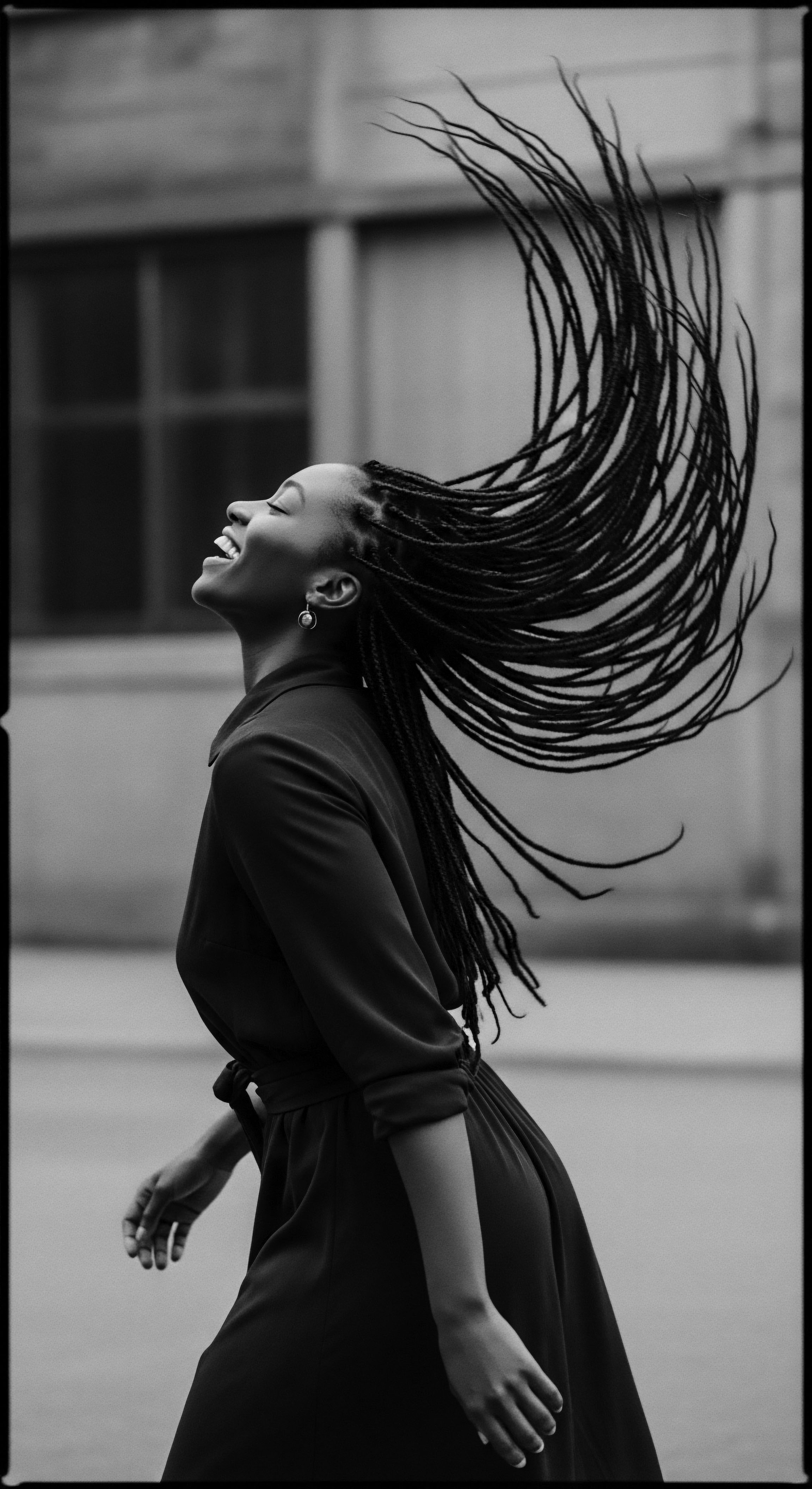

In What Ways Do Head Wraps Connect Individuals to Their Ancestral Heritage Today?
Head wraps connect individuals to their ancestral heritage by serving as enduring symbols of identity, resistance, and a practical means of protecting textured hair.
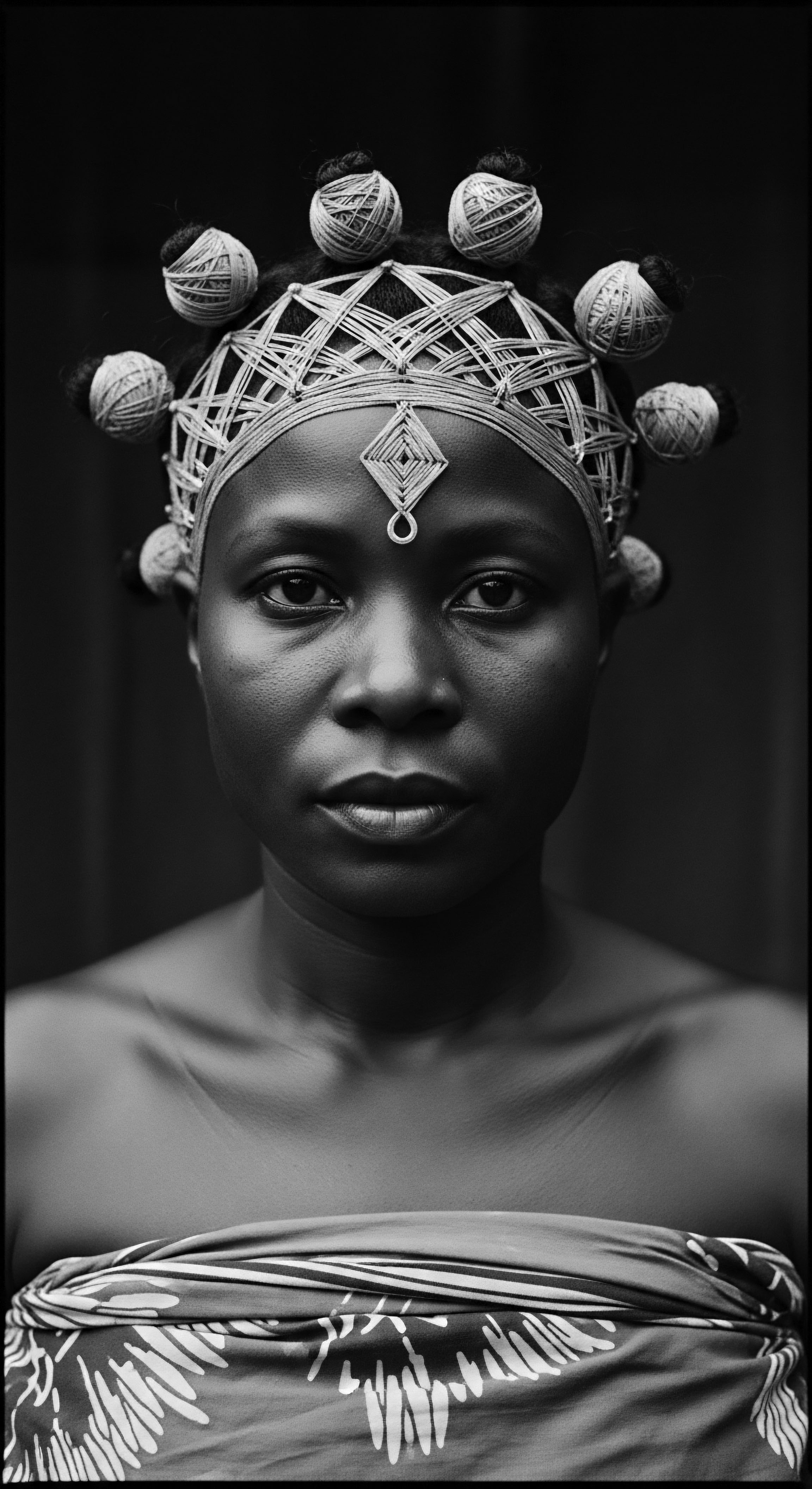

Ijaw Hair Practices
Meaning ❉ Ijaw Hair Practices encompass a profound system of cultural identity, communal bonds, and ancestral wisdom for textured hair care.

What Is the Cultural Significance of Traditional Hair Coverings?
Traditional hair coverings hold deep cultural importance, symbolizing heritage, resilience, and identity for textured hair communities.

What Cultural Significance Did Braids Hold in African Heritage?
Braids in African heritage are a profound expression of identity, history, status, and community, deeply rooted in textured hair's biological and cultural legacy.

Hair Whorl Patterns
Meaning ❉ Hair Whorl Patterns describe the spiral growth of hair on the scalp, a biological trait deeply intertwined with heritage and care practices.

In What Ways Did Head Wraps Express Cultural Identity during Slavery?
Head wraps during slavery transformed from symbols of forced subjugation into powerful declarations of Black textured hair heritage and identity.
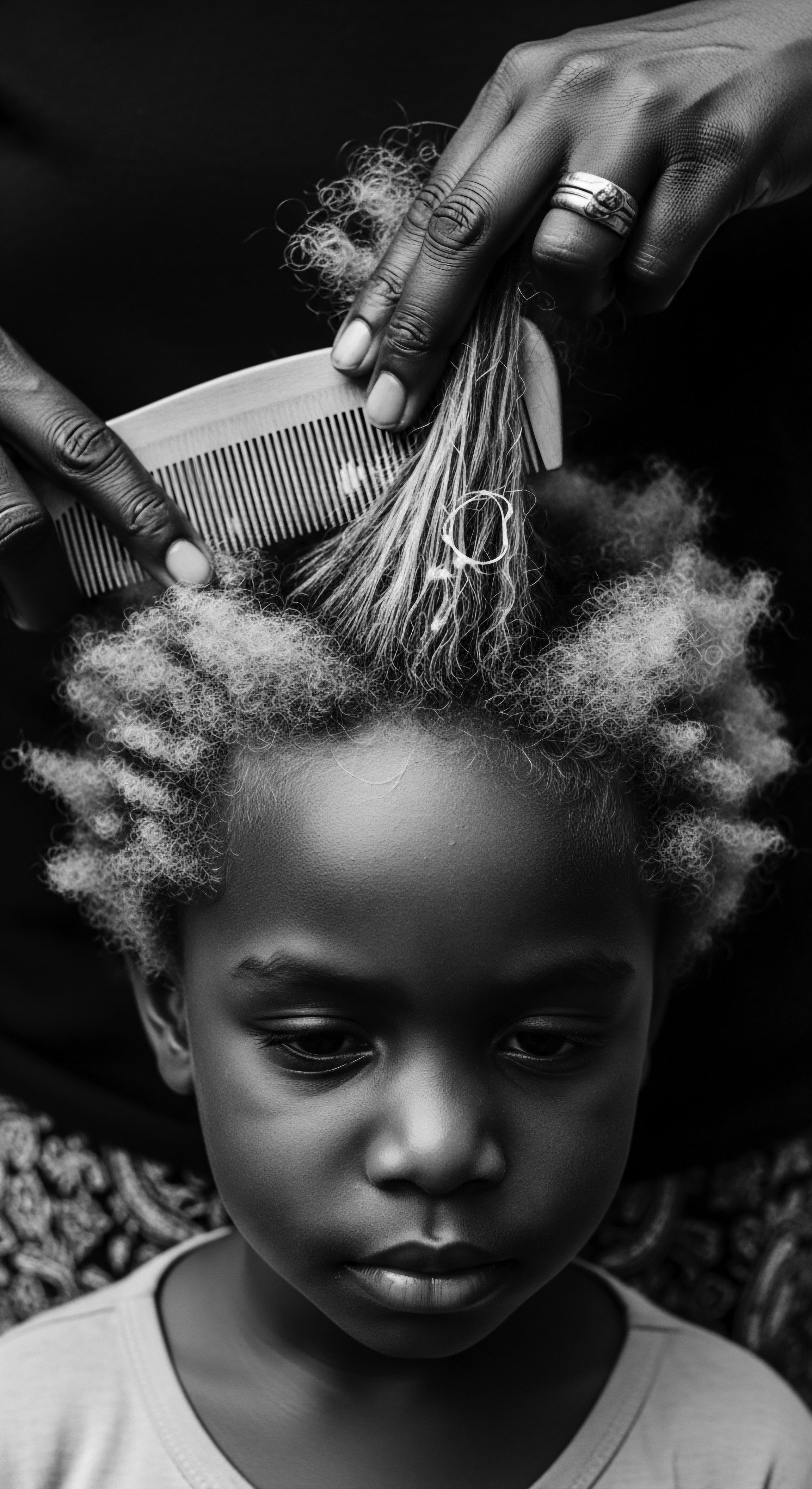

How Did Head Wraps Become a Symbol of Defiance?
Head wraps became a symbol of defiance by transforming from imposed markers of subjugation into vibrant expressions of cultural identity and resilience within textured hair heritage.

Black British Heritage
Meaning ❉ Black British Heritage represents the enduring cultural legacy of individuals of African and Caribbean descent in the UK.

Pokot Headdresses
Meaning ❉ Pokot headdresses are intricate head adornments symbolizing identity, social status, and life stages within a rich East African cultural heritage.

Myrrh Hair Care
Meaning ❉ Myrrh Hair Care refers to traditional and contemporary practices utilizing Commiphora myrrha resin for scalp health and hair resilience, deeply connected to textured hair heritage.

What Is the Historical Connection between Hair Rituals and Resistance?
Hair rituals have served as profound acts of resistance, preserving textured hair heritage and identity against centuries of oppression.

How Did Traditional African Hair Care Practices Adapt in the Diaspora?
Traditional African hair care practices adapted in the diaspora through ingenious substitutions and persistent cultural identity, preserving textured hair heritage.

How Do Historical Black Hair Traditions Influence Modern Self-Care?
Historical Black hair traditions influence modern self-care by centering identity, resilience, and ancestral wisdom in daily routines.

Traditional Hair Beauty
Meaning ❉ Traditional Hair Beauty defines the culturally valued aesthetic and holistic well-being of textured hair, grounded in ancestral practices and heritage.

Maasai Beadwork Heritage
Meaning ❉ Maasai Beadwork Heritage is a symbolic language of identity and life milestones, profoundly intertwined with ancestral hair traditions.

What Enduring Ancestral Wisdom Guides Modern Textured Hair Care?
Ancestral wisdom guides modern textured hair care by offering profound insights rooted in millennia of heritage and practice.

How Does Hair Discrimination Affect Textured Hair Communities?
Hair discrimination attacks textured hair heritage by forcing conformity and eroding cultural identity.

In What Ways Did Ancestral Practices Address the Unique Properties of Textured Hair?
Ancestral practices addressed textured hair through natural ingredients, protective styling, and communal rituals, reflecting deep heritage.

Chatzitzah
Meaning ❉ Chatzitzah, in the context of textured hair, is a concept illuminating historical and cultural barriers, alongside protective layers of ancestral care and identity.

What Historical Textiles Inspired Modern Hair Coverings?
Historical textiles for hair coverings originated in African traditions, evolving into symbols of identity and protection for textured hair heritage.

What Ancestral Hair Practices Are Recognized by Contemporary Statutes?
Contemporary statutes like the CROWN Act legally recognize protective styles and hair texture as protected racial characteristics.
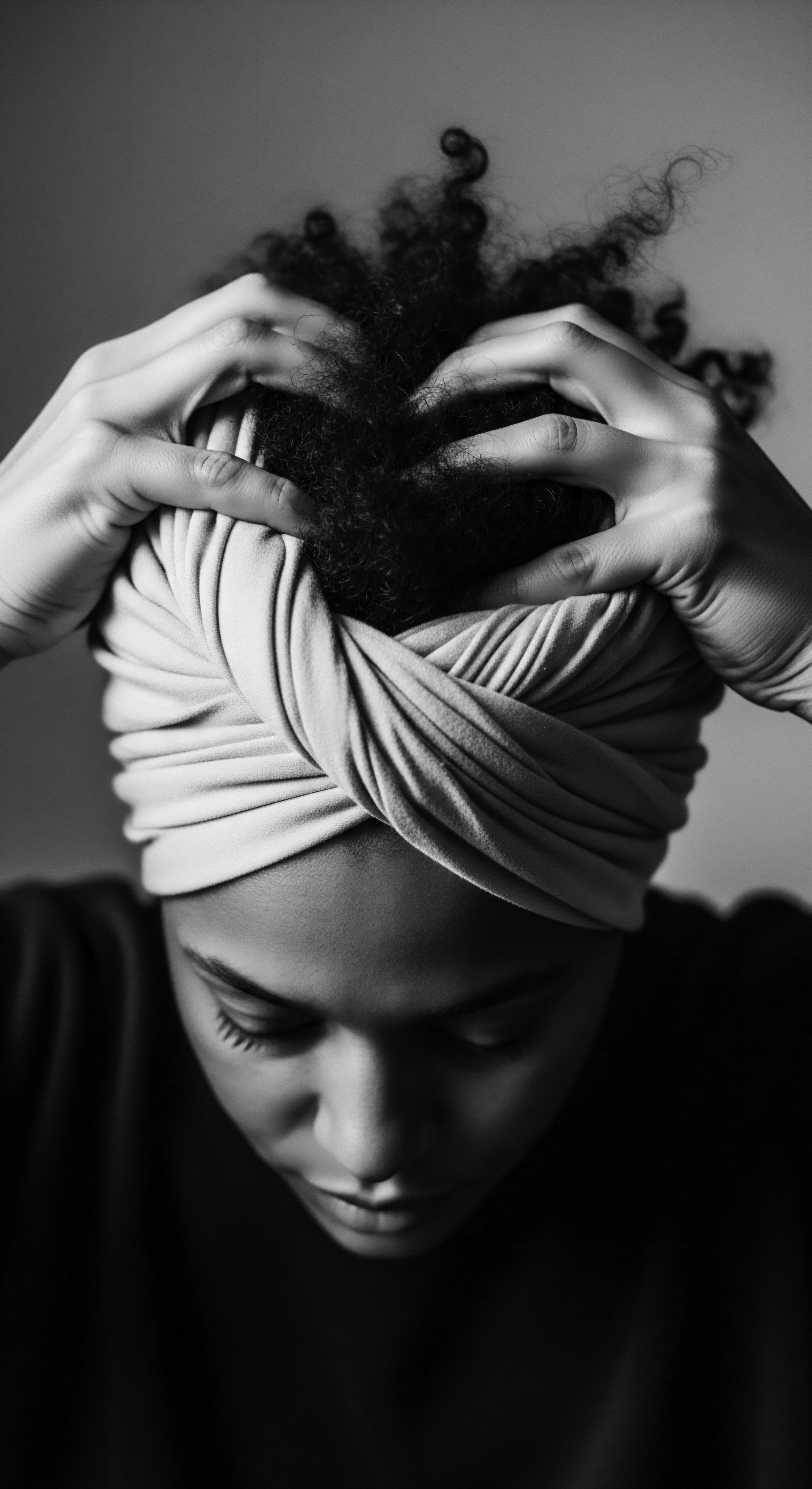

What Is the Cultural Background of Hair Bonnets?
The hair bonnet's cultural background is woven from ancestral African protection, enforced colonial concealment, and defiant self-expression for textured hair.

Afro Hair Policies
Meaning ❉ Afro Hair Policies define the formal and informal rules governing textured hair, often addressing historical and contemporary discrimination rooted in Eurocentric beauty standards.
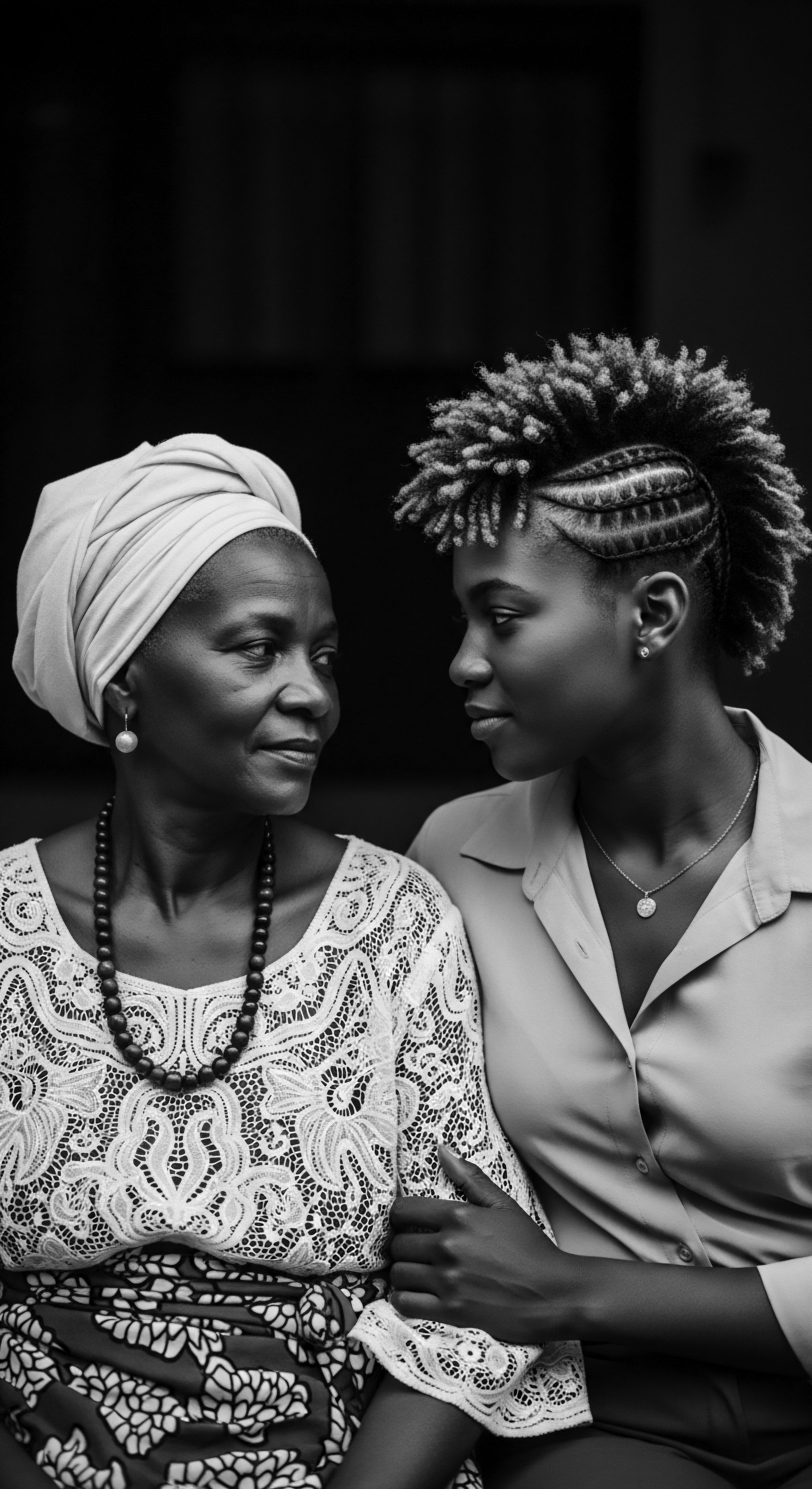
How Does Modern Natural Hair Embrace Heritage and Self-Acceptance?
Modern natural hair fosters self-acceptance by reclaiming textured hair heritage, connecting individuals to ancestral practices and cultural pride.

How Did Ancient Hair Practices Unite Communities?
Ancient hair practices, particularly styling and care rituals, created a shared language and space for community cohesion within textured hair heritage.

How Does Modern Care Reflect Textured Hair’s Ancient Heritage?
Modern care for textured hair profoundly reflects its ancient heritage by adapting ancestral biological understanding and traditional practices.

How Do Historical Styling Tools Reflect Cultural Identity in Textured Hair Heritage?
Historical styling tools mirror cultural identity by reflecting ancient practices, enduring resilience, and the evolving self-expression of textured hair **heritage**.

What Communal Aspects Defined Historical African Hair Oiling?
Historical African hair oiling practices were communal acts, deeply interwoven with identity, spirituality, and social cohesion, shaping textured hair heritage.

Can Understanding Hair Anatomy Deepen Appreciation for Traditional Care Rituals?
Understanding hair anatomy reveals deep appreciation for textured hair heritage, validating ancient care rituals through scientific insight.

