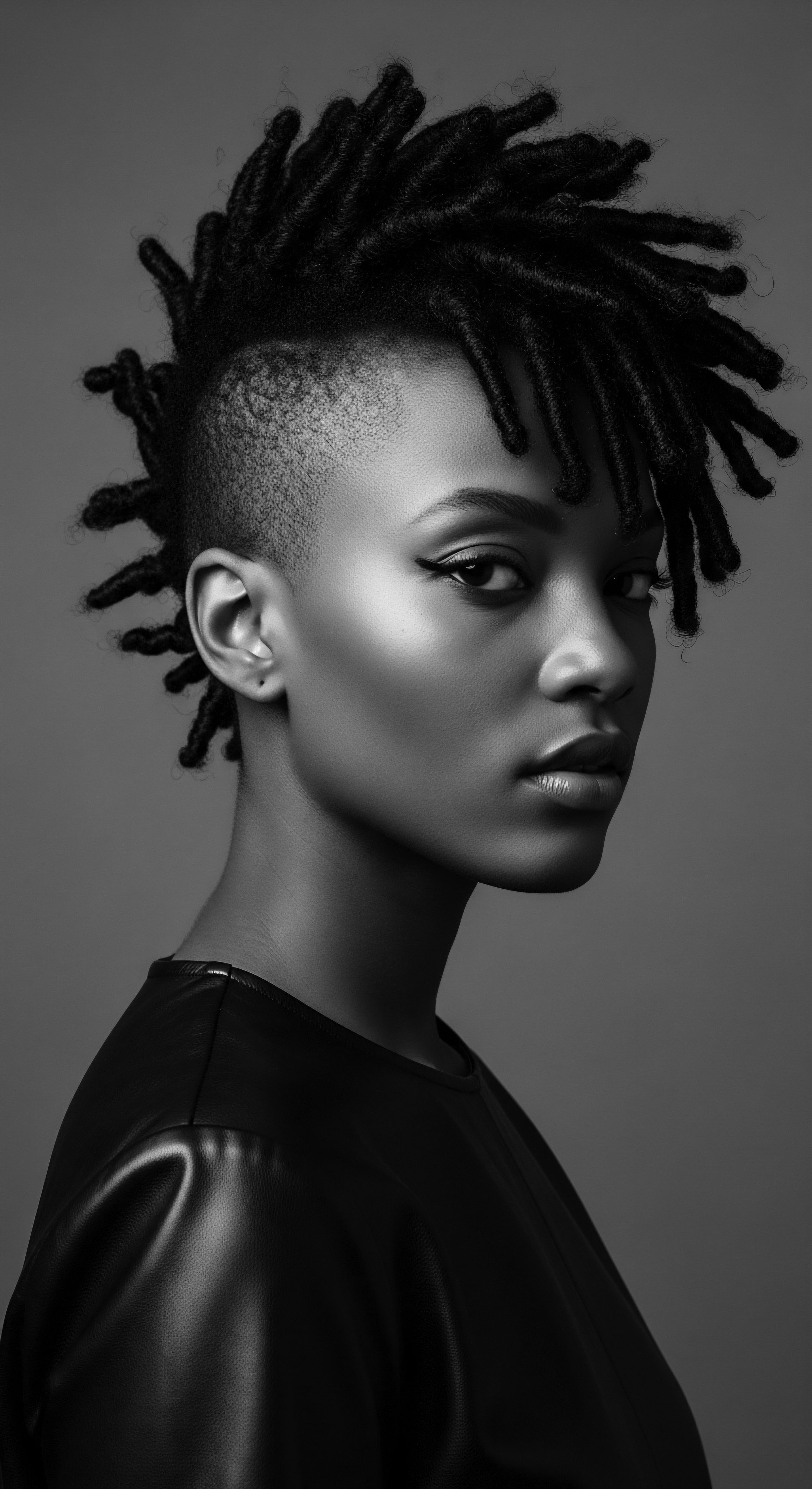How Did Ancestral African Hair Traditions Survive Periods of Oppression?
Ancestral African hair traditions survived oppression through covert practices, communal solidarity, and deep cultural meaning embedded in styling.

What Natural Ingredients from African Heritage Promote Hair Vitality?
African heritage offers natural ingredients like shea butter, Chebe powder, and baobab oil, promoting vitality and honoring textured hair's legacy.

What Is the Historical Link between Hair Care and Resistance in Black Communities?
Hair care and styles in Black communities have historically served as powerful acts of resistance and cultural preservation, deeply entwined with textured hair heritage.

In What Ways Did African Hair Traditions Serve as Tools of Resistance during Historical Oppression?
African hair traditions served as covert communication, identity preservation, and powerful symbols of resistance against oppression, deeply rooted in textured hair heritage.

Can Ancient Scalp Oiling Alleviate Modern Textured Hair Challenges?
Ancient scalp oiling offers deep moisture and protection for textured hair, building on centuries of heritage knowledge for modern challenges.

Salon as Community
Meaning ❉ A Salon as Community is a vital socio-cultural space where textured hair care intertwines with ancestral wisdom, identity, and collective well-being.

Ancestral Grains
Meaning ❉ Ancestral Grains embody ancient wisdom and historical resilience, profoundly connected to textured hair heritage and Black diasporic care traditions.

What Is the Historical Significance of Hair Oiling in Black Communities?
Hair oiling signifies a timeless ritual of care and cultural preservation deeply woven into Black textured hair heritage.

How Did Hair Serve as a Tool of Resistance during Enslavement?
Hair served as a profound tool of resistance by preserving cultural heritage and enabling covert communication among enslaved people.

How Did Braids Aid Survival during the Transatlantic Slave Trade?
Braids aided survival by concealing maps for escape and hiding seeds for sustenance, preserving textured hair heritage.

Botanical Sourcing Ethics
Meaning ❉ Botanical Sourcing Ethics upholds environmental balance and ancestral wisdom by ensuring plants for hair care are sourced with respect and equity.

Human Migration
Meaning ❉ Human Migration details the multifaceted movement of people, profoundly shaping the global distribution, heritage, and cultural significance of textured hair.

Griot History
Meaning ❉ Griot History represents the oral transmission of ancestral knowledge and cultural identity, profoundly shaping textured hair heritage and care practices.

How Did Historical Hair Practices Serve as Acts of Cultural Preservation and Resistance?
Historical hair practices preserved culture and resisted oppression by serving as communication, identity, and a bond to textured hair heritage.

Engkabang Butter Heritage
Meaning ❉ Engkabang Butter Heritage is the ancestral wisdom and ongoing cultural practice surrounding the use of Shorea tree butter by Borneo's indigenous communities for well-being.

How Did Historical Hair Practices Preserve Cultural Identity?
Historical hair practices preserved cultural identity by serving as visual markers of lineage, status, and collective memory.

Kru Hair Practices
Meaning ❉ Kru Hair Practices encapsulate the historical, cultural, and scientific understanding of hair care and identity within West African communities.

Botanical Impact
Meaning ❉ The Botanical Impact defines the enduring influence of plants on textured hair care, reflecting deep cultural heritage and ancestral wisdom.

How Do Traditional Shea Butter Extraction Methods Preserve Cultural Heritage?
Traditional shea butter extraction safeguards cultural heritage through ancient methods, community bonds, and economic empowerment for women.

Historical Resistance
Meaning ❉ Historical Resistance in textured hair signifies the inherent strength and cultural practices asserting identity against oppressive norms.

Plant Defense
Meaning ❉ Plant Defense for textured hair encompasses inherent resilience and ancestral plant-based methods for protection, nourishment, and cultural preservation.

Mutual Aid Hair Care
Meaning ❉ Mutual Aid Hair Care defines the collective, reciprocal systems of support, knowledge, and resources shared for tending to textured hair within communities.

Indigenous Botanical Uses
Meaning ❉ Indigenous Botanical Uses represent intergenerational plant knowledge, deeply intertwined with cultural identity and historical resilience in textured hair care.

Intergenerational Hair Traditions
Meaning ❉ Intergenerational Hair Traditions embody the collective wisdom and cultural continuity of hair care passed through generations, particularly for textured hair.

Can Ancient Oil Practices Still Shield Textured Hair Today?
Ancient oil practices continue to shield textured hair by echoing ancestral wisdom, providing essential moisture and protection.

Creole Headwrap History
Meaning ❉ The Creole Headwrap History delineates the profound cultural and historical significance of head coverings worn by women of African descent in the Americas.

How Did Textured Hair Styles Aid Resistance during Slavery?
Textured hair styles aided resistance during slavery by serving as hidden maps, communication networks, and concealment for survival items, deeply rooted in African heritage.

Cultural Environmentalism
Meaning ❉ Cultural Environmentalism advocates for the protection and cultivation of cultural expressions, practices, and identities, especially concerning textured hair heritage.

How Did Sleep Rituals Guard Textured Hair Heritage?
Sleep rituals shielded textured hair heritage by preserving delicate strands and embodying cultural resilience and identity.