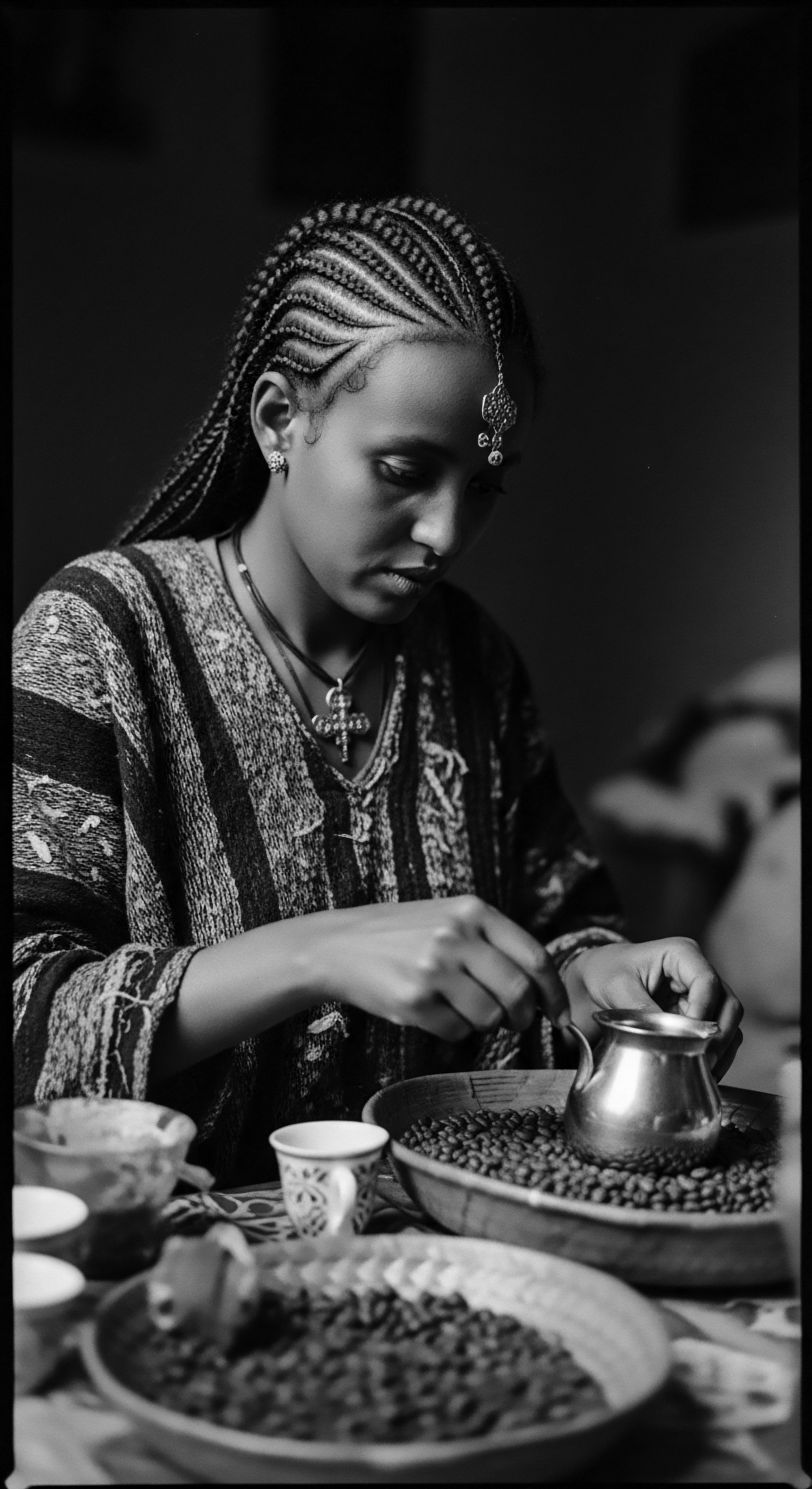
How Do Traditional Plant Oil Practices Reflect Enduring Textured Hair Heritage?
Traditional plant oil practices reflect textured hair heritage through ancestral wisdom, cultural resilience, and scientific validation of enduring care rituals.

Plant Materials Heritage
Meaning ❉ The Plant Materials Heritage is the ancestral wisdom and cultural practices of using botanical gifts for textured hair care.
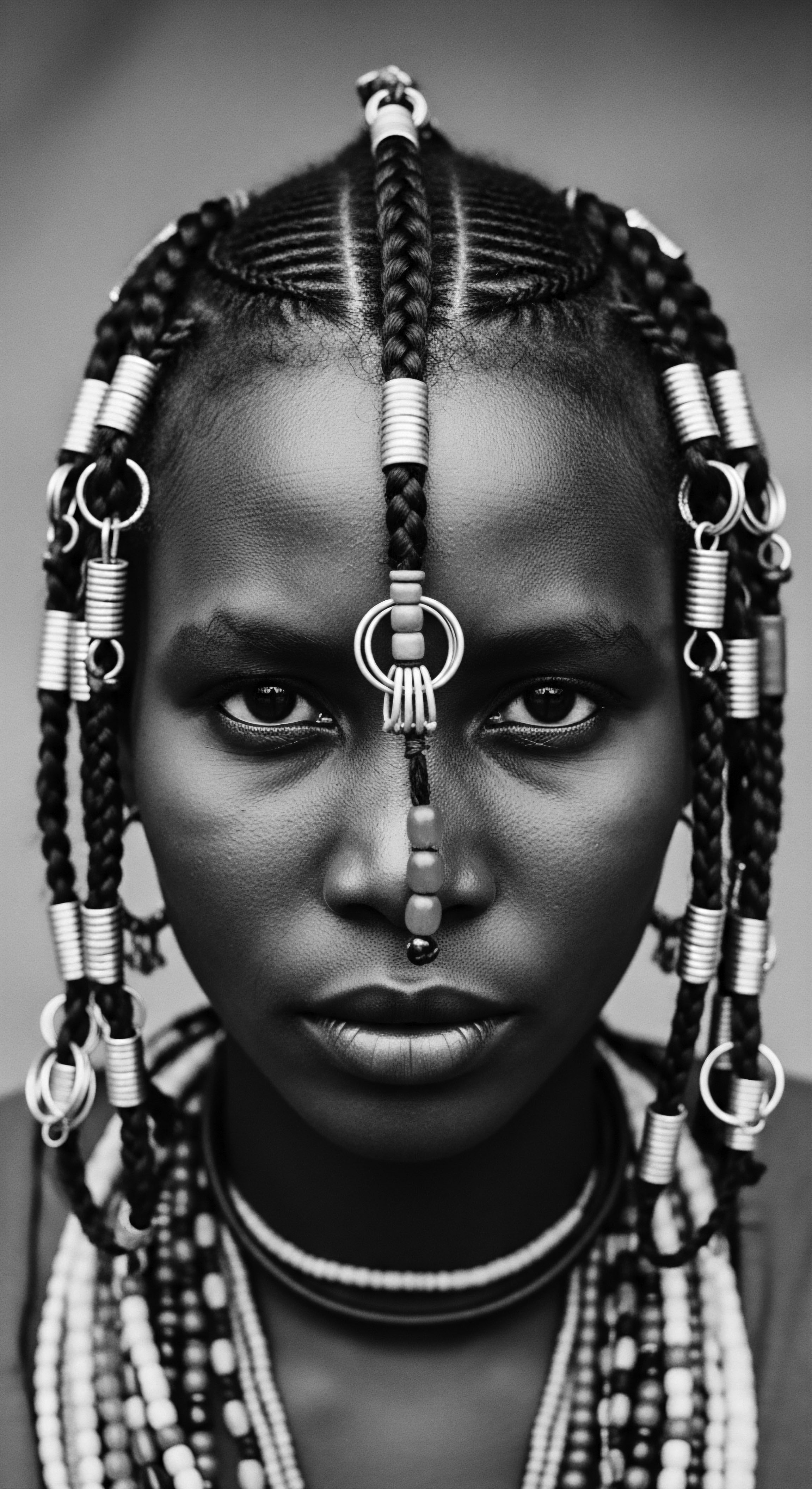

In What Ways Do Historical Hair Practices Shape Textured Hair Identity Today?
Historical hair practices deeply shape textured hair identity today by embedding ancestral wisdom, resistance, and cultural pride within every strand.

Melanin Definition
Meaning ❉ The "Melanin Definition" illuminates melanin's biological function in textured hair and its profound, evolving significance within Black and mixed-race cultural heritage and identity.

Ethnobotanical Wisdom
Meaning ❉ Ethnobotanical Wisdom is the intergenerational knowledge of plant-human interactions, especially regarding textured hair care and cultural identity within Black and mixed-race communities.

Afro-Creole Culture
Meaning ❉ Afro-Creole Culture defines a vibrant identity born from African, European, and Indigenous intersections, deeply expressed through textured hair heritage and care.

Caribbean Remedies
Meaning ❉ Caribbean Remedies encompass traditional botanical and ritualistic practices for textured hair, rooted in ancestral African and Indigenous wisdom.

Himba Heritage
Meaning ❉ Himba Heritage signifies the profound cultural, social, and protective meanings embedded in the traditional hair and skin practices of the Himba people.

What Historical Significance Do Traditional African Hair Ingredients Hold for Textured Hair?
Traditional African hair ingredients hold profound historical significance as foundational elements of ancestral hair care, symbolizing cultural resilience and deep botanical wisdom for textured hair heritage.
Cultural Syncretism
Meaning ❉ Cultural Syncretism is the dynamic fusion of distinct cultural elements into new forms, profoundly shaping textured hair heritage through adaptation and resilience.

In What Ways Do Traditional Hydrating Ingredients for Textured Hair Reflect Cultural Resilience and Identity?
Traditional hydrating ingredients for textured hair represent centuries of ancestral wisdom, embodying cultural resilience and identity.

Maori Hair Culture
Meaning ❉ Maori Hair Culture signifies a profound system where hair embodies identity, spiritual power, and ancestral lineage, dictating meticulous care and adornment.

Diasporic Plant Wisdom
Meaning ❉ Diasporic Plant Wisdom encompasses the ancestral botanical knowledge and cultural practices of Black and mixed-race communities for holistic hair care.

Inherited Hair Knowledge
Meaning ❉ Inherited Hair Knowledge is the ancestral wisdom and intuitive understanding of textured hair's biology and care, passed through generations.

How Did Historical Challenges Influence Textured Hair Practices?
Historical challenges forged resilient textured hair practices, transforming care into a powerful act of heritage preservation and identity.

Mbalantu Hair Care
Meaning ❉ Mbalantu Hair Care is an ancestral Namibian tradition of cultivating long, textured hair using natural pastes and evolving styles that signify life stages.

Marie Laveau Heritage
Meaning ❉ The Marie Laveau Heritage embodies the cultural resilience and spiritual agency expressed through textured hair in historical New Orleans.

In What Ways Did Historical Hair Care Rituals Shape Cultural Identity for Textured Hair?
Historical hair care rituals shaped cultural identity for textured hair by serving as profound expressions of belonging, communication, and resilience.

Diné Traditions
Meaning ❉ Diné Traditions encompass a holistic system of beliefs and practices where hair is revered as a sacred extension of being, intimately tied to identity, spiritual well-being, and ancestral wisdom.

Namibian Heritage
Meaning ❉ A unique exploration of Namibian Heritage through its textured hair traditions, revealing deep cultural meaning and ancestral wisdom.

What Is the Cultural Significance of Oil-Based Cleansing in Black Hair Heritage?
Oil-based cleansing in Black hair heritage signifies a profound connection to ancestral wisdom, cultural resilience, and the inherent needs of textured hair.

Afro-Indigenous Identity
Meaning ❉ Afro-Indigenous Identity signifies the interwoven cultural heritage and shared experiences of individuals with African and Indigenous ancestral lineages, deeply reflected in their textured hair traditions.

In What Ways Did Colonial Forces Psychologically Influence Textured Hair Identity?
Colonial forces psychologically influenced textured hair identity by devaluing ancestral aesthetics, imposing Eurocentric beauty norms, and creating a profound sense of internalized inferiority, which continues to be decolonized through heritage reclamation.

Kinaaldá Ceremony
Meaning ❉ The Kinaaldá Ceremony is a Navajo coming-of-age rite for young women, deeply honoring textured hair as a sacred symbol of identity, spiritual connection, and cultural heritage.

Afro-Brazilian Aesthetics
Meaning ❉ Afro-Brazilian Aesthetics defines the unique beauty, identity, and care practices of textured hair, rooted in African heritage and historical resilience within Brazil.

How Does Cultural Heritage Shape Contemporary Textured Hair Care Choices?
Cultural heritage profoundly shapes contemporary textured hair care by grounding choices in ancestral wisdom, resilience, and identity affirmation.

Cultural Meanings
Meaning ❉ The Cultural Meanings of textured hair encompass its profound historical, social, and spiritual significance as a carrier of identity and heritage.

Collective Defiance
Meaning ❉ Collective Defiance defines the inherent strength and cultural affirmation of textured hair against societal pressures and historical devaluations.

Traditional Ethnobotany
Meaning ❉ Traditional Ethnobotany is the cultural knowledge of plant use, deeply significant for textured hair care and ancestral heritage.

