
Tzniut and Hair
Meaning ❉ Tzniut and Hair signifies the inherent reverence, cultural sanctity, and enduring dignity of textured hair within Black and mixed-race heritage.

How Did the Tignon Laws Transform Headwear’s Heritage for Black Women?
Tignon Laws compelled Black women to cover hair, yet they transformed headwraps into symbols of cultural pride and enduring heritage.

How Has Textured Hair Care Been a Form of Resistance?
Textured hair care has served as a powerful act of resistance, preserving Black and mixed-race heritage and identity against systemic oppression.

Sumptuary Law
Meaning ❉ Sumptuary Law defines historical societal mandates regulating personal display, often impacting hair as a marker of identity and status.

Muridiyya Hair Heritage
Meaning ❉ Conceptual framework for the historical, spiritual, and communal approaches to textured hair within the Muridiyya Sufi order of Senegal.
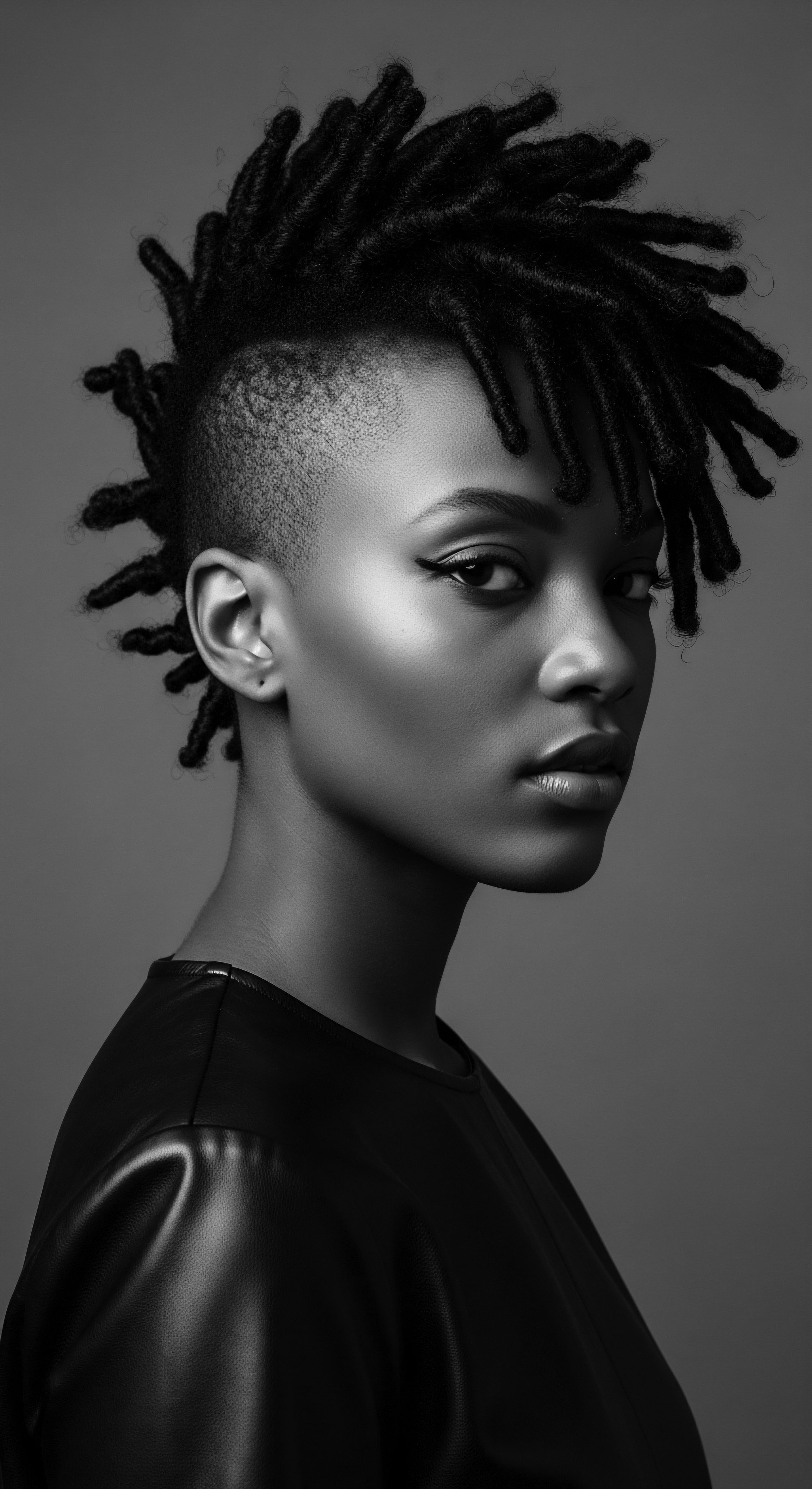
Why Did Textured Hair Become a Political Statement?
Textured hair became a political statement due to its deep heritage as an identity marker, subsequently targeted by colonial oppression.

Louisiana Tignon
Meaning ❉ The Louisiana Tignon is a historical head covering that became a symbol of cultural defiance and identity for women of color.

How Did Tignon Laws Influence Textured Hair?
The Tignon Laws, enacted in 1786 New Orleans, forced Black women to cover their hair, yet prompted a powerful display of cultural resilience and defiant self-expression.

Hair Covering Laws
Meaning ❉ Hair Covering Laws are dictates governing hair concealment, reflecting complex histories of cultural reverence and oppressive societal control over textured hair heritage.

How Have Textured Hair Styles Resisted Oppression across History?
Textured hair styles have resisted oppression throughout history by serving as profound cultural declarations, embodying heritage, and acting as symbols of identity and resilience.

Cultural Significance Headwear
Meaning ❉ Cultural Significance Headwear refers to head coverings embodying historical, social, and spiritual meanings within specific communities, especially textured hair heritage.

How Did Headwraps Become Symbols of Black Identity and Heritage?
Headwraps became symbols of Black identity and heritage through ancestral African practices, forced colonial mandates, and powerful reclamation of self-expression.

Candomblé Rituals
Meaning ❉ Candomblé Rituals are a spiritual system from West Africa, sustained in Brazil, profoundly linking sacred practices to textured hair heritage and identity.

Freedom Seekers
Meaning ❉ Freedom Seekers signifies the pursuit of liberation by enslaved individuals, profoundly expressed and aided by their textured hair heritage.

In What Ways Do Modern Hair Practices Continue to Honor a Heritage of Cultural Resistance and Identity?
Modern hair practices for textured hair honor a heritage of cultural resistance and identity by continuing ancestral traditions and challenging oppressive beauty standards.

How Did Ancestral Hair Practices Influence Resistance?
Ancestral hair practices influenced resistance by serving as vital cultural expressions, clandestine communication, and powerful affirmations of textured hair heritage.

How Did Tignon Laws Influence Black Women’s Self-Expression?
Tignon Laws forced Black women to cover their hair, yet they transformed wraps into defiant expressions of textured hair heritage.

What Is the Lasting Cultural Significance of the Tignon Law?
The Tignon Law, meant to suppress, became a powerful symbol of Black women's creative defiance and enduring textured hair heritage.

How Did the Tignon Law Change Hair Expression?
The Tignon Law compelled women of color to cover their hair, paradoxically transforming headwraps into powerful symbols of defiance and cultural pride within textured hair heritage.

What Enduring Heritage Does Textured Hair Represent in Diasporic Communities?
Textured hair represents a living archive of heritage, identity, and profound resistance within diasporic communities.

In What Ways Did Hair Become a Symbol of Cultural Resistance through History?
Textured hair's journey from ancestral reverence to contemporary pride encapsulates centuries of cultural resistance.
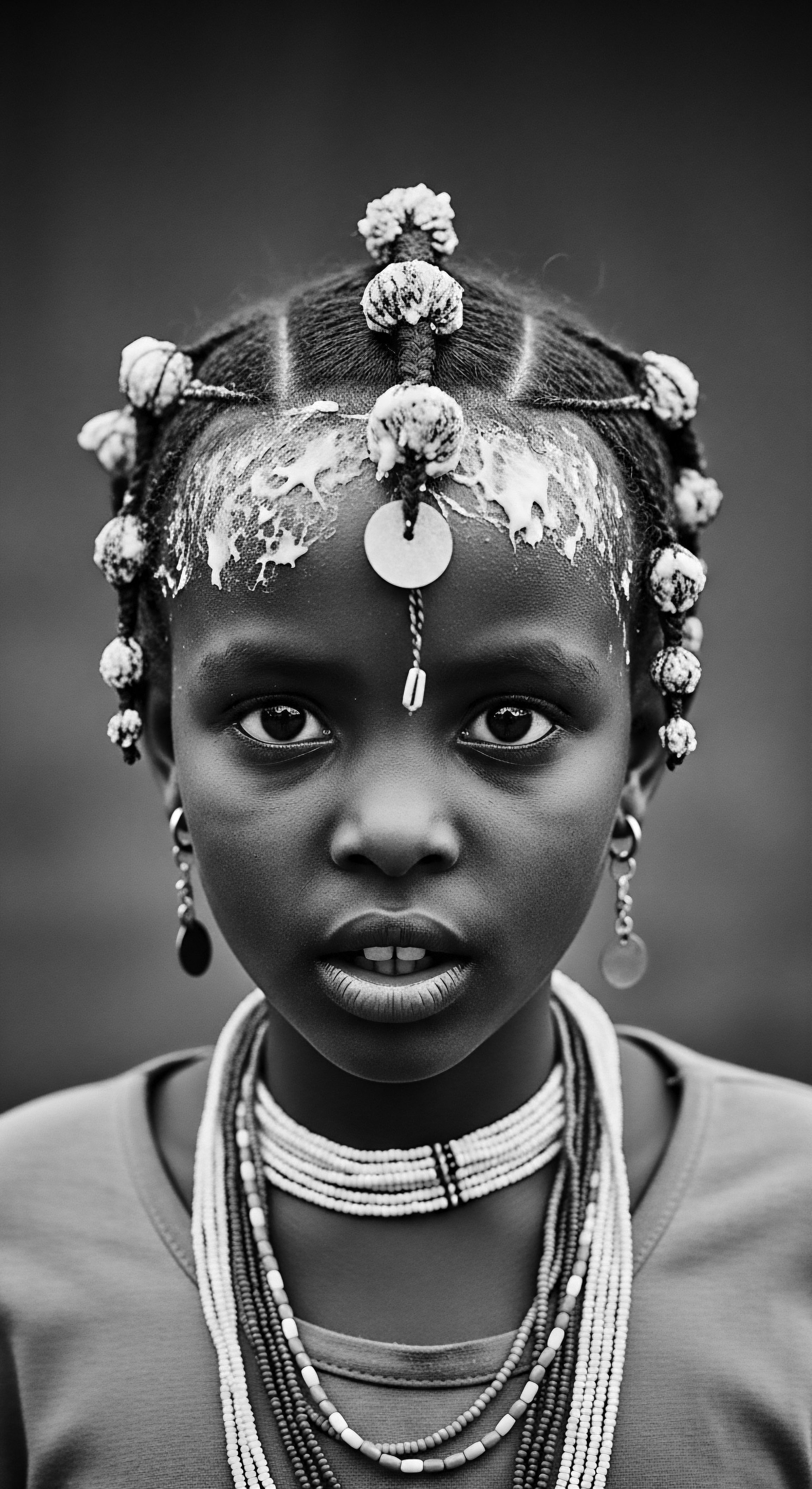

How Did Tignon Laws Control Black Women’s Appearance?
The Tignon Laws aimed to control Black women's appearance by forcing head coverings, yet they sparked powerful expressions of textured hair heritage.

How Did Headwraps Become Symbols of Black Women’s Defiance?
Headwraps became symbols of Black women's defiance by transforming imposed coverings into vibrant expressions of cultural heritage and resistance.

How Did the Tignon Laws Influence Black Women’s Hair Practices?
The Tignon Laws, intended to suppress Black women's beauty, sparked a transformative redefinition of textured hair heritage through artistic headwraps and resilient self-expression.

Traditional Oromo Hair Care
Meaning ❉ Traditional Oromo Hair Care encompasses ancestral methods, natural ingredients, and communal rituals embodying Oromo cultural identity and textured hair heritage.

How Did the Tignon Laws Shape Headwrap Heritage in the American South?
The Tignon Laws compelled head coverings, but Black women transformed them into symbols of defiance and enduring textured hair heritage.

What Historical Examples Show Hair’s Role in Cultural Resistance?
Hair served as a visual testament to identity and a covert tool for survival, deeply rooted in textured hair heritage.

Qing Dynasty Hair
Meaning ❉ The Qing Dynasty hair, known as the queue, was a forced hairstyle symbolizing submission that sparked profound resistance rooted in cultural heritage.


