
Natural Hair Self-Governance
Meaning ❉ Natural Hair Self-Governance is the sovereign right to determine one's hair presentation and care, deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom and cultural identity.

Black Hair Decolonization
Meaning ❉ Black Hair Decolonization is the reclaiming of textured hair identity from Eurocentric beauty standards, rooted in ancestral practices and cultural heritage.

What Historical Meanings Do Textured Hairstyles Carry?
Textured hairstyles are a living archive, communicating identity, status, and resistance across generations, deeply rooted in Black heritage.

In What Ways Do past Legal Controls Influence Present-Day Textured Hair Acceptance?
Past legal controls, like the Tignon Laws, directly influenced textured hair acceptance by attempting to suppress cultural expression, yet inadvertently solidified its heritage as a symbol of defiance and identity.

Decolonization Practices
Meaning ❉ Decolonization Practices dismantle colonial legacies, reclaiming cultural integrity and self-determination, particularly for textured hair heritage.

Hair Dehumanization
Meaning ❉ Hair Dehumanization is the systemic invalidation of textured hair, severing its deep ties to identity, culture, and ancestral heritage.

Afro-Diaspora Hair
Meaning ❉ Afro-Diaspora Hair signifies the unique hair textures of African descent, embodying a rich heritage of cultural identity and enduring resilience.

What Historical Biases against Textured Hair Does Current Legislation Challenge?
Current legislation confronts historical biases against textured hair by affirming its cultural significance and protecting ancestral styles.

How Do CROWN Act Provisions Impact Textured Hair Identity?
CROWN Act provisions protect textured hair identity by affirming ancestral styles and challenging historical discrimination.

What Historical Events Influenced Perceptions of Textured Hair?
Historical events reshaped textured hair perceptions from ancestral pride to symbols of oppression and, ultimately, powerful heritage reclamation.

Credibility Deficit
Meaning ❉ The Credibility Deficit is the unjust withholding of deserved belief or authority, often based on identity, profoundly impacting textured hair heritage.

Hair as Cultural Text
Meaning ❉ Hair as Cultural Text is the dynamic interpretation of hair as a symbolic language conveying identity, heritage, and socio-political narratives.

Hair Policy
Meaning ❉ Hair Policy is the intricate set of formal and informal strictures governing hair's perception, presentation, and management, deeply rooted in cultural heritage.

Resistance Styling
Meaning ❉ Resistance Styling is the inherent capacity of textured hair to defy and transform external forces while maintaining its natural form.

Indigotin Heritage
Meaning ❉ Indigotin Heritage denotes the deep ancestral and biological meaning of textured hair within Black and mixed-race communities, a living cultural archive.

How Do Historical Hair Rituals Connect to Contemporary Textured Hair Identity and Wellness?
Historical hair rituals for textured hair are vital links to ancestral identity, fostering well-being through communal care and cultural reclamation.

What Historical Hair Practices Shaped Contemporary Textured Hair Care?
Historical hair practices shaped contemporary textured hair care by embedding a heritage of resilience, identity, and profound ancestral wisdom in every strand.

Indigenous Hair Significance
Meaning ❉ Indigenous Hair Significance is the profound cultural, spiritual, and historical meaning hair holds, particularly for textured hair, as a living link to ancestry and identity.

Workplace Appearance Norms
Meaning ❉ Workplace Appearance Norms are societal and organizational expectations for professional presentation, often impacting textured hair due to Eurocentric biases.

What Legal Protections Affirm Textured Hair Identity in Contemporary Society?
Legal protections affirm textured hair identity by recognizing its deep cultural heritage and inherent biological traits, challenging discriminatory norms.

Social Delineation
Meaning ❉ Social Delineation, within textured hair heritage, is the societal classification of individuals based on hair, influencing identity and opportunity.

Natural Hair Revolution
Meaning ❉ The Natural Hair Revolution is a cultural and personal reclamation of textured hair, celebrating ancestral heritage and authentic identity.
Rastafarian Locs Heritage
Meaning ❉ Rastafarian Locs Heritage is a spiritual and cultural practice of growing naturally matted hair, embodying identity, resistance, and ancestral connection.

Coiled Hair Safeguarding
Meaning ❉ Coiled Hair Safeguarding is the intentional preservation and honoring of textured hair through culturally resonant and biologically informed practices.

Holistic Student Health
Meaning ❉ Holistic Student Health is the comprehensive well-being of a student, deeply intertwined with their cultural identity and hair heritage.
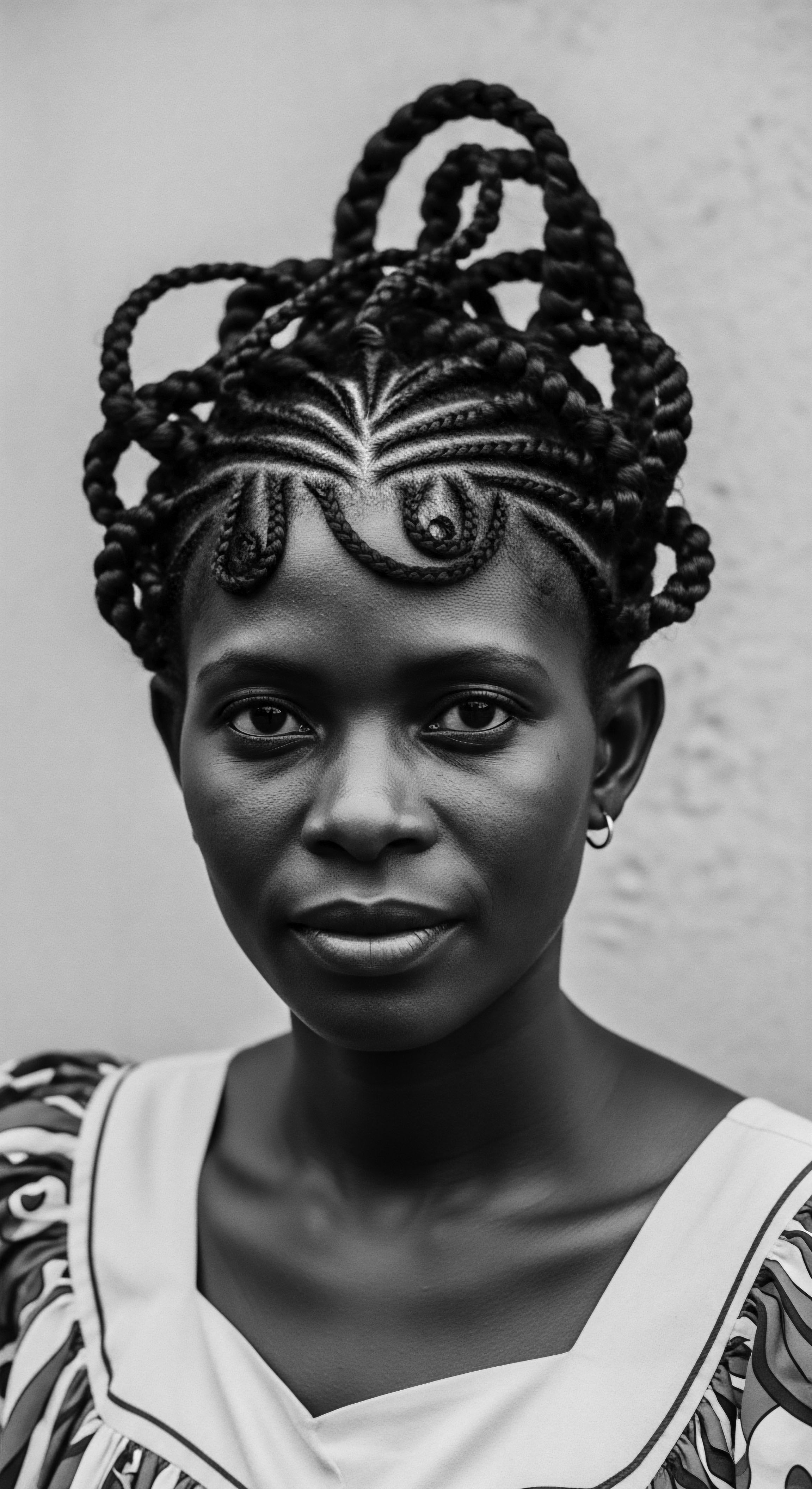

What Is the Historical Significance of Hair Care Practices in Black Heritage?
Hair care in Black heritage is a profound, living chronicle of identity, resistance, and ancestral wisdom, deeply rooted in textured hair.

In What Ways Do Legal Movements Reinforce the Ancestral Heritage of Textured Hair Care?
Legal movements protect textured hair by outlawing discrimination, thereby reinforcing its deep ancestral and cultural significance.

Community Building Hair
Meaning ❉ Community Building Hair signifies the power of textured hair to foster collective identity and transmit cultural knowledge across generations.
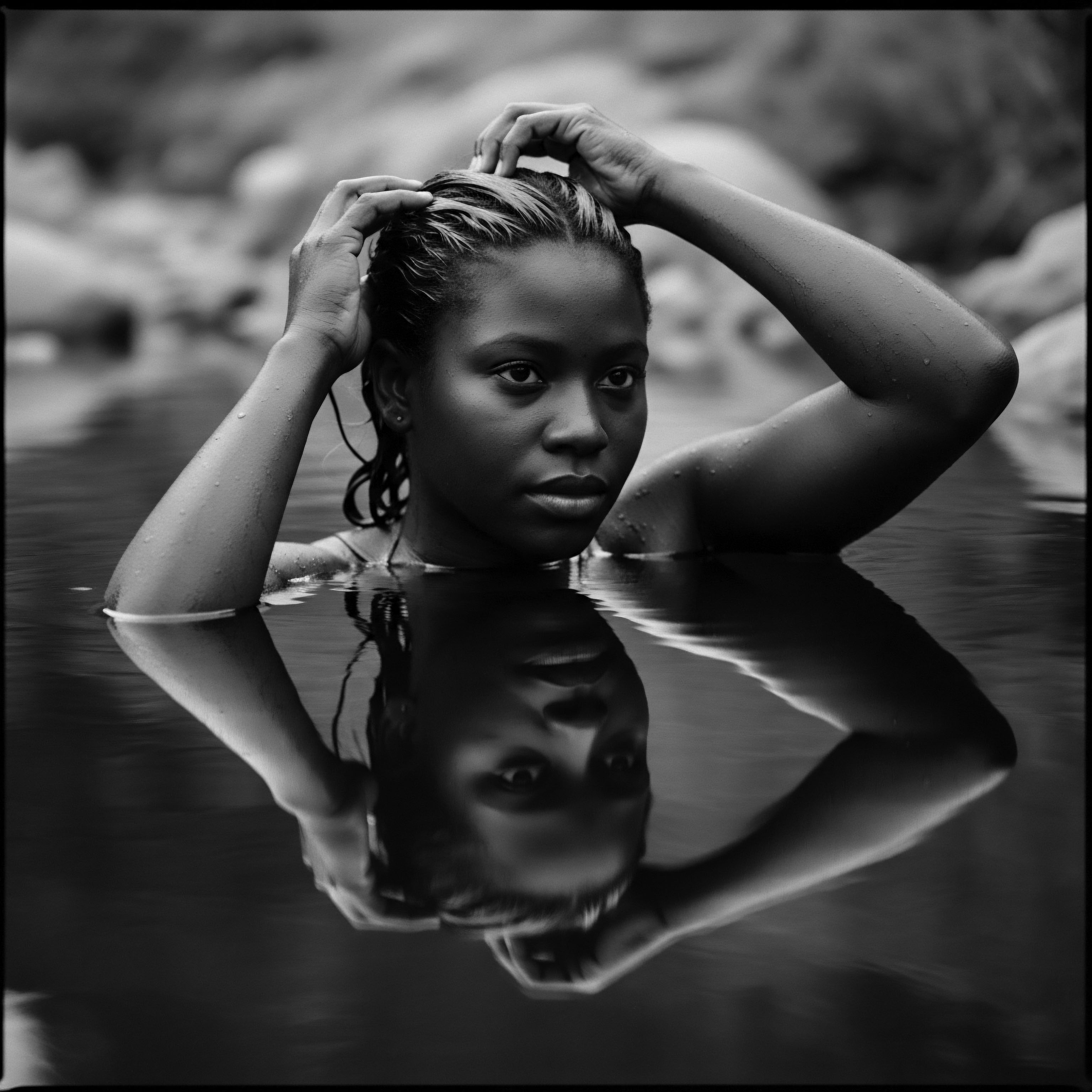

African Heritage Hair
Meaning ❉ African Heritage Hair signifies the diverse textured hair types rooted in African lineage, embodying ancestral wisdom, cultural identity, and historical resilience.

