
Soapnut Definition
Meaning ❉ The 'Soapnut Definition' encompasses the botanical, chemical, and profound cultural significance of Sapindus fruit as a gentle, ancestral cleanser for textured hair.

Traditional Photoprotection
Meaning ❉ Traditional Photoprotection is the ancestral practice of shielding textured hair from environmental elements, deeply rooted in cultural heritage and natural wisdom.

Diasporic Wellness
Meaning ❉ Diasporic Wellness defines holistic well-being for people of African descent, honoring their unique historical experiences and textured hair heritage.

How Did the Tignon Laws Impact Black Women’s Self-Expression and Cultural Heritage?
The Tignon Laws, intended to suppress Black women's visible self-expression, were transformed into powerful statements of cultural heritage and resistance through ingenious styling.
Cultural Foodways
Meaning ❉ Cultural Foodways refers to the inherited practices and ancestral wisdom surrounding hair care, defining identity and resilience within textured hair communities.

In What Ways Do Heritage Oils Connect Black Identity to Historical Hair Care?
Heritage oils serve as tangible links, connecting Black identity to historical hair care through ancestral practices, cultural resilience, and communal rituals.

Tsiiyéél Bun
Meaning ❉ Tsiiyéél Bun is the epigenetic legacy and ancestral memory embedded in textured hair, reflecting its unique resilience and cultural adaptability.

Psychological Impacts
Meaning ❉ The psychological impacts of textured hair describe the profound influence of historical, social, and cultural forces on identity and well-being within Black and mixed-race communities.

In What Ways Did Colonial Forces Suppress African Hair Heritage?
Colonial forces suppressed African hair heritage by imposing Eurocentric beauty standards and enacting laws to strip identity.

What Were the Tignon Laws and Their Hair Heritage Implications?
The Tignon Laws were 18th-century mandates in colonial Louisiana forcing free women of color to cover their textured hair, aiming to suppress their visible status and heritage.

What Traditional Hair Practices Honor Black Heritage?
Traditional Black hair practices honor heritage through intricate styles, natural care, and a powerful legacy of identity and resistance.
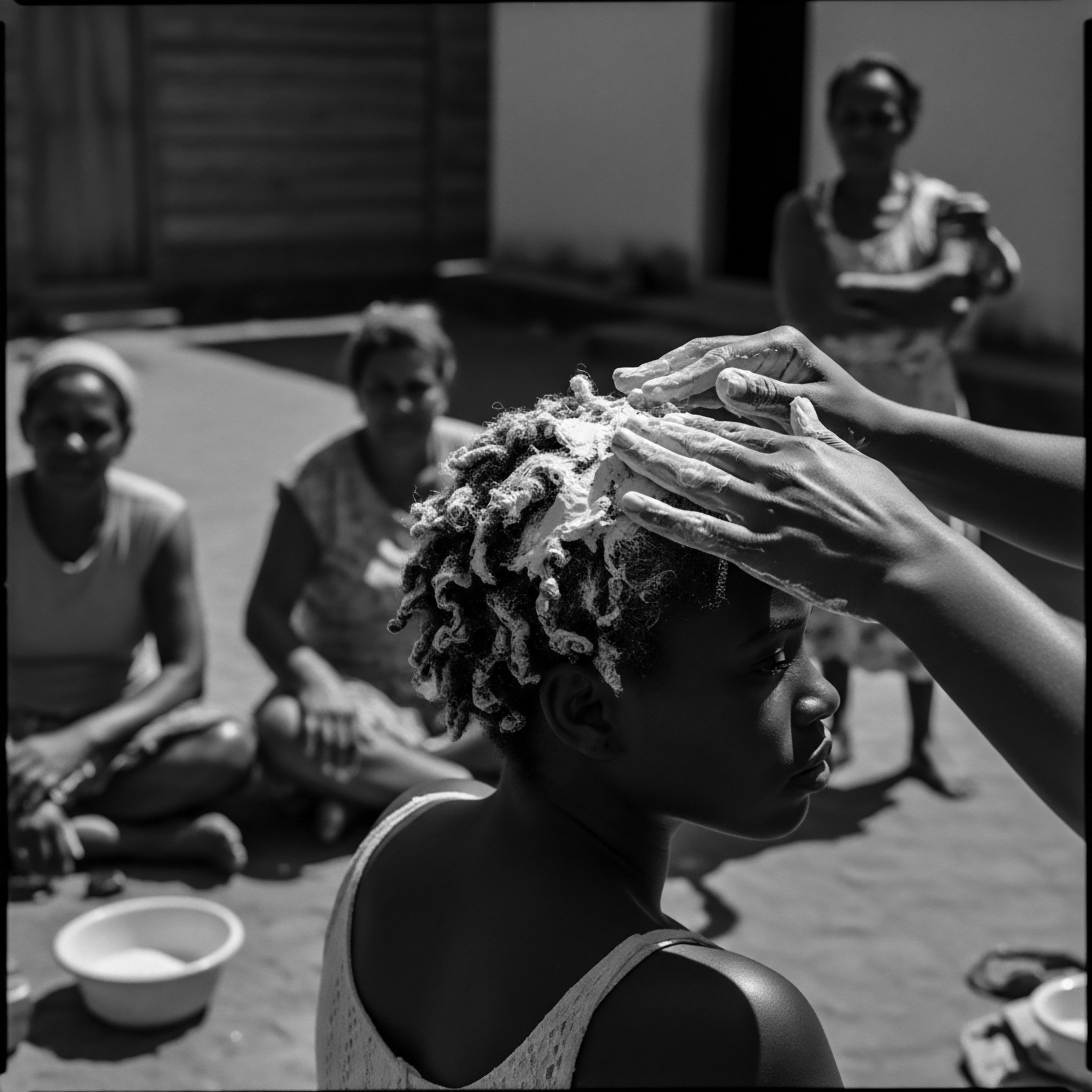

How Did Textured Hair Practices Build Community Heritage?
Textured hair practices built community heritage by serving as ancestral archives, fostering social bonds, and symbolizing resilience.

Marie Laveau
Meaning ❉ The Marie Laveau embodies ancestral wisdom, spiritual resilience, and cultural continuity as expressed through the sacred practices and profound symbolism of textured hair.
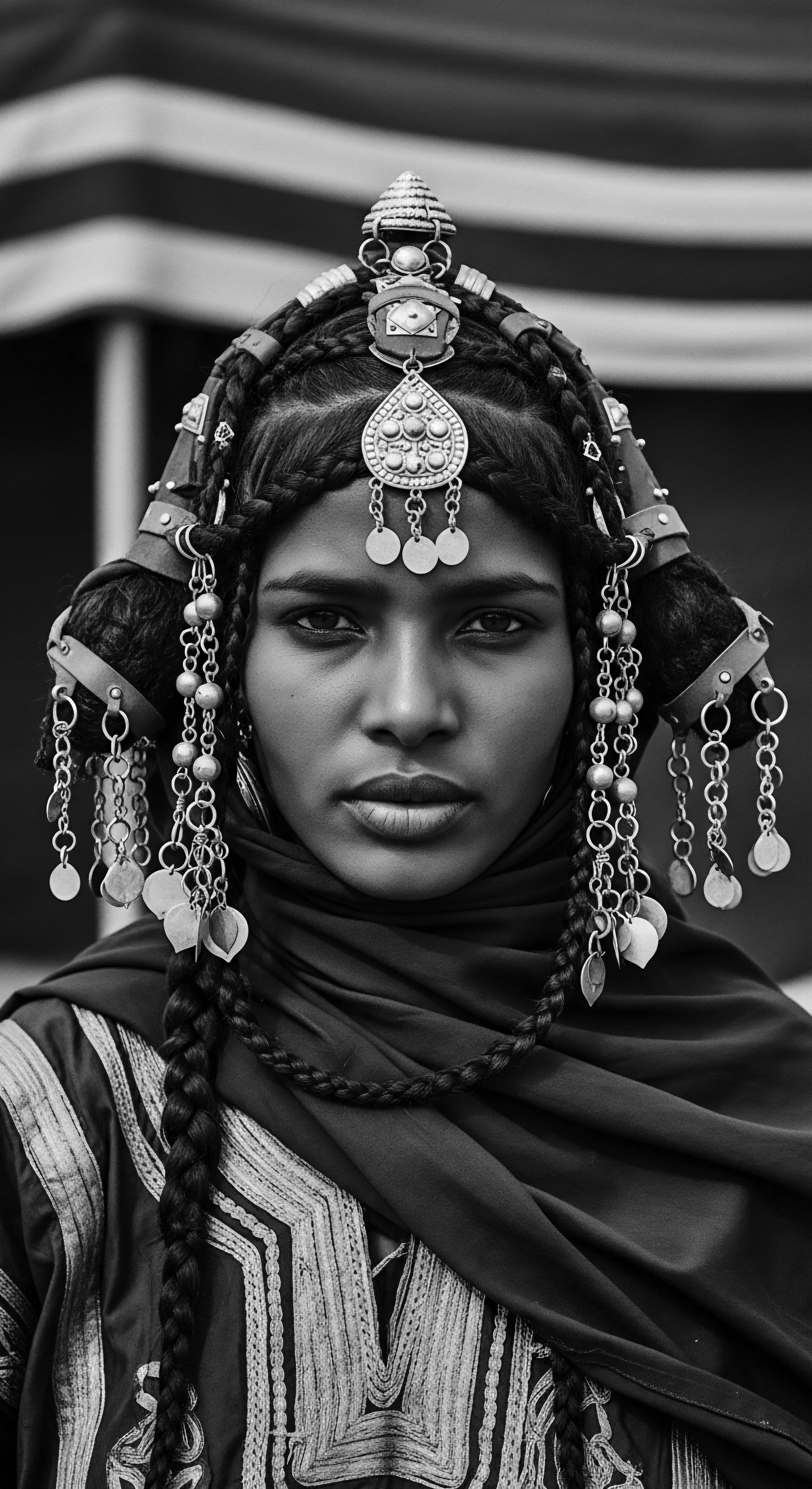

How Do Traditional Hair Practices Connect to Holistic Well-Being and Community Heritage?
Traditional hair practices deeply connect to holistic well-being and community heritage by embodying cultural identity, spiritual reverence, and collective resilience within textured hair lineages.

What Historical Significance Do Head Wraps Hold for Black Hair Heritage?
Head wraps embody a rich heritage of protection, identity, and defiance for Black hair, tracing roots from ancient African traditions to modern cultural expression.

How Did Traditional Oils Influence Black Hair Styling Heritage?
Traditional oils profoundly shaped Black hair styling heritage by providing essential nourishment and protection, becoming symbols of cultural identity and resilience.

Indigenous Hair Rights
Meaning ❉ Indigenous Hair Rights signify the inherent entitlement to wear and maintain hair according to cultural, ancestral, and natural expressions, free from discrimination.

How Did Colonial Laws Impact Hair Heritage?
Colonial laws systematically devalued textured hair, attempting to erase identity, yet sparked resilient cultural adaptation and preservation of hair heritage.

What Is the Cultural Significance of Plant-Based Hair Care for Black Heritage?
Plant-based hair care for Black heritage embodies a profound cultural language, connecting textured hair to ancestral wisdom, resilience, and identity.

In What Ways Do Ancestral Hair Tools Shape Modern Textured Hair Heritage?
Ancestral hair tools shape modern textured hair heritage by embodying timeless principles of care, identity, and cultural resilience.

Louisiana Voodoo Heritage
Meaning ❉ Louisiana Voodoo Heritage embodies the enduring spiritual traditions and cultural resilience of African diaspora communities in New Orleans, profoundly linked to textured hair experiences.

Afro-Caribbean Hair Care
Meaning ❉ Afro-Caribbean Hair Care signifies a deeply rooted tradition of nurturing textured hair, embodying cultural continuity and ancestral wisdom.

San Basilio Palenque
Meaning ❉ San Basilio Palenque is a Colombian community, a living testament to self-liberated African heritage, deeply rooted in ancestral hair traditions.

Ancestral Hair Strength
Meaning ❉ Ancestral Hair Strength signifies the inherited biological fortitude and profound cultural resilience of textured hair across generations.
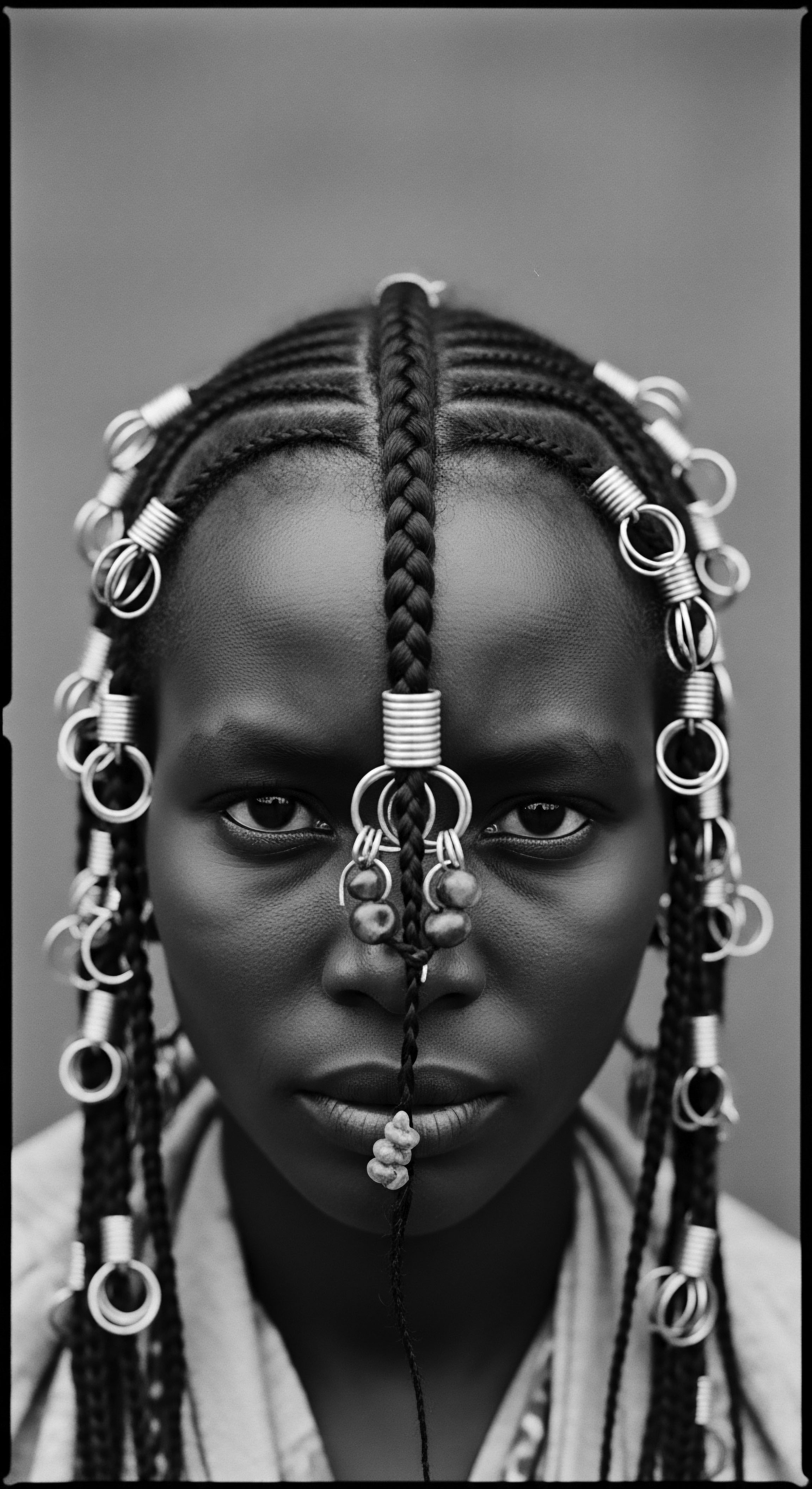

Palenque Culture
Meaning ❉ The 'Palenque Culture' defines communities of ancestral resilience where textured hair traditions became profound symbols of identity and liberation.

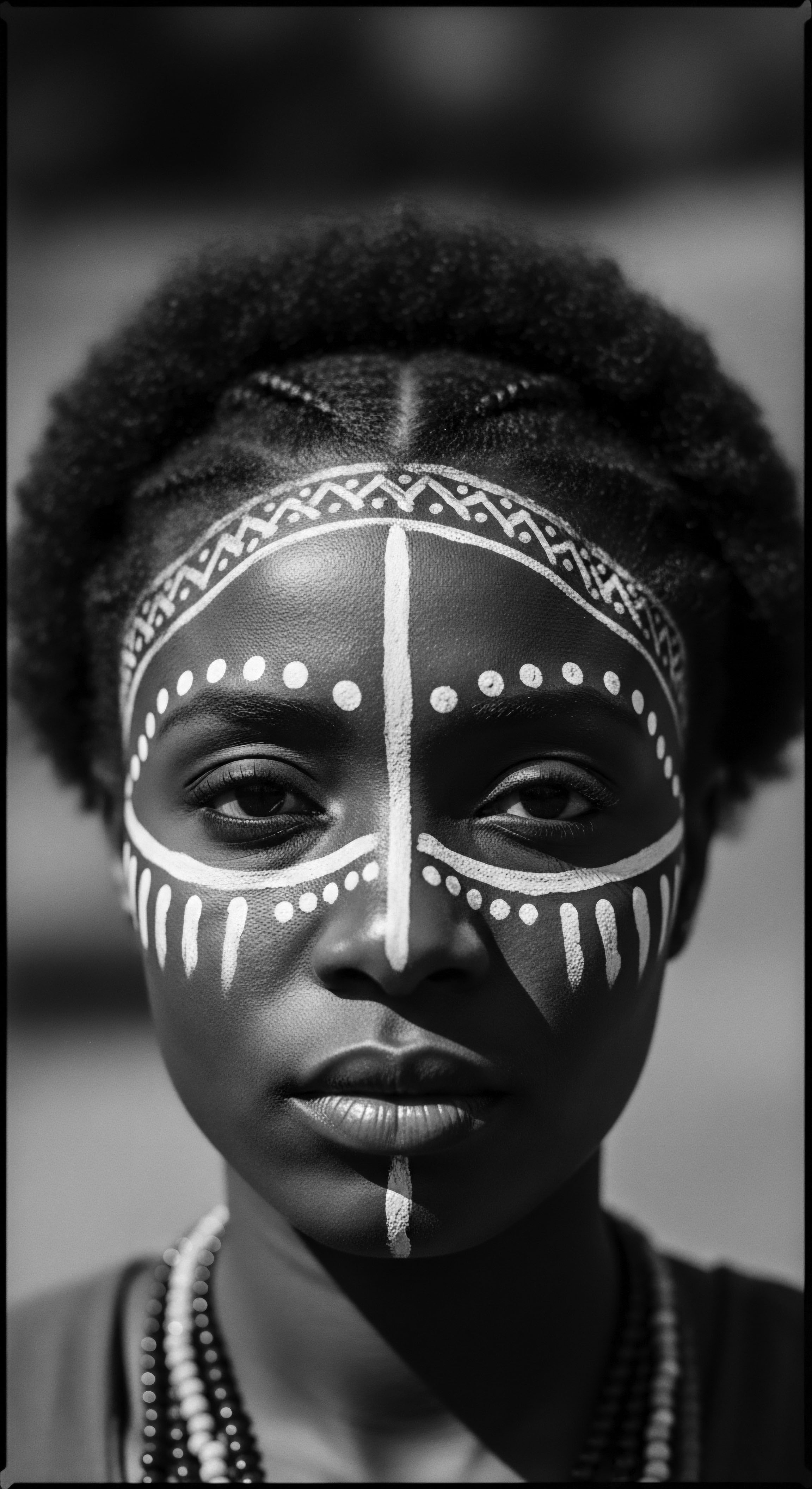
Candomblé Hair Rituals
Meaning ❉ Candomblé Hair Rituals are profound spiritual practices that honor textured hair as a sacred conduit for ancestral connection and divine alignment.

What Was the Historical Impact of the Transatlantic Slave Trade on Textured Hair?
The transatlantic slave trade profoundly disrupted textured hair heritage, forcing adaptation and birthing new symbols of resistance and identity.

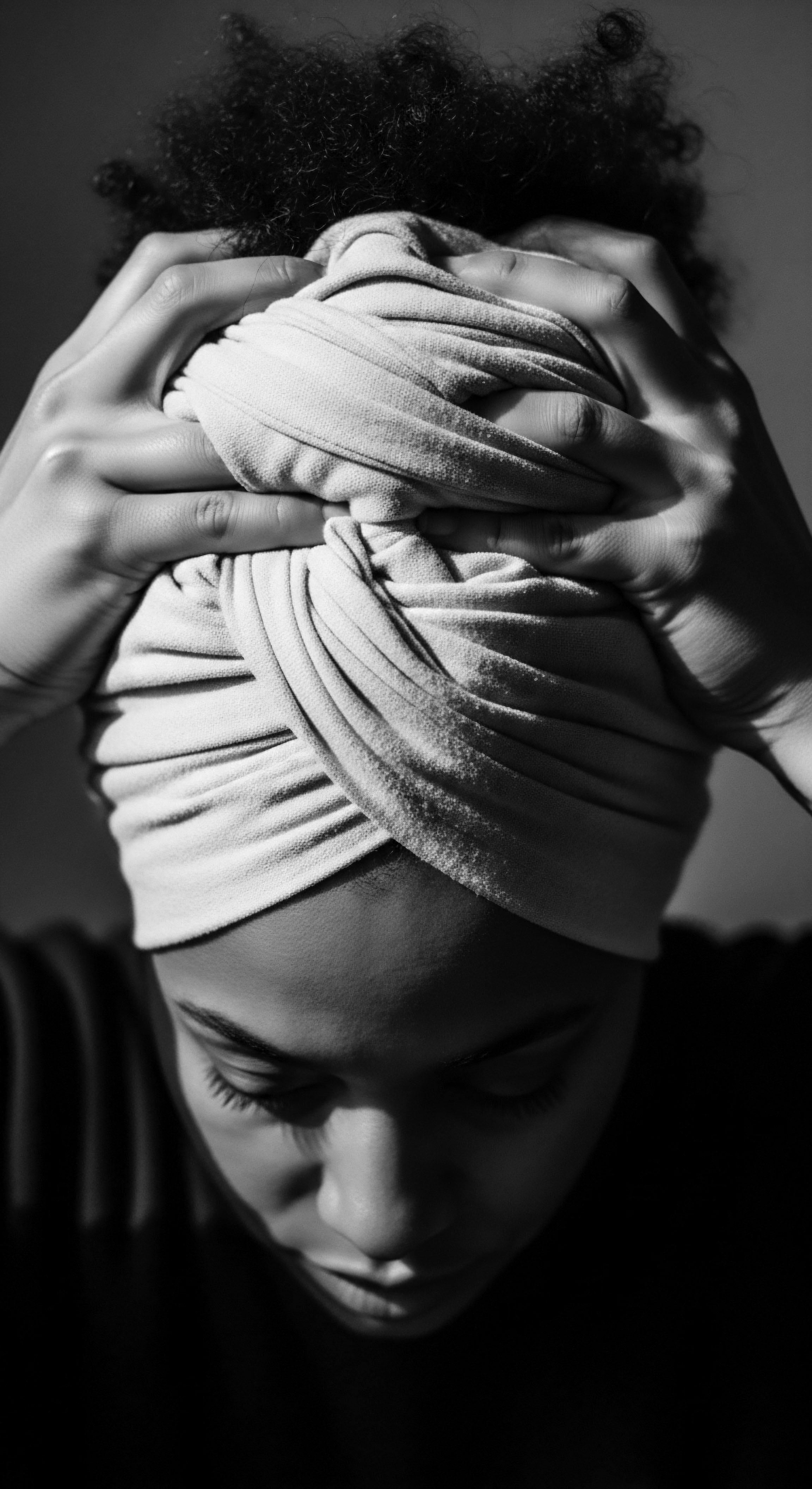
In What Ways Did Head Coverings Embody Cultural Resilience for Textured Hair?
Head coverings for textured hair embodied cultural resilience by offering physical protection, preserving traditional styles, and serving as powerful symbols of identity and heritage.
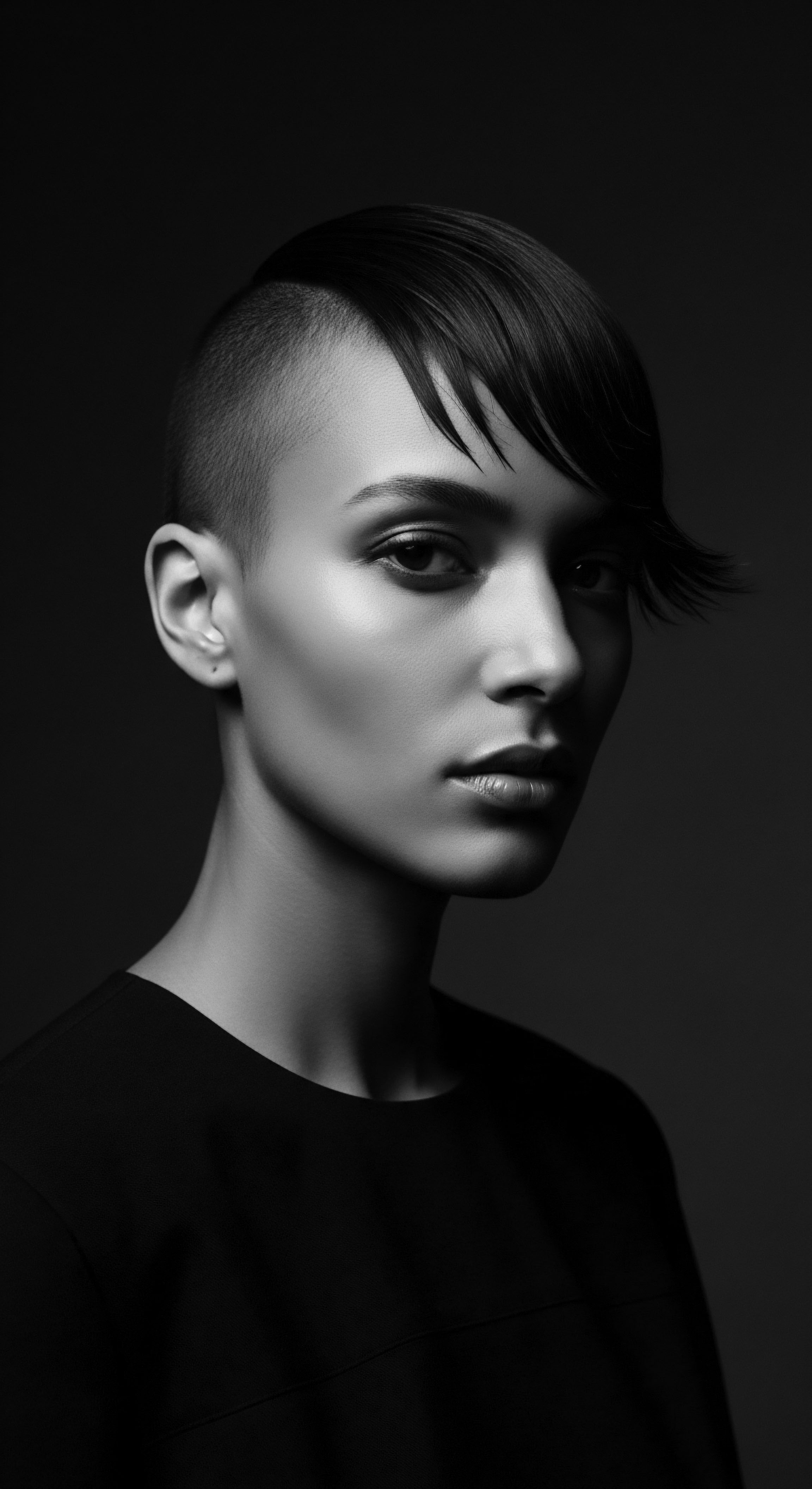

How Does Textured Hair Heritage Influence Modern Care Choices?
Textured hair heritage profoundly shapes modern care choices by informing ingredient selection, styling techniques, and fostering a deep sense of cultural identity and resilience.

