
What Is the Historical and Cultural Significance of Natural Ingredients in Black Hair Care Heritage?
Natural ingredients in Black hair care represent a profound heritage of ancestral wisdom, cultural identity, and enduring resilience.

How Did Historical Hair Practices Shape Black Identity and Heritage?
Historical hair practices for Black individuals profoundly shaped identity and heritage through symbolism, community, and acts of resistance.

Bambara Traditions
Meaning ❉ The Bambara Traditions represent a deep cultural and spiritual heritage of hair care and symbolism, particularly for textured hair, rooted in West African ancestral wisdom.

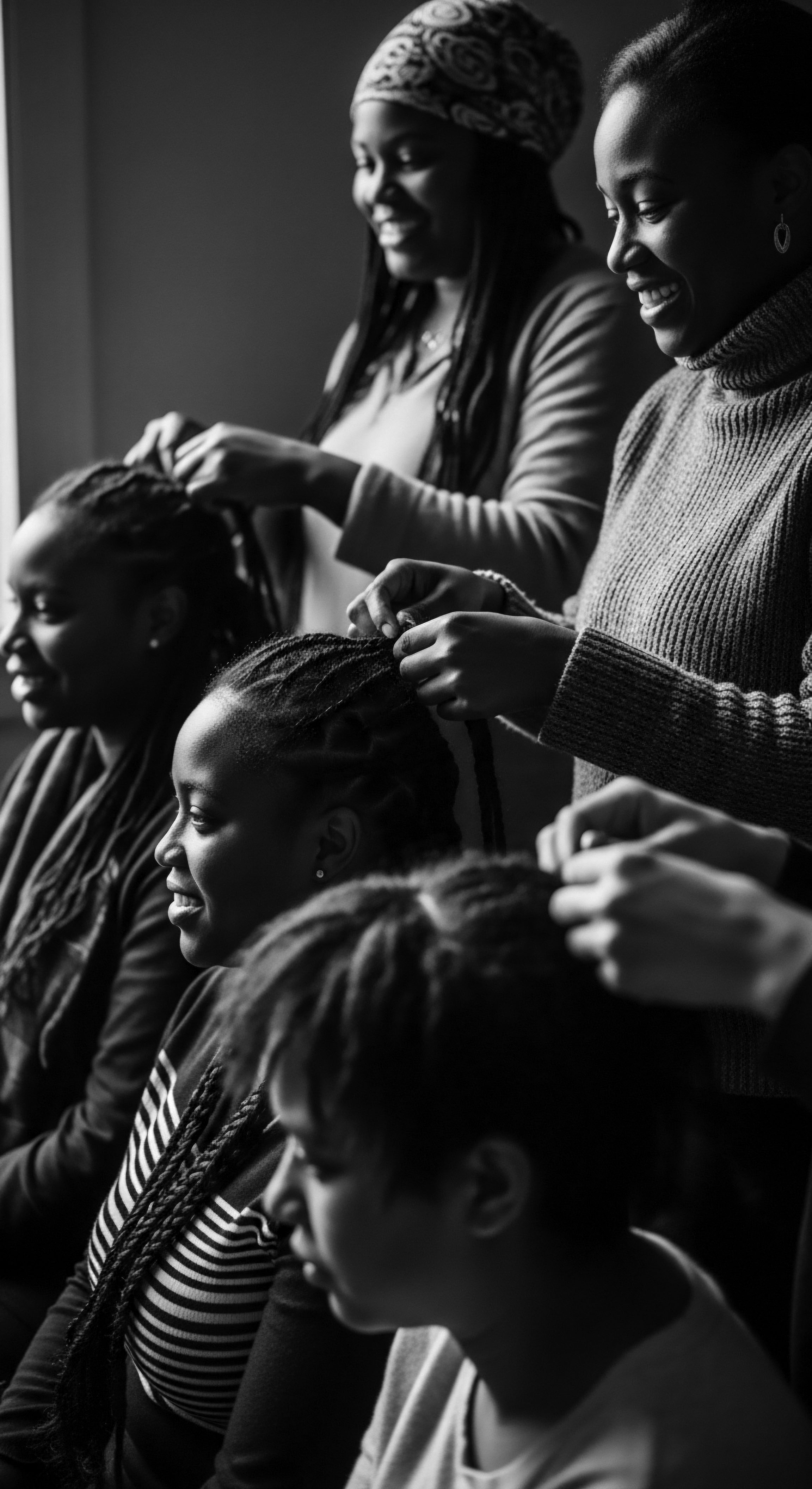
Hair Societal Impact
Meaning ❉ Hair Societal Impact describes how hair, especially textured hair, shapes and is shaped by societal norms, history, and individual identity.

Colorism Definition
Meaning ❉ Colorism is a system of prejudice or preference within a racial group based on skin tone, deeply impacting textured hair heritage.

Textured Hair Regulations
Meaning ❉ Textured Hair Regulations are societal and historical guidelines governing the perception and acceptance of coiled, curled, and wavy hair, deeply tied to cultural heritage.

Hair Social Construct
Meaning ❉ The Hair Social Construct defines societal meanings and values assigned to hair, profoundly shaping identity and experience, particularly for textured hair.
Cultural Decolonization
Meaning ❉ Cultural Decolonization reclaims and revalues textured hair heritage, dismantling colonial beauty standards and fostering self-acceptance.

School Hair Policies
Meaning ❉ School Hair Policies are institutional rules governing student hair appearance, often reflecting and perpetuating societal biases against textured hair heritage.

Matrilineal Heritage
Meaning ❉ Matrilineal Heritage describes the intergenerational transfer of cultural knowledge, practices, and identity related to textured hair through the maternal line.

Ancestral Aromas
Meaning ❉ Ancestral Aromas are the fragrant signatures of historical hair traditions, evoking collective memories and connecting individuals to a lineage of care and cultural affirmation.

Hidden Practices
Meaning ❉ Hidden Practices are the unwritten, inherited traditions of textured hair care and styling, deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom and cultural significance.

Niuniu Practices
Meaning ❉ Niuniu Practices define traditional hair care methods and communal rituals deeply rooted in the heritage and identity of textured hair communities.

How Have Historical Events Shaped the Identity of Textured Hair in Contemporary Society?
Historical events transformed textured hair from a cultural marker into a symbol of both oppression and profound heritage reclamation.

Cultural Identity Schools
Meaning ❉ Cultural Identity Schools illuminate how textured hair embodies ancestral knowledge, communal memory, and individual expression within Black and mixed-race communities.

In What Ways Does Textured Hair Connect to Cultural Resilience and Identity?
Textured hair is a living archive of ancestral wisdom, cultural resilience, and enduring identity, rooted deeply in shared heritage.

Frankincense Hair
Meaning ❉ Frankincense Hair is Roothea's conceptual designation for textured hair embodying ancient wisdom, resilience, and deep ancestral connection.

One-Drop Rule
Meaning ❉ The One-Drop Rule is a historical and sociological principle asserting that any African ancestry designates an individual as Black, deeply impacting identity and textured hair experiences.

CROWN Act Education
Meaning ❉ CROWN Act Education promotes understanding and acceptance of diverse hair textures and styles, particularly those rooted in Black and mixed-race heritage, combating discrimination.

In What Ways Did Textured Hair Become a Symbol of Cultural Resistance?
Textured hair became a symbol of cultural resistance by embodying ancestral heritage and challenging oppressive beauty norms.

Legal Rulings Heritage
Meaning ❉ Legal Rulings Heritage defines the historical and ongoing legal decisions shaping the recognition and protection of textured hair identity.

Fa’a Samoa Care
Meaning ❉ Fa'a Samoa Care is a holistic cultural system that guides respectful living, with hair care as a deeply connected expression of identity and ancestral wisdom.

What Historical Precedents Shaped Legal Frameworks around Black Hair Heritage?
Historical laws often sought to control Black hair, but ancestral practices and modern legislation like the CROWN Act reclaim textured hair heritage.

Mixed Hair Protection
Meaning ❉ Mixed Hair Protection is the comprehensive safeguarding of diverse hair textures, acknowledging their unique needs, historical significance, and cultural resilience.

Decolonial Hair Beauty
Meaning ❉ Decolonial Hair Beauty is the recognition and celebration of textured hair's inherent worth, reclaiming ancestral wisdom and rejecting colonial beauty standards.

How Did the Civil Rights Movement Reshape Textured Hair’s Cultural Meaning?
The Civil Rights Movement transformed textured hair's meaning by affirming its beauty, rejecting assimilation, and reclaiming it as a powerful symbol of Black pride and heritage.

Can Legal Frameworks Truly Shift Cultural Perceptions of Textured Hair Heritage?
Legal frameworks, by affirming protections, can begin to shift perceptions of textured hair heritage, legitimizing its cultural significance.


