
How Does Shea Butter Link to Textured Hair Legacy?
Shea butter links to textured hair legacy through ancient practices of deep moisture, protection, and cultural identity.

How Do Historical Hair Practices Influence Modern Textured Hair Wellness Philosophies?
Historical hair practices profoundly inform modern textured hair wellness philosophies by anchoring care in ancestral knowledge, cultural identity, and resilience.

What Is Shea Butter’s Enduring Significance for Textured Hair Heritage?
Shea butter provides a tangible link to textured hair heritage, offering deep moisture and protection rooted in ancestral African practices.

What Significance Did Ancient Braids Hold in African Heritage?
Ancient African braids signified identity, status, and spirituality, protecting textured hair while serving as a vital communicative heritage tool.

6-Gingerol
Meaning ❉ 6-Gingerol, a primary compound in ginger, offers anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits for scalp health, yet research indicates it may inhibit hair growth.
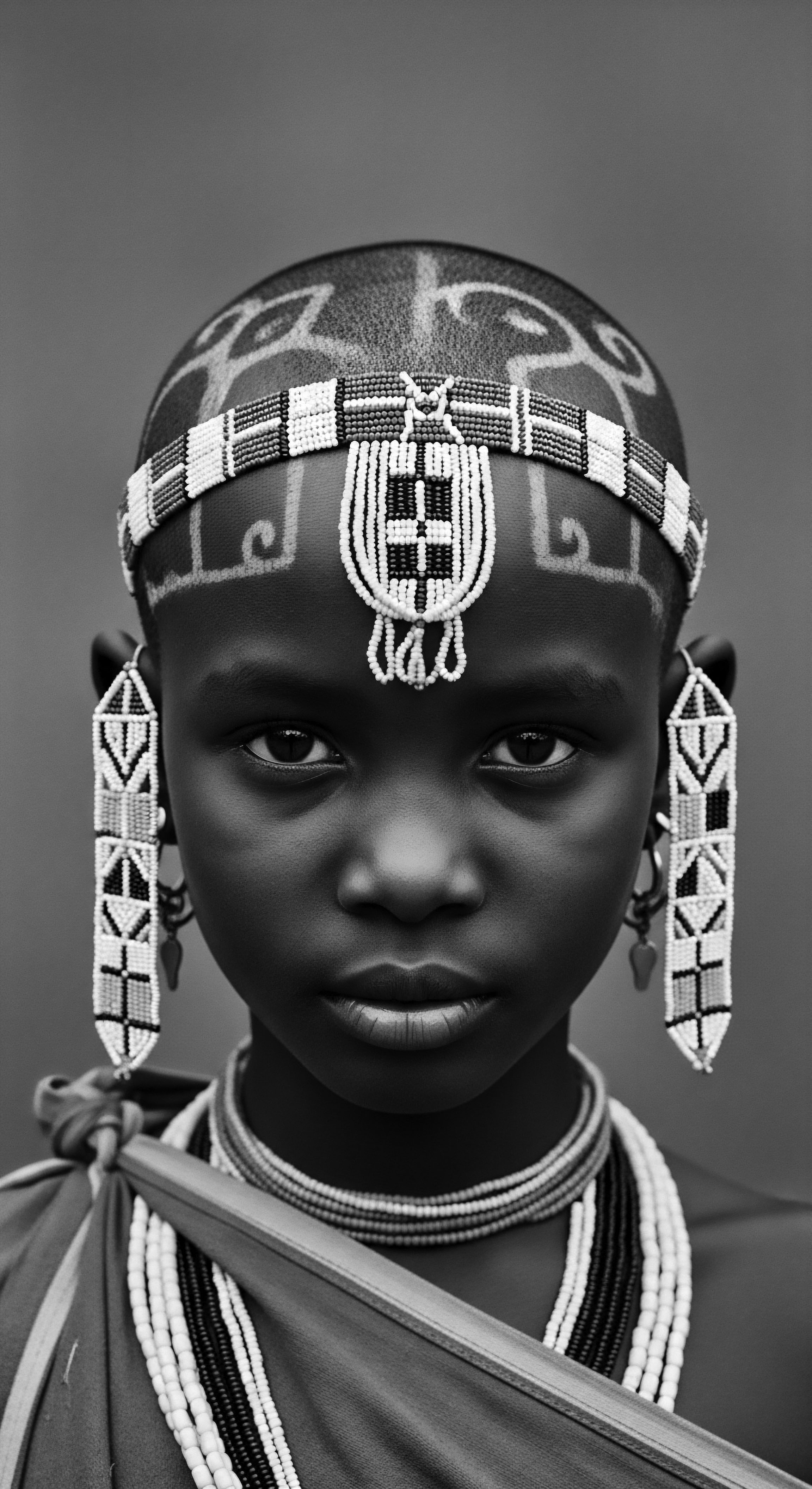

How Do Ancestral Hair Rituals Shape Modern Identity?
Ancestral hair rituals shape modern identity by imbuing textured hair with deep cultural, social, and spiritual significance, linking individuals to their heritage.

What Ancestral Practices Influence Head Wrap Use?
Ancestral practices influencing head wrap use center on protecting textured hair, communicating cultural identity, and preserving heritage across generations.

In What Ways Did Braids Serve as a Tool for Resistance during Slavery?
Braids served as covert maps, hiding sustenance, and affirming cultural identity, powerfully linking survival to textured hair heritage.
How Did Ancient African Societies Use Hairstyles to Communicate?
Ancient African societies used intricate hairstyles as a visual lexicon, communicating complex details of identity, status, and spiritual connection.

What Symbolic Meanings Does Otjize Hold for Himba Women?
Otjize, a red ochre and butterfat blend, symbolically grounds Himba women to their land, ancestry, and textured hair heritage.
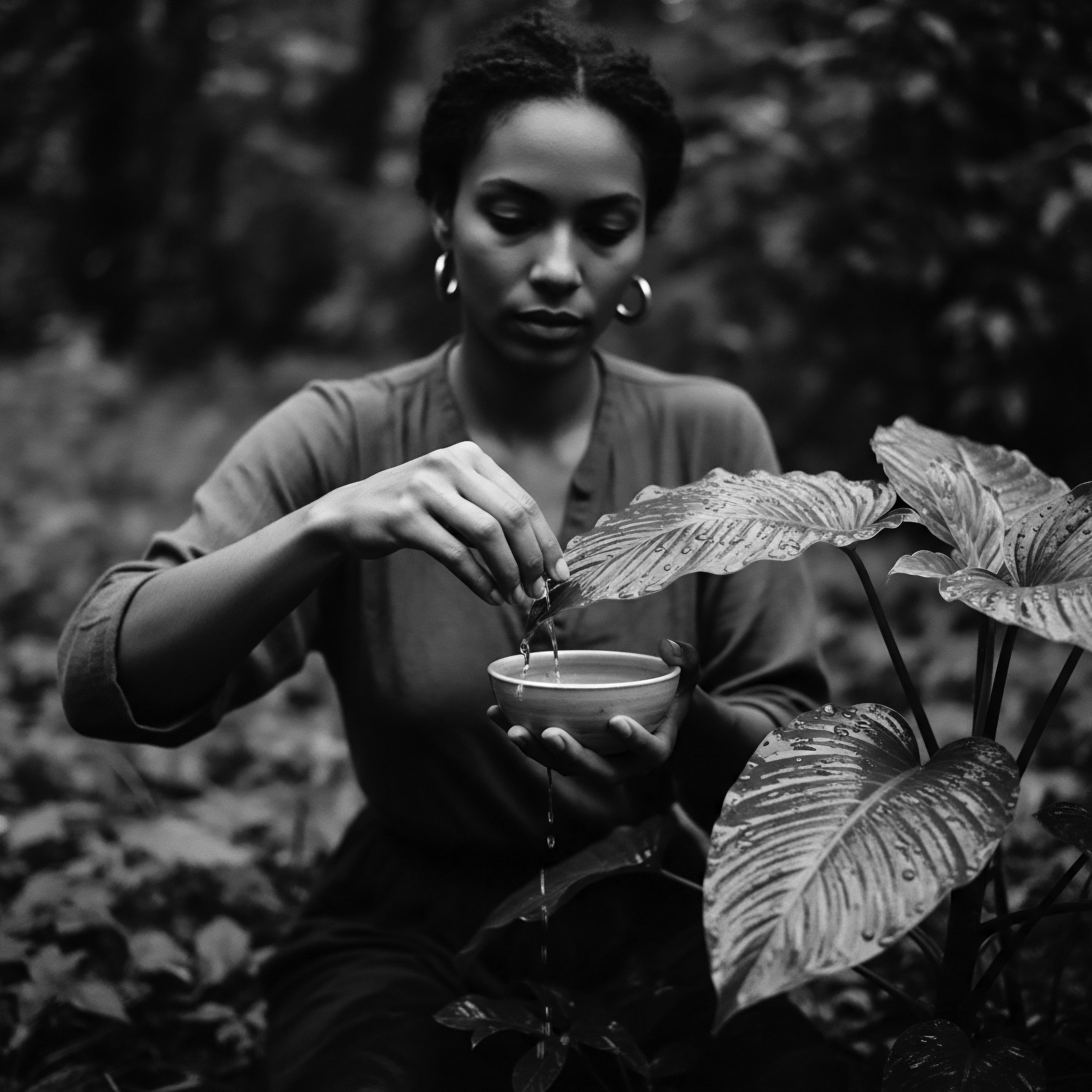

What Ancestral Oils Nurtured Coiled Hair?
Ancestral oils like shea, palm, and castor nurtured coiled hair through deep moisture, protection, and cultural ritual.

What Cultural Meanings Are Embedded in Traditional Black Protective Hairstyles?
Traditional Black protective hairstyles hold deep cultural meanings, serving as living testaments to ancestry, identity, and resilience within textured hair heritage.

What Historical Discrimination Did the CROWN Act Address regarding Hair?
The CROWN Act legally addresses a long history of systemic discrimination against textured hair and protective styles, affirming their deep connection to racial and cultural heritage.

How Do CROWN Act Provisions Recognize Ancestral Styles?
CROWN Act provisions protect ancestral hair textures and styles, recognizing them as integral to racial and cultural heritage.

Feminine Principle Archetype
Meaning ❉ The Feminine Principle Archetype signifies the receptive, nurturing, and connective force inherent in textured hair's enduring heritage and care traditions.
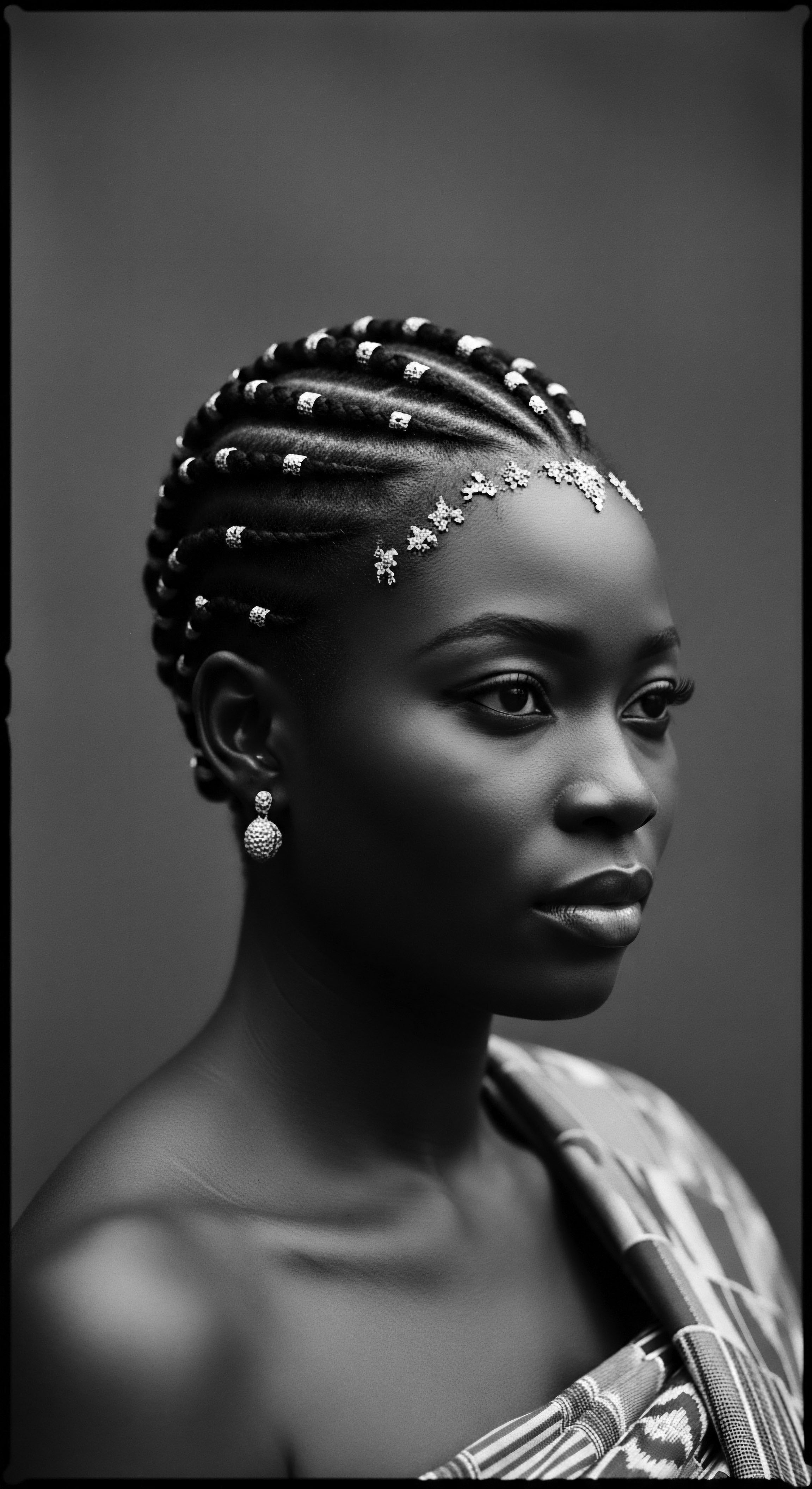

What Scientific Insights Confirm the Historical Efficacy of Plant-Based Hair Practices?
Scientific inquiry validates ancestral plant practices for textured hair, confirming their efficacy in moisture retention, strengthening, and promoting scalp health.

What Is the Historical Meaning of Black Hair Styles?
Black hair styles are a profound historical record, reflecting identity, resistance, and ancestral wisdom through textured hair heritage.

In What Ways Do Textured Hair Traditions Reflect Communal Resilience?
Textured hair traditions reflect communal resilience by preserving heritage, facilitating communication, and serving as visible acts of identity and defiance.

How Do Ancestral Plant Uses Connect with Modern Hair Health?
Ancestral plant uses connect with modern hair health by validating ancient wisdom through scientific insight, affirming heritage's role in vibrant strands.

How Does Hair Heritage Shape Current Self-Perception?
Hair heritage, particularly textured hair, profoundly shapes self-perception through ancestral practices, historical resilience, and cultural affirmation.

What Historical Prejudices Did the CROWN Act Address regarding Hair?
The CROWN Act confronts historical prejudices that marginalized textured hair, restoring dignity and protecting Black hair heritage from systemic discrimination.

Do Modern Hair Care Practices Reflect Ancient African Hair Rituals?
Many modern textured hair practices directly mirror ancient African rituals, especially in their deep respect for hair's moisture and protective styling needs.

What Is the Historical Significance of Protective Hairstyles?
Protective hairstyles embody centuries of textured hair heritage, serving as cultural markers, tools for survival, and symbols of identity and resistance.

What Roles Did Textured Hair Rituals Play in Cultural Identity?
Textured hair rituals historically served as powerful markers of identity, status, and resistance within diverse Black and mixed-race communities.

What Ancestral Oils Nurtured Textured Hair’s Unique Structure?
Ancestral oils like shea butter, palm oil, and castor oil provided deep moisture and protection, honoring textured hair’s unique structure.

What Cultural Impact Does Hair Heritage Have on Personal Identity and Wellness?
Textured hair heritage profoundly shapes identity and wellness, serving as a powerful link to ancestral wisdom and a site of enduring cultural affirmation.

What Ancestral Practices Honor Textured Hair Biology?
Ancestral practices honor textured hair biology through protective styles, natural emollients, and communal rituals rooted deeply in heritage.

What Is the Spiritual Meaning of African Hair Tools?
African hair tools embody ancestral wisdom and spiritual connection, transforming hair care into a ritual honoring textured hair heritage.

How Does Modern Legislation Honor Ancestral Hair Traditions and Cultural Practices?
Modern legislation like the CROWN Act honors ancestral hair traditions by legally protecting textured hair styles and cultural practices against discrimination, affirming their heritage.

