
What Ancestral Ingredients Are Still Relevant in Modern Textured Hair Care?
Ancestral ingredients like shea butter and coconut oil remain vital for textured hair care, connecting modern routines to rich heritage.

Soapnut Heritage
Meaning ❉ The Soapnut Heritage is the enduring legacy of Sapindus fruit as a natural cleanser, embodying ancestral wisdom for textured hair care and cultural resilience.

What Scientific Principles Affirm the Efficacy of Traditional Oil Cleansing for Textured Hair?
Traditional oil cleansing for textured hair is affirmed by scientific principles of lipid affinity and cuticle protection, rooted deeply in Black hair heritage.

How Did Communal Hair Care Sustain Cultural Heritage in Slavery?
Communal hair care in slavery preserved African identity, knowledge, and community through shared grooming rituals, embodying textured hair heritage.

How Do Women’s Cooperatives Preserve Shea Butter Heritage?
Women's cooperatives preserve shea butter heritage by safeguarding ancestral processing methods and empowering communities, deeply connecting to textured hair's legacy.

What Historical Moments Connected Textured Hair to Resistance?
Textured hair has served as a powerful symbol of cultural preservation, identity, and resistance throughout historical moments of oppression and liberation.

Cultural Integrity
Meaning ❉ Cultural Integrity is the steadfast preservation and honoring of a community's distinct worldview, ancestral wisdom, and collective expressions, particularly concerning textured hair.

African Regalia
Meaning ❉ African Regalia, in the context of textured hair, represents culturally significant objects, practices, and the hair itself as profound expressions of identity and ancestral wisdom.

Indigenous Plant Care
Meaning ❉ Indigenous Plant Care is the traditional, heritage-driven utilization of botanicals for the holistic wellbeing and cultural affirmation of textured hair.

Mayan Hair Heritage
Meaning ❉ Mayan Hair Heritage encompasses the ancient and ongoing traditions, beliefs, and practices surrounding hair within Mayan communities, reflecting deep cultural, spiritual, and medicinal significance.
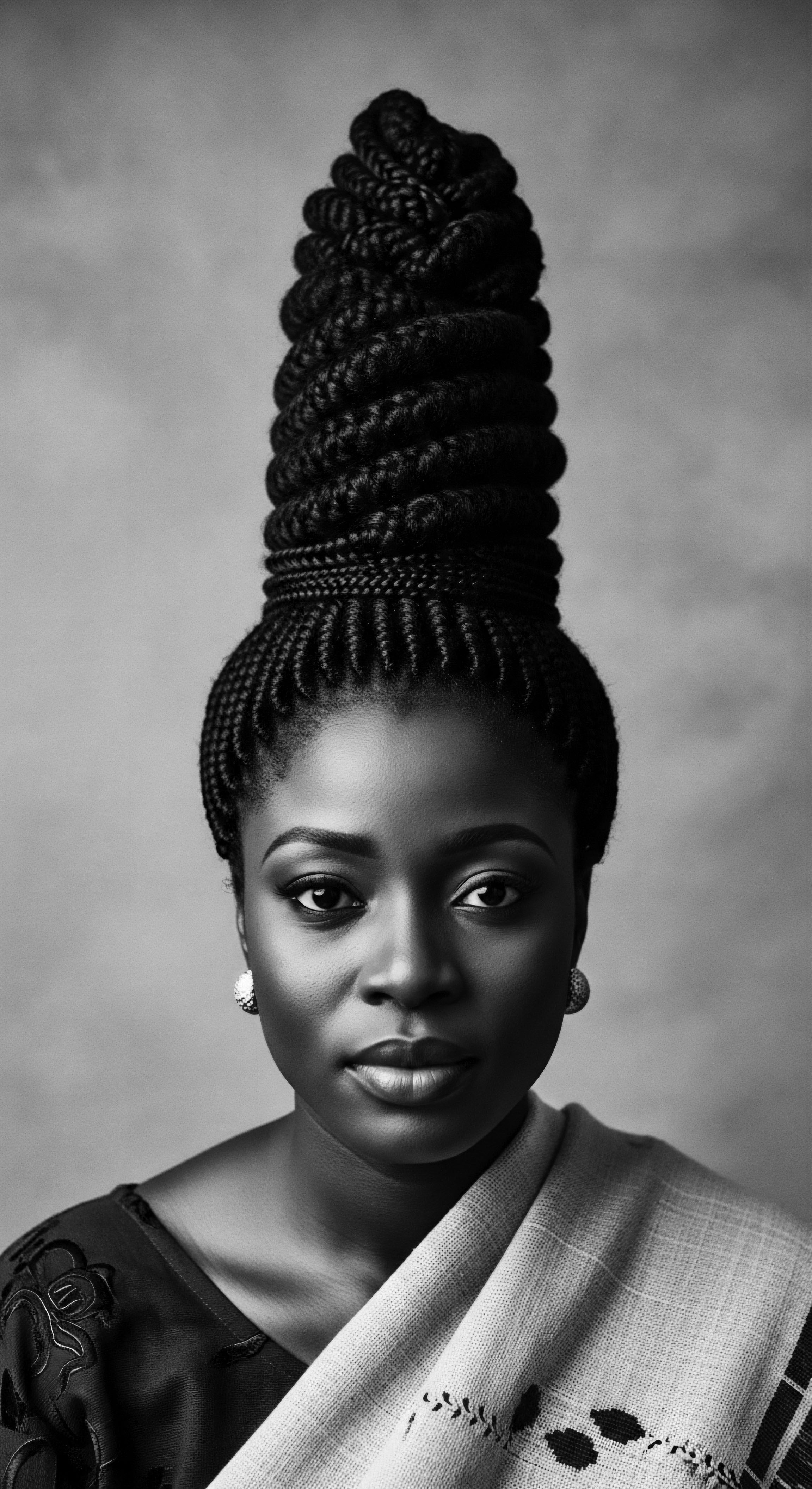

Nigerian Hair Artistry
Meaning ❉ Nigerian Hair Artistry is the profound cultural expression of identity and heritage through the intricate styling and adornment of textured hair.

Hair Identity Madagascar
Meaning ❉ Hair Identity Madagascar is the profound cultural and historical significance of hair as a marker of identity, heritage, and community in Madagascar.
Oryza Glaberrima
Meaning ❉ Oryza Glaberrima is African rice, a domesticated grain with deep historical ties to West African heritage and its profound connection to textured hair traditions.
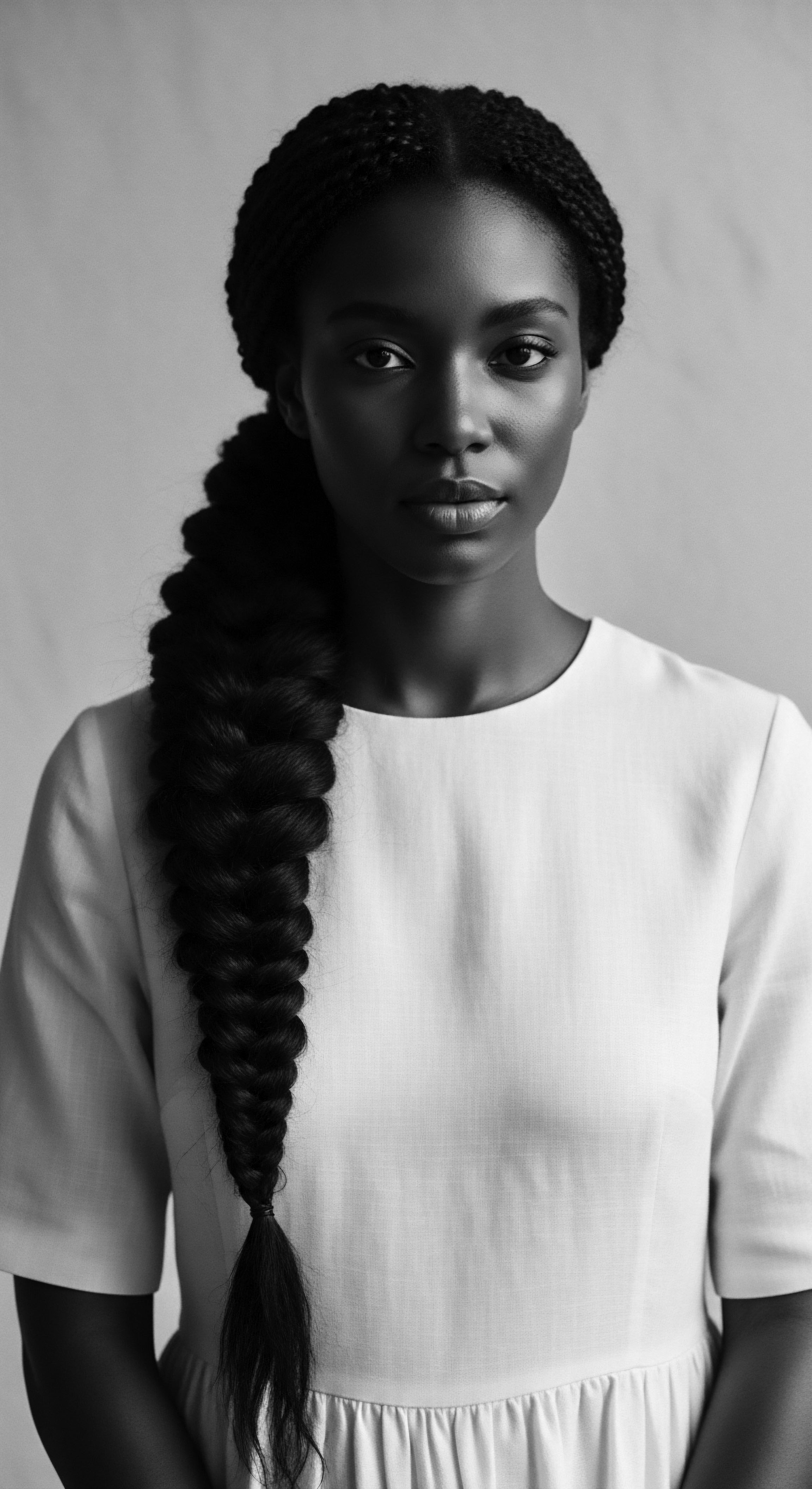

Ancestral Botanical Oil
Meaning ❉ Ancestral Botanical Oil embodies generations of traditional plant-derived care for textured hair, rooted in heritage and cultural significance.

What Historical Significance Does Hair Protection Hold for Textured Hair?
Hair protection for textured hair is a profound historical narrative of resilience, cultural preservation, and ancestral wisdom.

Black Hair Salons
Meaning ❉ Black Hair Salons are vital cultural institutions for textured hair care, fostering community, economic independence, and heritage preservation.

Indentured Labor
Meaning ❉ Indentured Labor signifies a historical system of coerced migration that profoundly impacted and reshaped textured hair heritage and identity.

Can Traditional African Ingredients Benefit Modern Textured Hair Regimens?
Traditional African ingredients offer deep nourishment and protection, honoring textured hair's heritage and promoting holistic wellness.

Fa’a Samoa Cultural Code
Meaning ❉ The Fa'a Samoa Cultural Code is the ancestral framework of Samoan life, deeply influencing communal values, respectful relationships, and the cultural significance of textured hair heritage.

How Did Hair Practices Preserve Cultural Heritage during the Transatlantic Slave Trade?
Hair practices during the transatlantic slave trade preserved cultural heritage by serving as covert communication, symbols of identity, and anchors to ancestral wisdom.

Sudanese Cultural Practices
Meaning ❉ Sudanese Cultural Practices encompass ancient, holistic hair care rituals and adornments deeply rooted in identity, spirituality, and communal heritage.
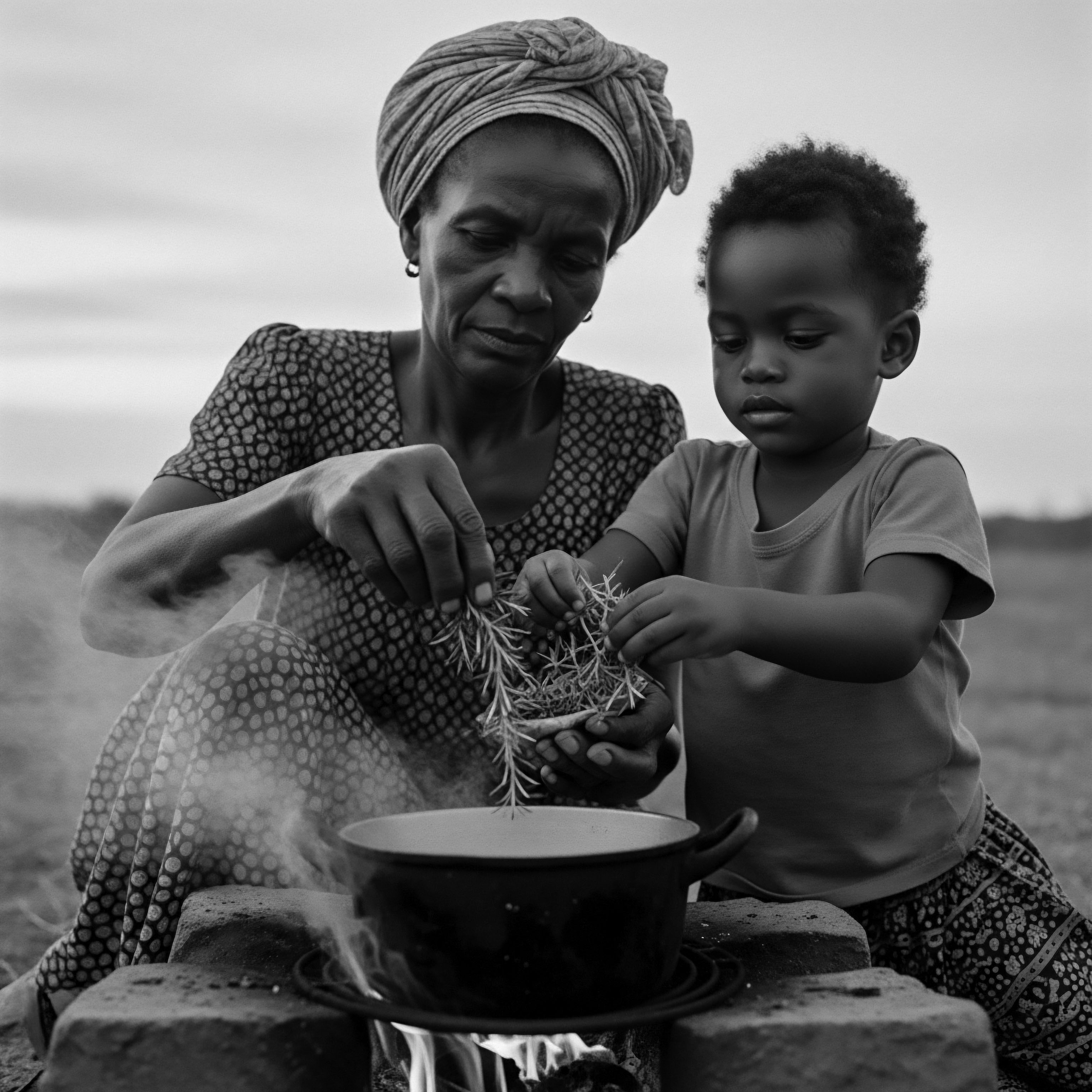

What Cultural Significance Did Plant Remedies Hold for Textured Hair Heritage?
Plant remedies for textured hair served as profound cultural anchors, preserving heritage and identity across generations.
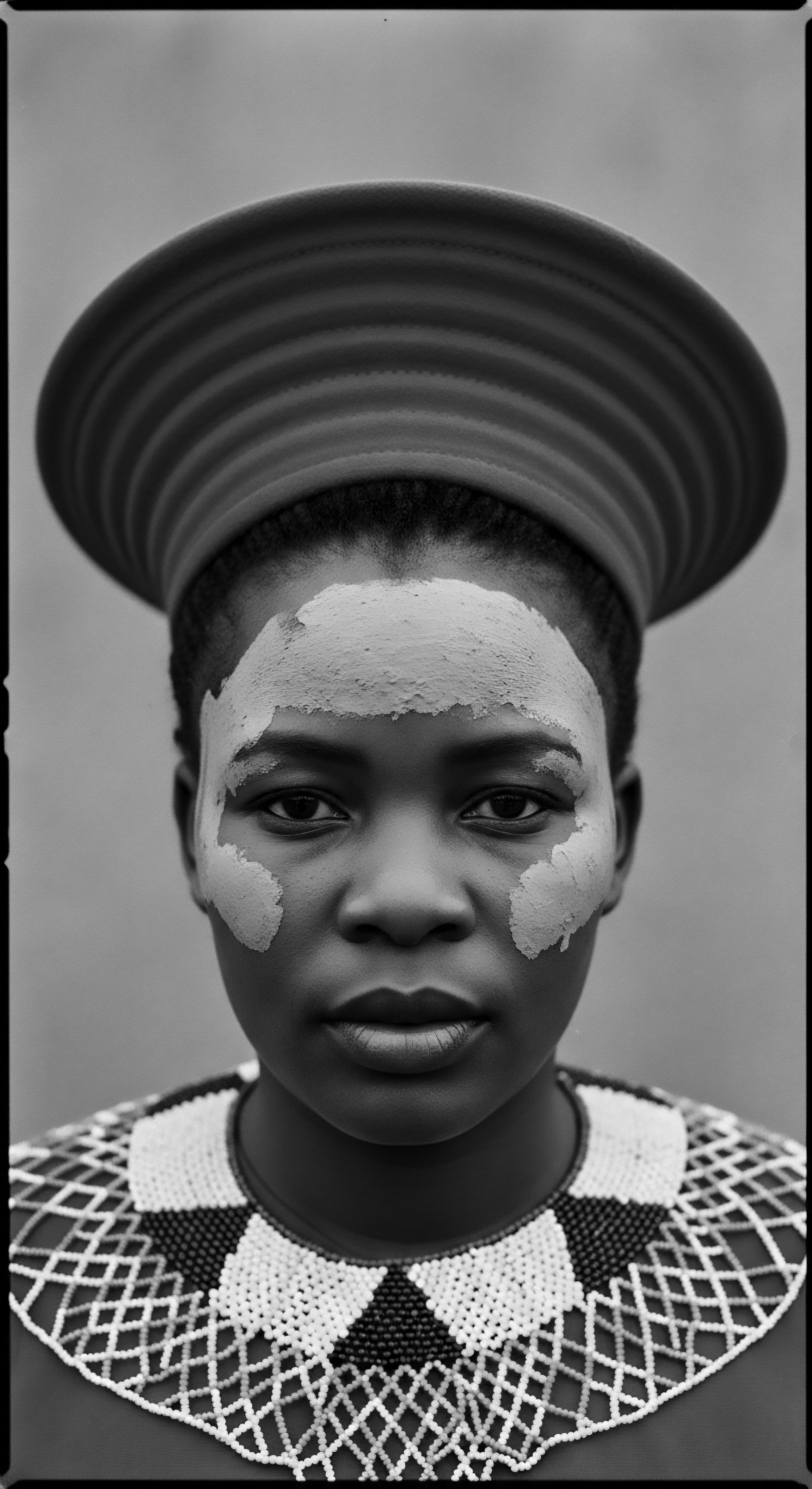

How Did Cleansing Rituals Reflect Cultural Identity in Textured Hair Heritage?
Cleansing rituals for textured hair deeply mirror cultural identity, reflecting ancestral wisdom, resilience, and spiritual connections.

In What Ways Does Textured Hair Heritage Connect to Plant-Based Remedies Globally?
Textured hair heritage connects to plant-based remedies globally through centuries of ancestral wisdom, ecological adaptation, and cultural preservation.

Can Traditional Plant Knowledge Shape the Future of Textured Hair Heritage?
Traditional plant knowledge offers profound insights, rooted in ancestral wisdom, to shape the future of textured hair heritage through holistic care and cultural affirmation.

Ancestral Health
Meaning ❉ Ancestral Health, for textured hair, is the inherited wisdom and enduring practices that sustain its vitality, deeply rooted in generational heritage and cultural identity.

Ancient Headwraps
Meaning ❉ Ancient Headwraps are historically rich head coverings signifying identity, status, and resilience across diverse cultures, especially within textured hair heritage.

Diasporic Dietetics
Meaning ❉ Diasporic Dietetics examines how ancestral foodways and cultural adaptations profoundly influence the health and vitality of textured hair.

Natural Oil Wisdom
Meaning ❉ Natural Oil Wisdom is the ancestral, culturally integrated knowledge of using plant-derived oils for textured hair health, identity, and cultural preservation.

