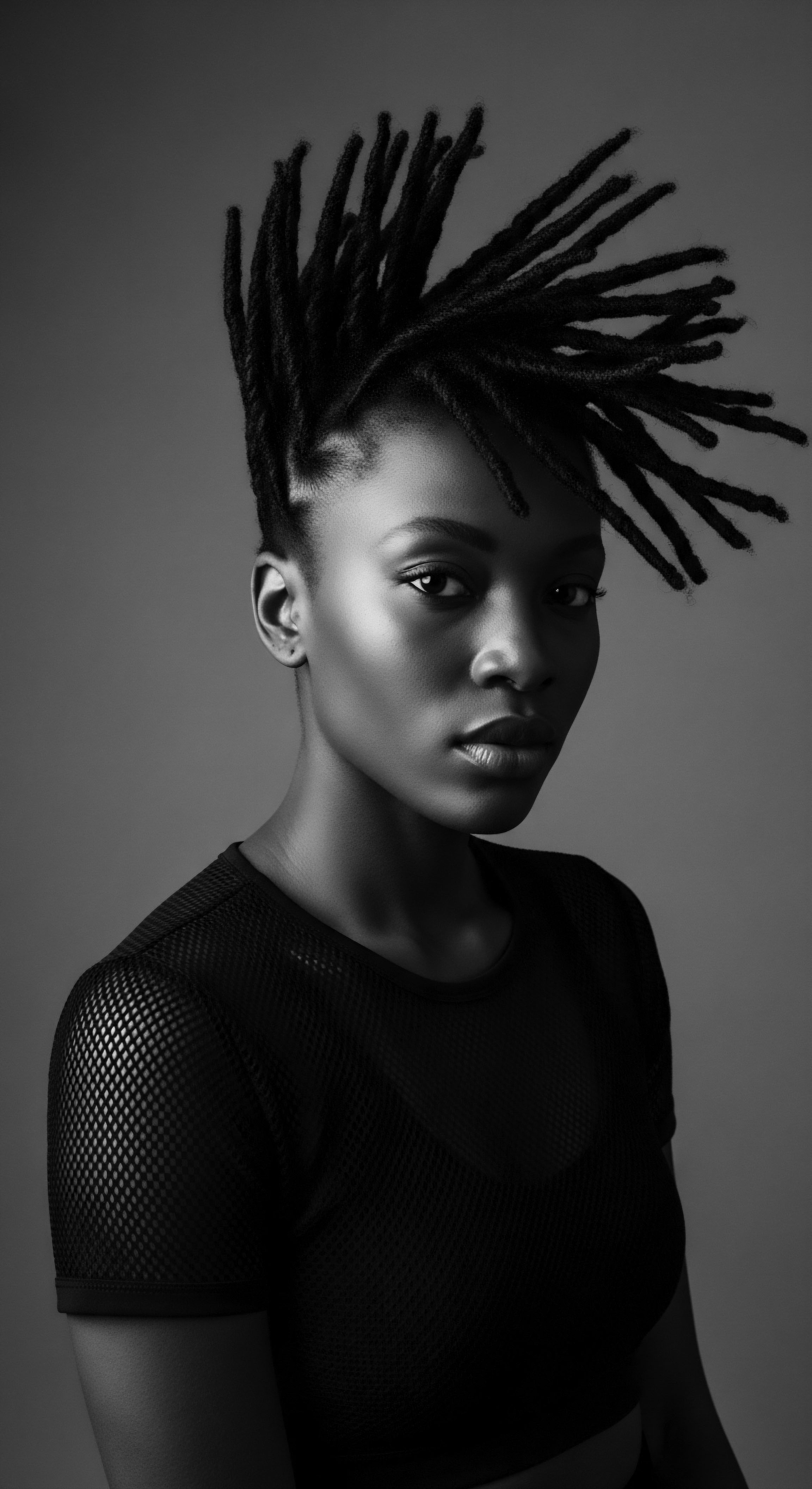
In What Ways Did Textured Hair Serve as a Symbol of Defiance Historically?
Textured hair historically served as a symbol of defiance by embodying cultural heritage, communicating covert messages, and asserting identity against oppressive norms.

What Is the Ancestral Connection of Textured Hair Discrimination?
Textured hair discrimination is ancestrally rooted in colonial efforts to erase Black identity by devaluing natural hair and imposing Eurocentric beauty standards.
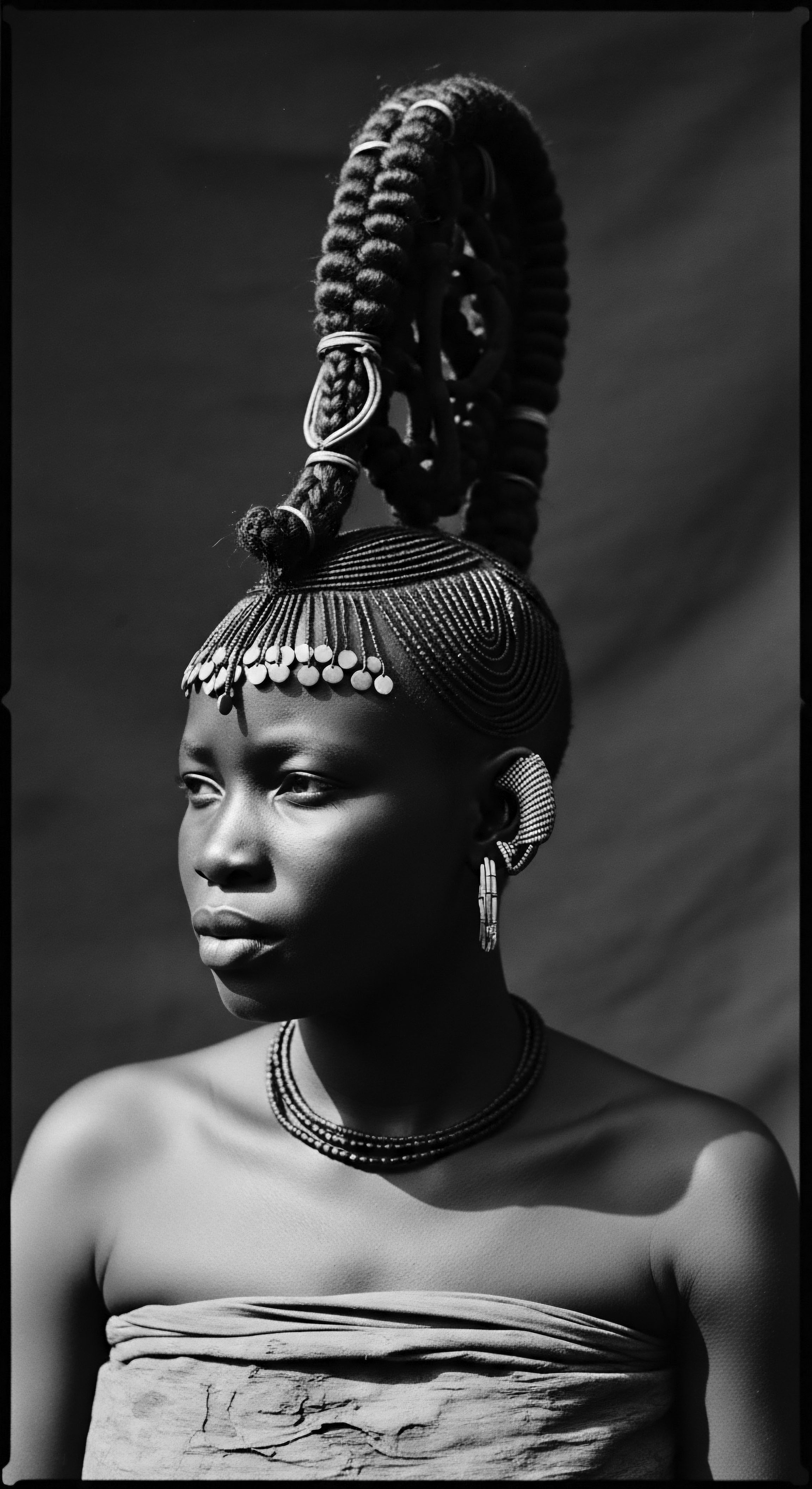

How Did Tignon Laws Shape Black Hair Heritage?
The Tignon Laws compelled free Black women to cover their elaborate hairstyles, yet they responded by transforming headwraps into symbols of resistance and cultural artistry, profoundly shaping textured hair heritage.
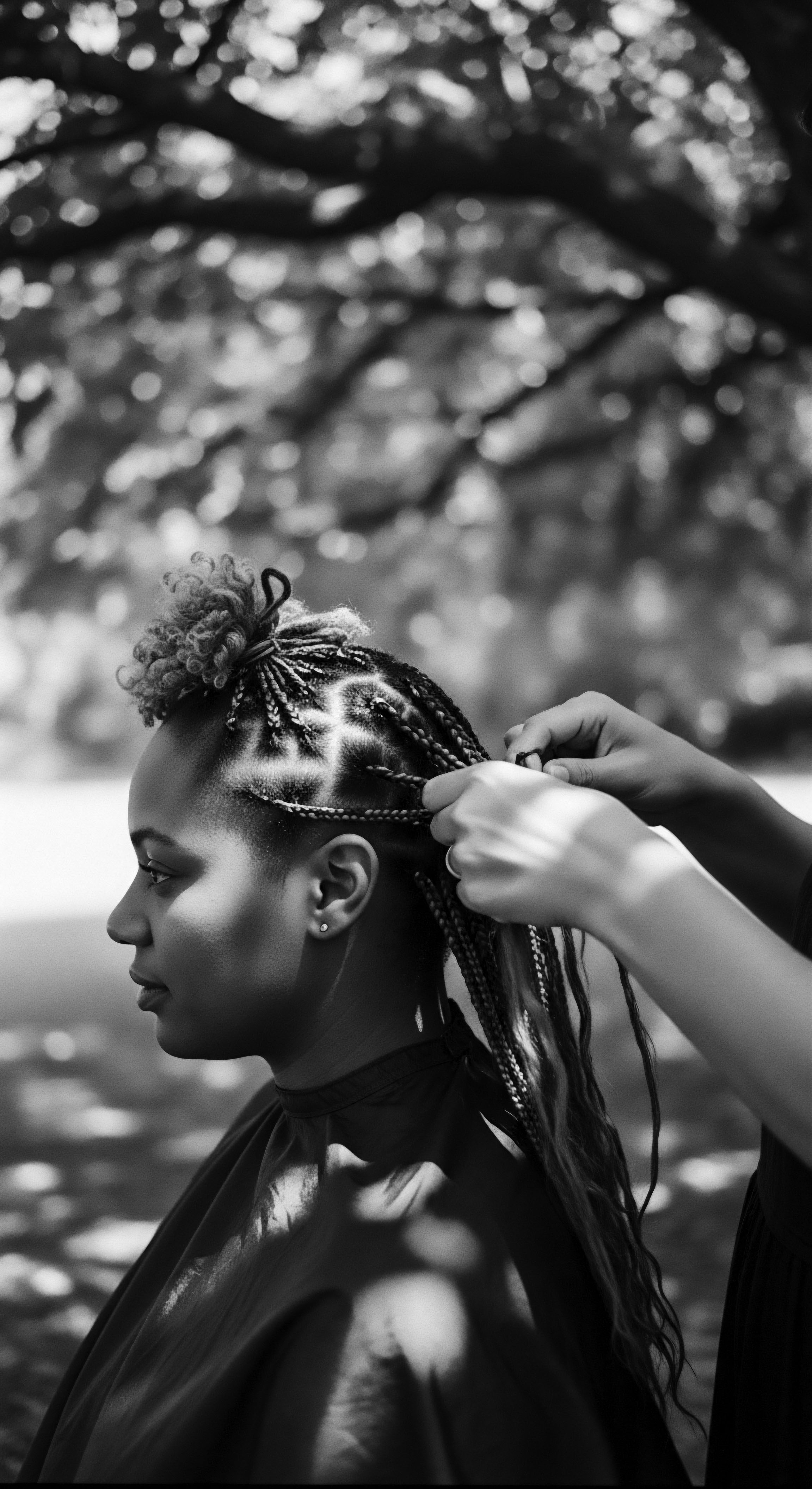
Ethnobotany Diaspora
Meaning ❉ Ethnobotany Diaspora defines the journey of ancestral plant knowledge for textured hair care, embodying cultural resilience across African descendant communities.

What Historical Acts of Resistance Involved Textured Hair?
Textured hair has served as a powerful historical tool of resistance, embodying cultural heritage and self-determination against oppression.
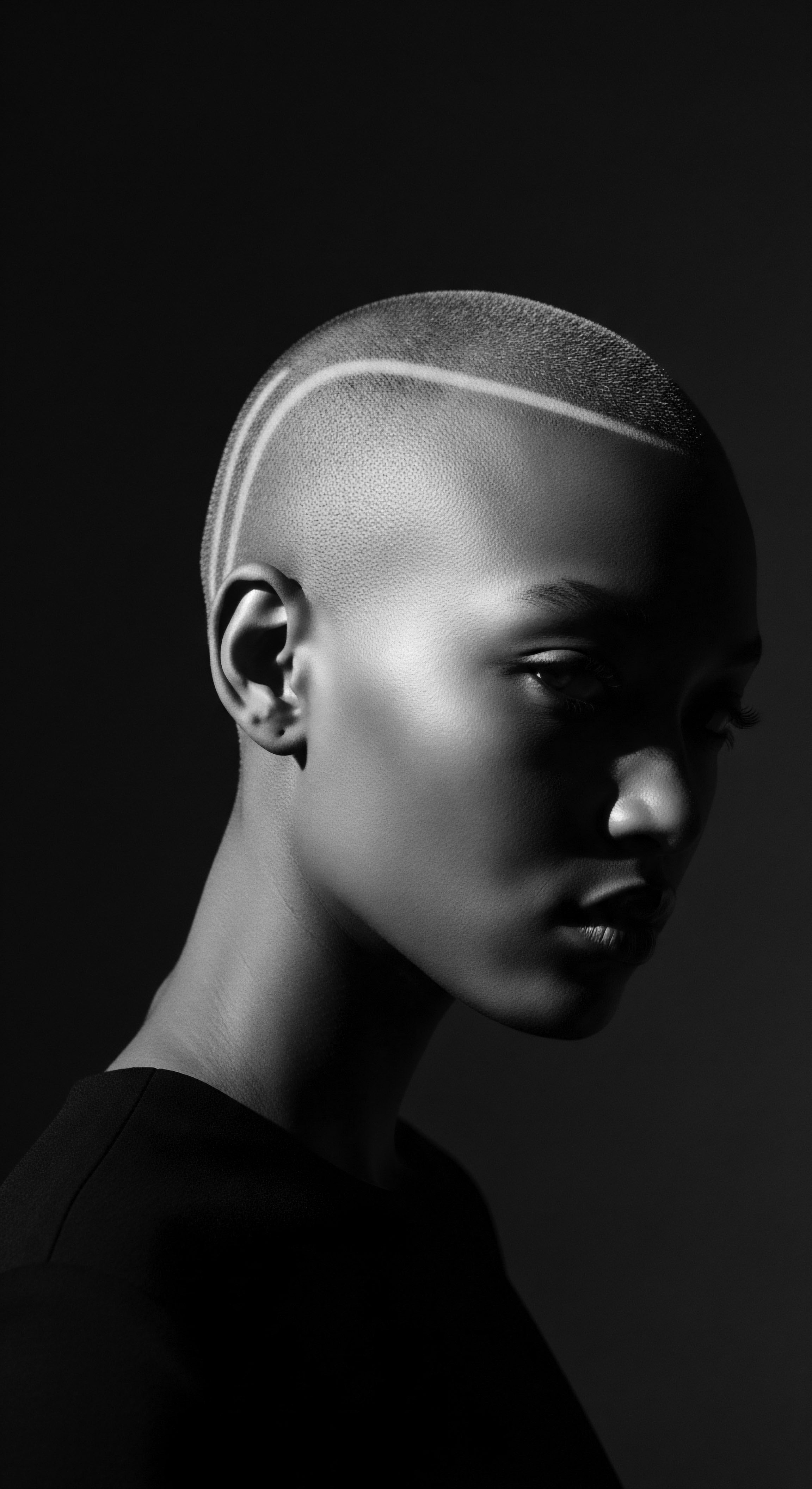

How Did Cornrows Become a Symbol of Resistance and Heritage?
Cornrows symbolize resistance and heritage by carrying ancestral knowledge, acting as coded communication for freedom, and serving as a visual affirmation of Black identity.
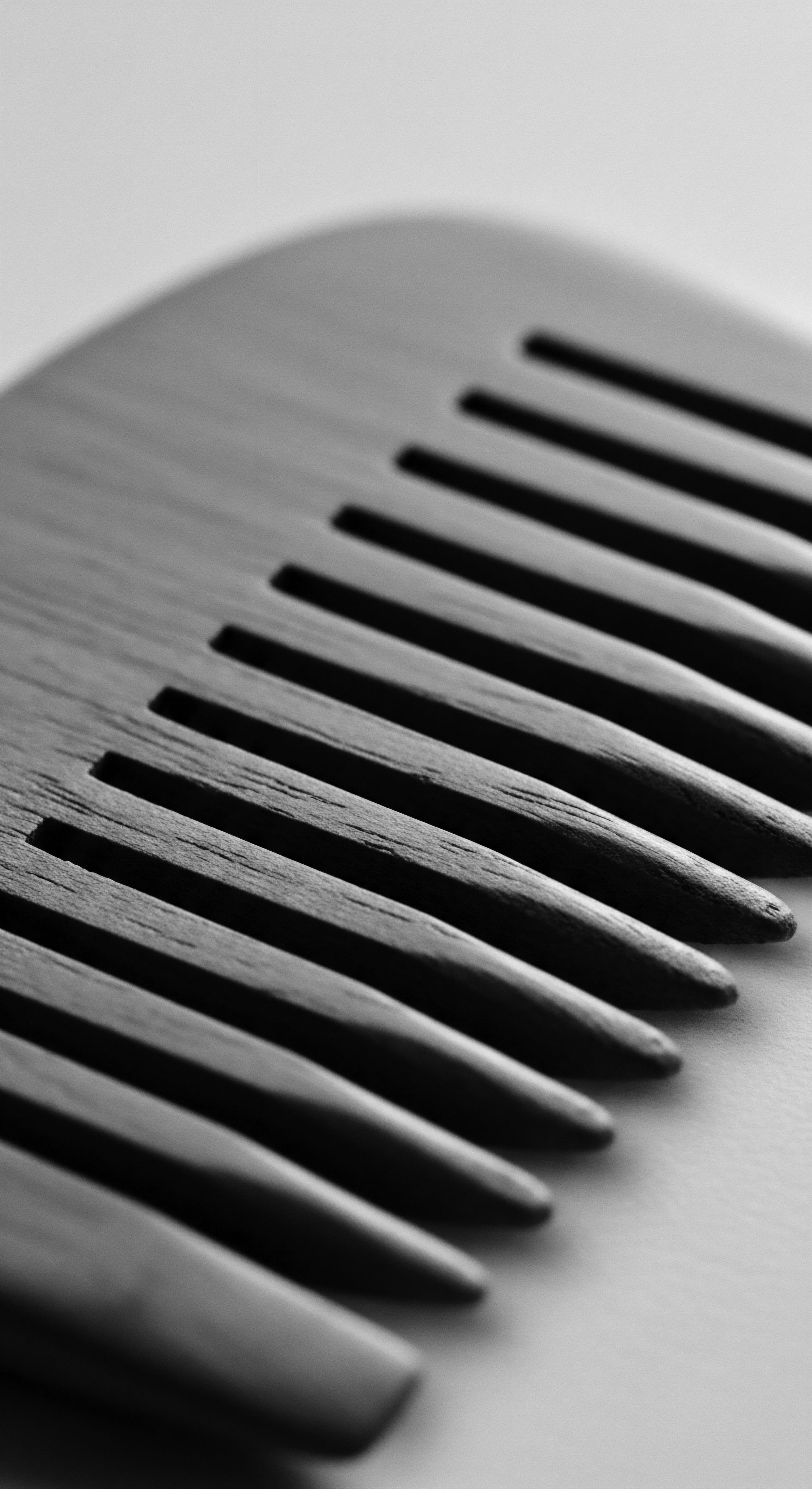

What Traditional Ingredients Connect Hair Care to Environmental Heritage?
Traditional ingredients like shea butter and African black soap link textured hair care to environmental heritage through sustainable practices and ancestral wisdom.

How Did Tignon Laws Affect Hair Heritage?
The Tignon laws forced Black women to cover their hair, but they transformed headwraps into powerful symbols of cultural heritage and resistance.
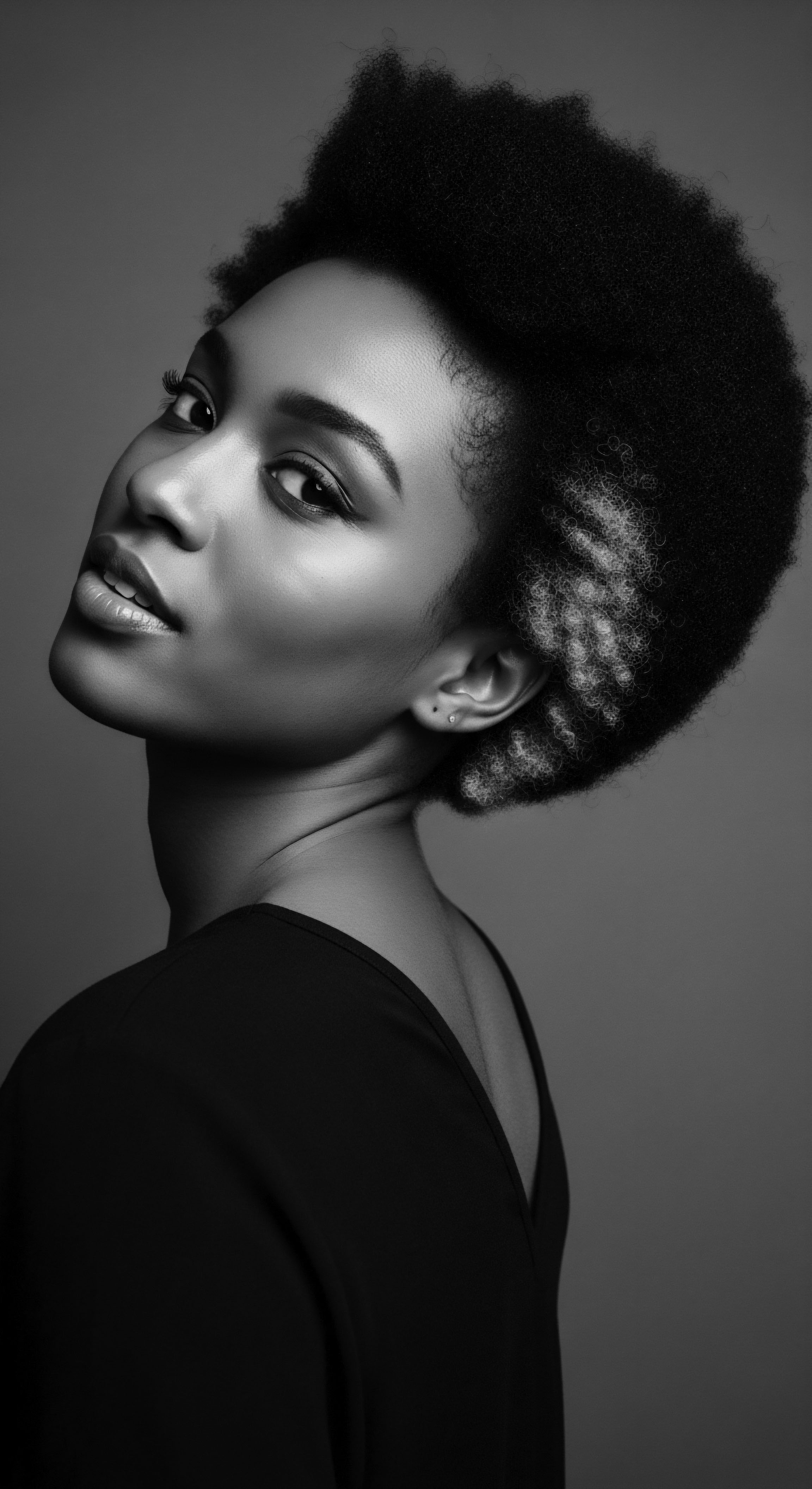

In What Ways Did the Tignon Laws Attempt to Suppress Black Hair Heritage?
The Tignon Laws attempted to suppress Black hair heritage by forcing free women of color to cover their culturally significant hairstyles, marking them as subordinate.

What Is the Cultural Significance of Headwraps in Black Heritage?
Headwraps embody Black heritage through ancestral wisdom, resilience, and identity, deeply intertwined with textured hair care and cultural expression.

Natural Hair Detox
Meaning ❉ Natural Hair Detox is the deliberate purification of textured hair and scalp, deeply rooted in ancestral cleansing rituals and cultural heritage.
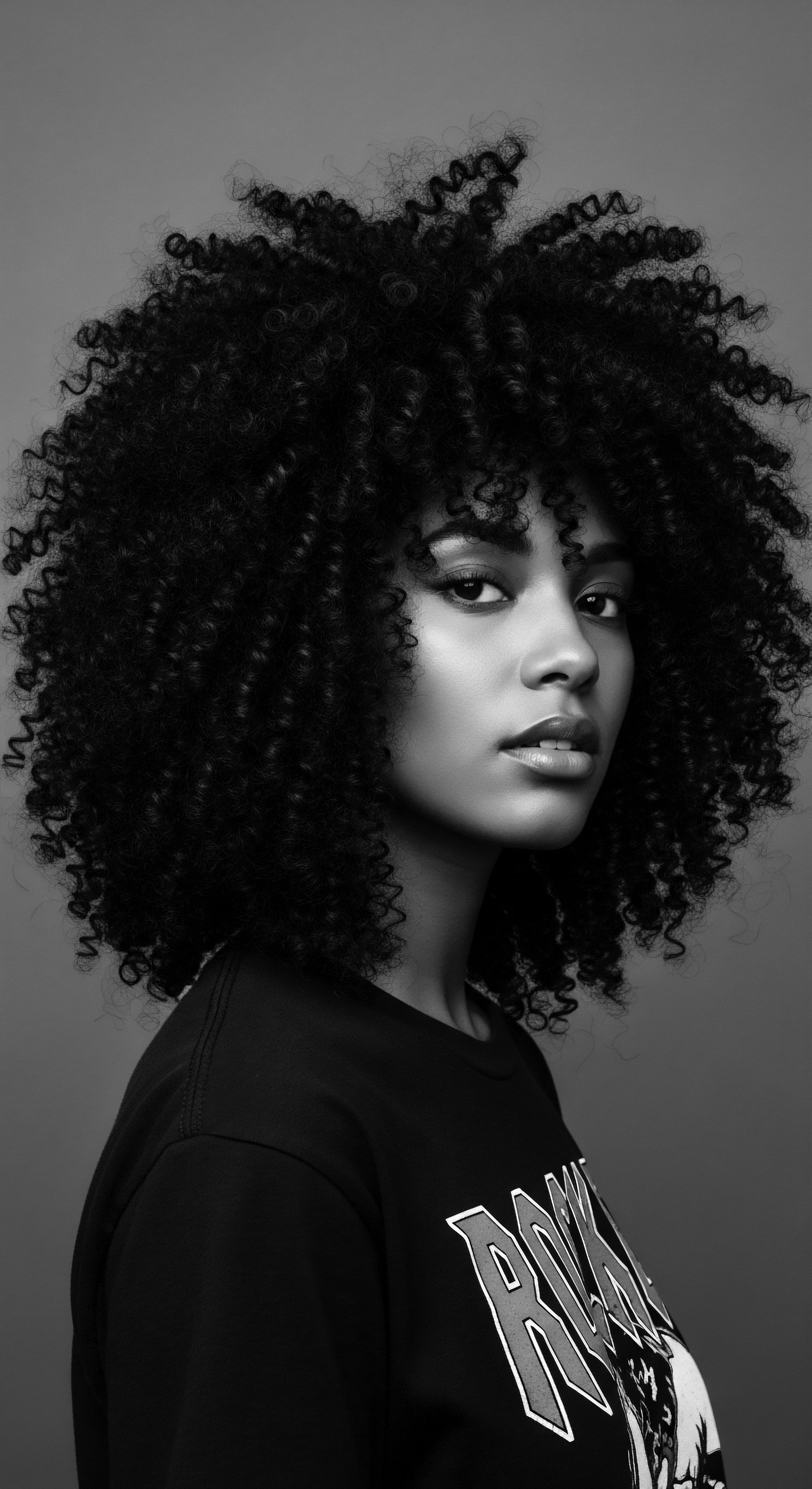

How Did Tignon Laws Restrict Black Women’s Hair Heritage?
Tignon Laws restricted Black women's hair heritage by mandating head coverings, yet sparked a defiant transformation of the tignon into a symbol of cultural pride.

Quilombola Ethnobotany
Meaning ❉ Quilombola Ethnobotany is the ancestral plant knowledge and practices of Afro-Brazilian communities, profoundly shaping their heritage, identity, and textured hair care.

Afro-Colombian Hair Braids
Meaning ❉ Afro-Colombian hair braids are intricate styles deeply rooted in heritage, signifying cultural identity, historical resistance, and ancestral wisdom within Colombia's Black communities.

How Did Head Coverings Transform into Symbols of Heritage and Resistance?
Head coverings transformed into heritage and resistance symbols by protecting textured hair and serving as defiant cultural declarations.

Political Resistance
Meaning ❉ Political Resistance, within textured hair heritage, is the steadfast preservation of identity and ancestral practices against suppression.

Botanical Elements
Meaning ❉ Botanical Elements embody ancestral wisdom and cultural resilience through plant-derived ingredients for textured hair care.

Colonial Hair Laws
Meaning ❉ Colonial Hair Laws were mandates and societal pressures regulating hair to enforce racial hierarchies and suppress cultural identity, especially for textured hair.
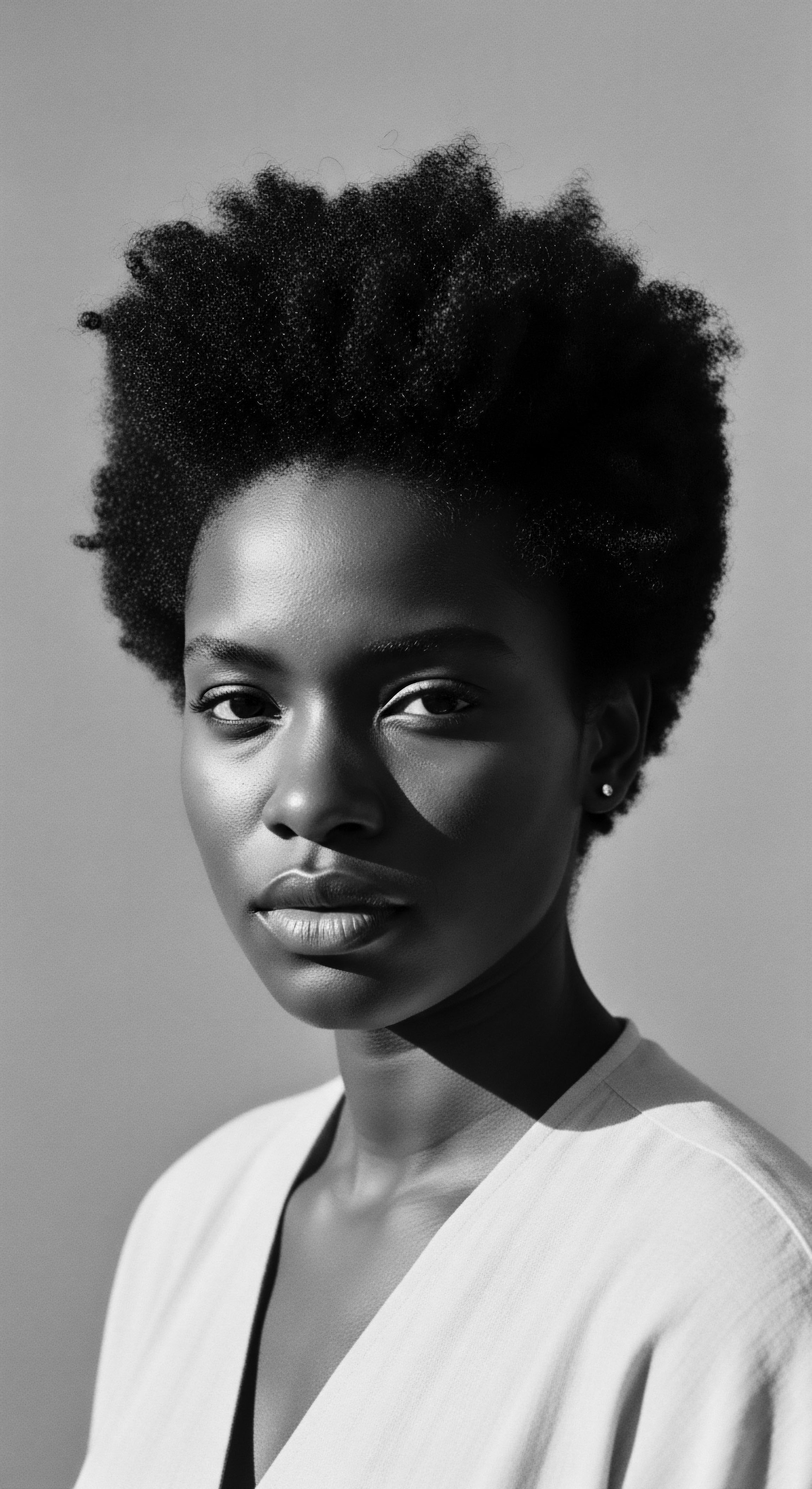

What Role Did Textured Hair Rituals Play in Community Identity and Resistance through History?
Textured hair rituals, from ancient times, served as vital expressions of community identity and quiet resistance, preserving ancestral heritage.
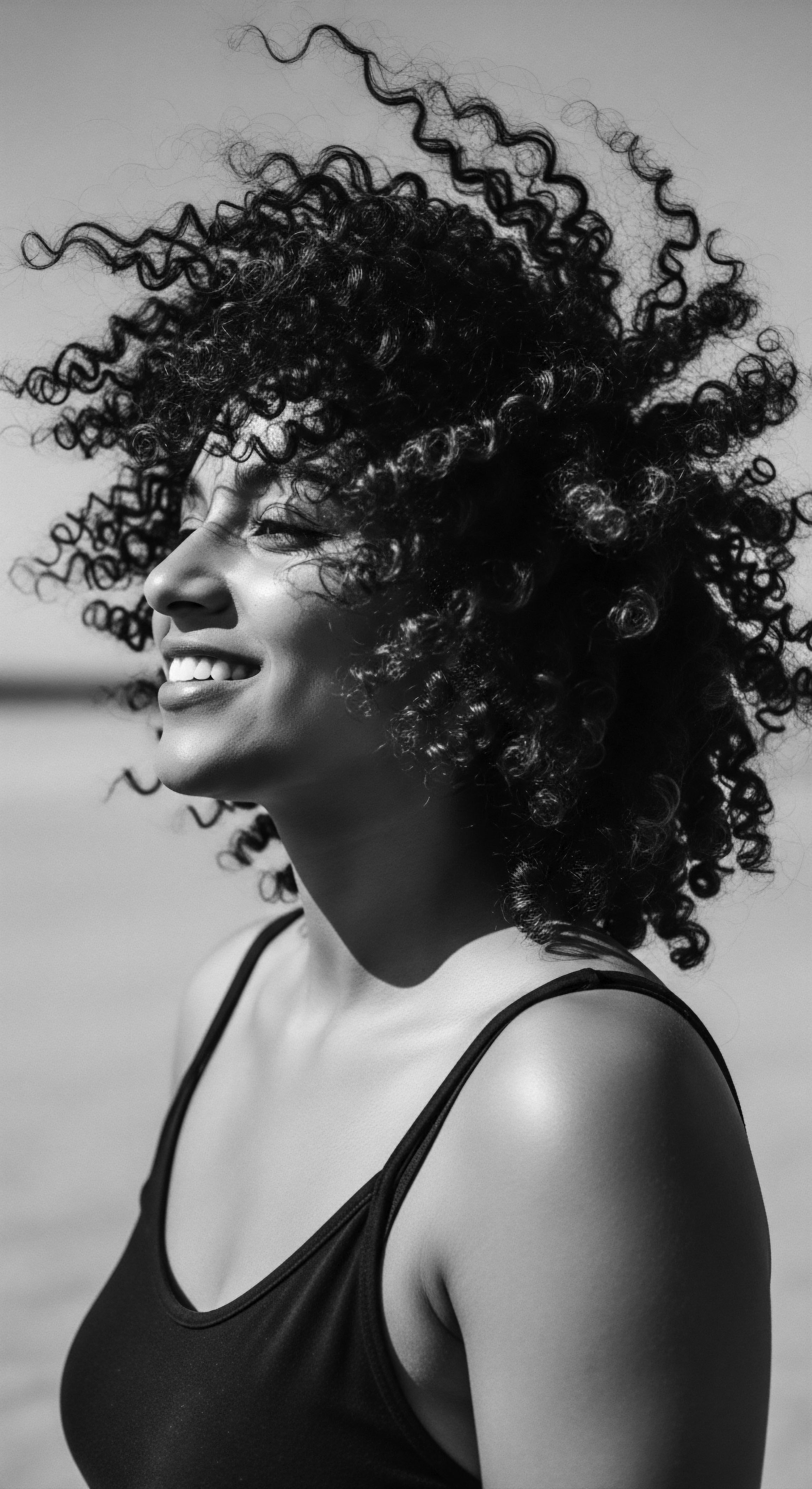

How Did Textured Hair Symbolize Freedom in the Diaspora?
Textured hair symbolized freedom in the diaspora through covert communication, cultural preservation, and a powerful assertion of self against oppression.
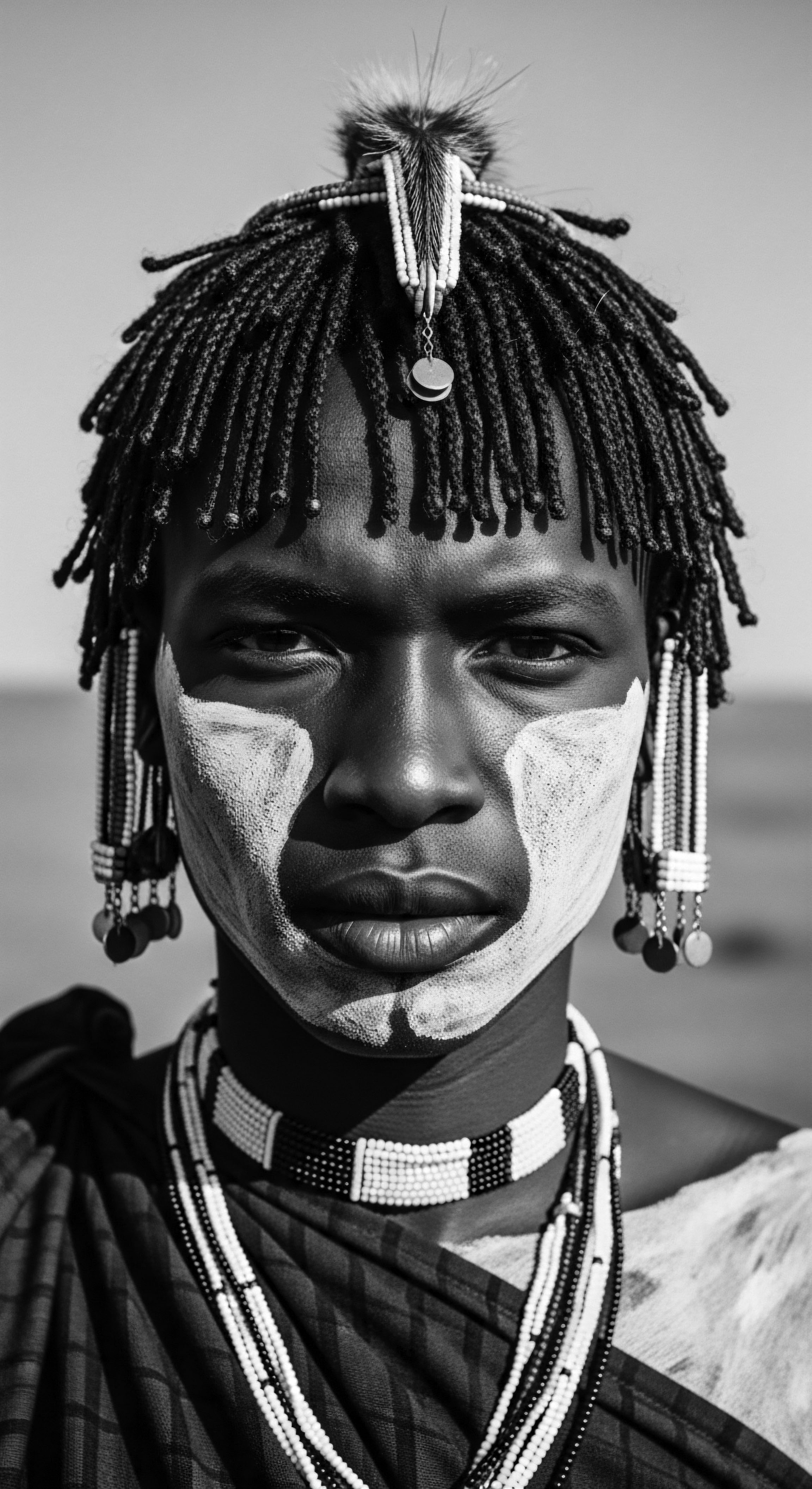

Marie Laveau Hair
Meaning ❉ Marie Laveau Hair signifies the enduring spirit of Black and mixed-race women who transformed hair adornment into a powerful statement of cultural defiance and identity.

Cornrow Cultural Heritage
Meaning ❉ Cornrow Cultural Heritage is the historical and cultural significance of braiding hair close to the scalp, embodying identity, resilience, and ancestral wisdom for textured hair.
Epistemicide
Meaning ❉ Epistemicide describes the systematic suppression of a group's knowledge systems, particularly ancestral textured hair practices and cultural wisdom.
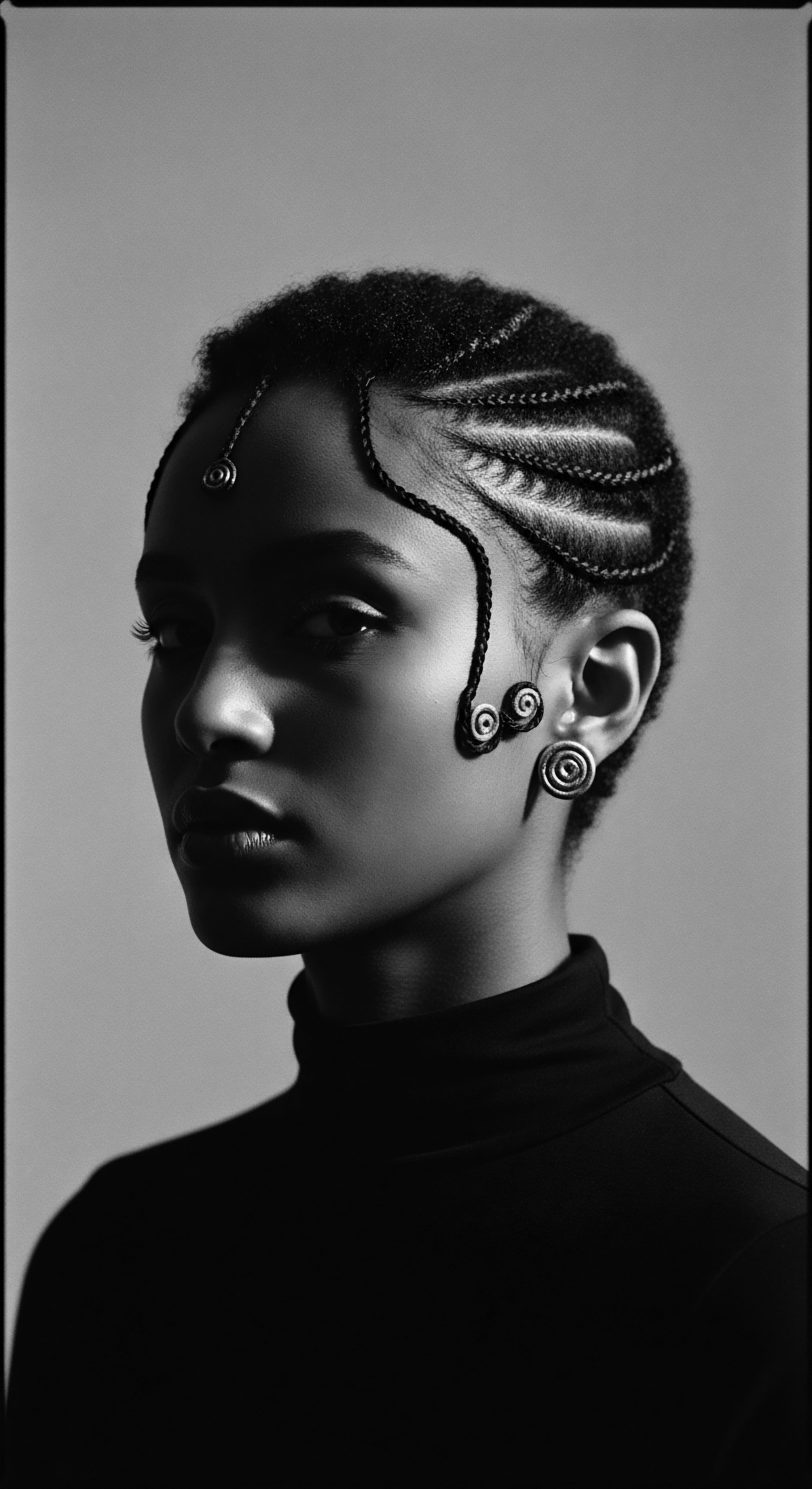

Traditional Headwraps
Meaning ❉ Traditional Headwraps are cultural adornments for textured hair, embodying historical identity, resistance, and ancestral wisdom across the African diaspora.

