What Historical Ingredients Influenced Textured Hair’s Ph?
Historical ingredients like alkaline plant ash and acidic fruit rinses shaped textured hair's pH, reflecting ancestral wisdom in hair heritage.

Which Plant Oils Calm Textured Scalps?
Plant oils like coconut, castor, baobab, argan, and neem, rooted in textured hair heritage, calm textured scalps.

Which Plant Oils Aided Ancient Textured Hair?
Ancient textured hair thrived with plant oils like shea, castor, and moringa, deeply connecting care to cultural heritage.

In What Ways Did Oiling Preserve the Cultural Meaning of Textured Hair through History?
Oiling protected textured hair physically and acted as a powerful cultural vessel, preserving ancestral care, identity, and community narratives across history.

How Do Historical Styling Practices Inform Current Textured Hair Protection?
Historical styling practices, rooted in ancestral wisdom, offer direct blueprints for current textured hair protection, emphasizing moisture retention and minimal manipulation.

Why Do Certain Traditional Oils Penetrate Textured Hair Better?
Traditional oils often penetrate textured hair due to their unique molecular structures, reflecting ancestral wisdom and hair's unique porosity.
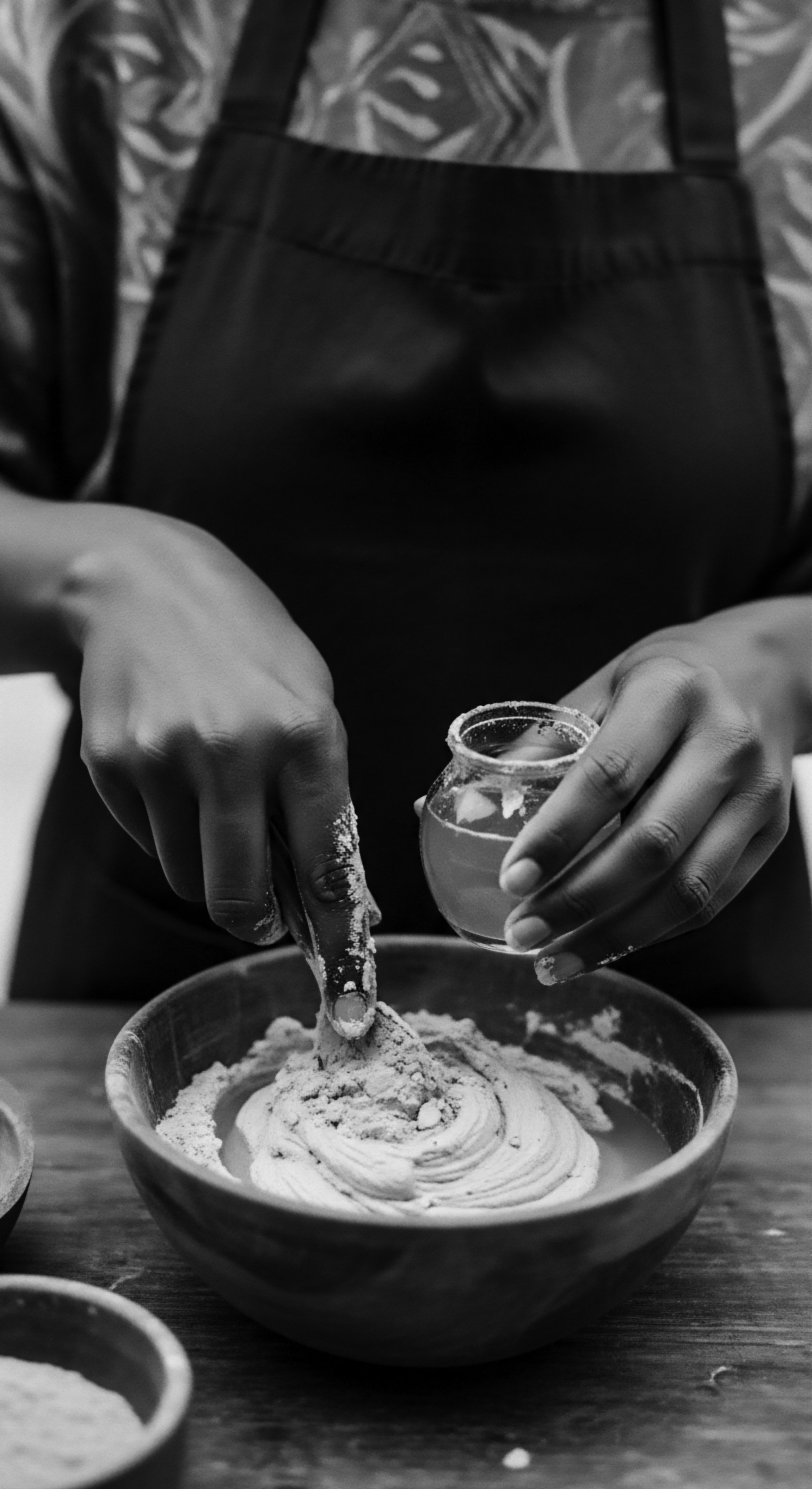

What Historical Ingredients Were Staples for Textured Hair Care?
Ancestral textured hair care centered on plant-derived oils, rich butters, and natural cleansing agents, deeply rooted in cultural heritage.

What Traditional Ingredients Benefit Textured Hair Cuticles?
Traditional ingredients like shea butter and Chebe powder benefit textured hair cuticles by providing protective layers, smoothing scales, and retaining moisture through ancestral wisdom.

Waterless Hair Care
Meaning ❉ Waterless Hair Care refers to methods of cleansing, conditioning, and styling hair without the traditional use of liquid water, often reflecting ancestral practices.
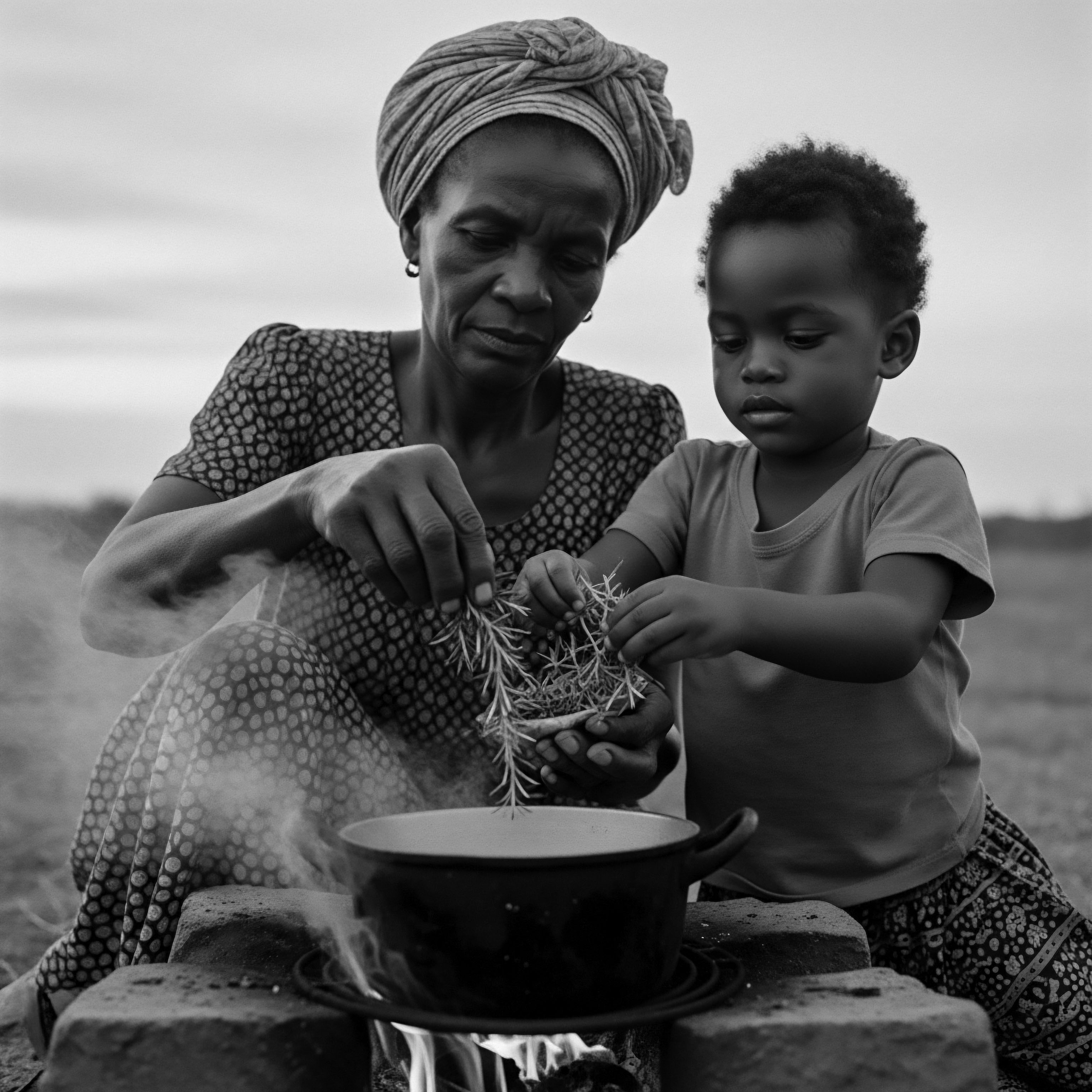

How Did Ancient Remedies Protect Textured Hair?
Ancient remedies guarded textured hair through deep understanding of its structure, protective styling, and natural ingredients, all rooted in cultural heritage.

Can Historical Botanical Remedies Apply to Modern Textured Hair Care?
Historical botanical remedies offer proven efficacy and deep cultural significance, directly applying to modern textured hair care.
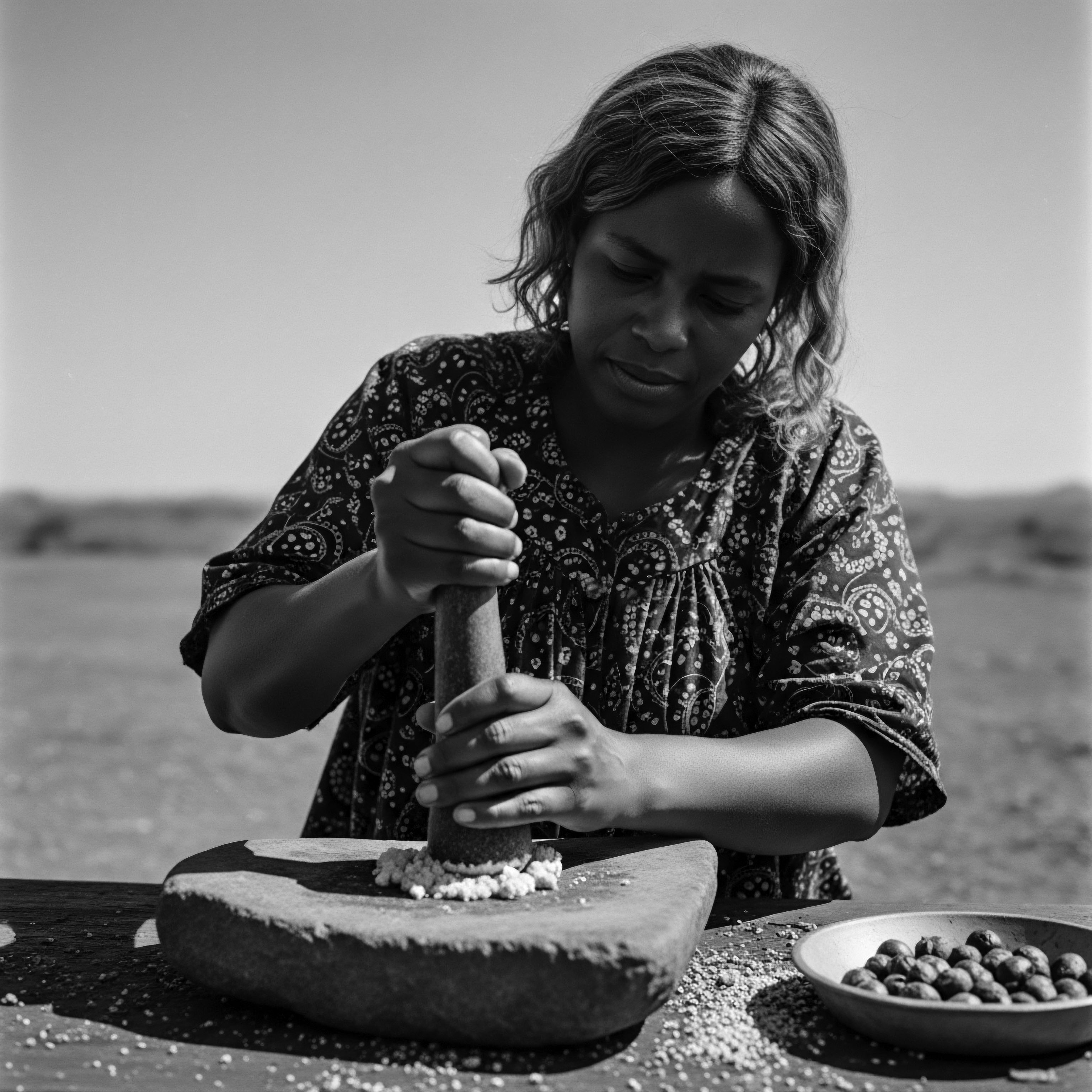

Can Science Explain the Benefits of Traditional Textured Hair Care?
Science affirms traditional textured hair care methods, often confirming ancestral wisdom for optimal strand health and heritage preservation.

Can Modern Science Validate Ancient Hair Oiling Practices for Textured Hair?
Modern science confirms ancient hair oiling practices for textured hair protect, strengthen, and moisturize, validating a profound ancestral heritage.

In What Ways Do Traditional Plant-Based Remedies Impact Modern Textured Hair Health?
Traditional plant remedies nourish textured hair by drawing upon centuries of ancestral wisdom and botanical efficacy.

Can Modern Hair Science Affirm Ancestral Practices for Textured Hair Health?
Modern hair science increasingly affirms the efficacy of ancestral textured hair practices, underscoring their enduring value and heritage connection.

What Historical Natural Ingredients Protected Textured Hair from Environmental Elements?
Ancestors used natural ingredients like oils, butters, and plants to form a protective barrier for textured hair against environmental elements.

What Historical Role Did Protective Styles Have in Hair Heritage?
Protective styles for textured hair historically served as vital cultural communication, a means of survival, and a profound expression of heritage.

How Do Protective Styles Enhance Hydration for Textured Strands?
Protective styles shield textured strands from external elements, preserving applied hydration and nurturing hair's ancestral resilience.

What Is the Historical Significance of Specific Oils in Textured Hair Care?
Specific oils hold historical weight in textured hair care, embodying ancestral wisdom, cultural identity, and enduring resilience.

What Plant Compounds Were Used for Cleansing Textured Hair Traditionally?
Traditional cleansing for textured hair relied on plant compounds like African Black Soap, rhassoul clay, and yucca root, deeply rooted in heritage.

Can Science Explain the Efficacy of Traditional Hair Oiling for Textured Hair?
Science affirms traditional hair oiling for textured strands, explaining its profound efficacy in moisture retention and breakage prevention, deeply rooted in ancestral heritage.

Why Does Coconut Oil Uniquely Benefit Textured Hair across Generations?
Coconut oil benefits textured hair uniquely due to its ancestral use and scientific ability to prevent protein loss.

What Historical Rules Impacted Textured Hair Care?
Historical rules profoundly impacted textured hair care by attempting to control appearance and identity, forcing adaptation while sparking resilience and preservation of heritage.

How Do Traditional Oiling Practices Honor Textured Hair Heritage?
Traditional oiling practices honor textured hair heritage by linking historical care methods with cultural identity and physical well-being.

How Do Traditional Oils Benefit Textured Hair Strength?
Traditional oils enhance textured hair strength by preserving protein and shielding against damage, a legacy from ancestral care practices.

What Historical Role Did Oiling Play in Textured Hair Styling?
Oiling played an ancestral role in textured hair styling, deeply rooted in preserving moisture, protecting strands, and honoring cultural heritage.

What Traditional Care Methods Preserved Textured Hair Hydration through Generations?
Generational traditions preserved textured hair hydration through natural oils, protective styles, and holistic community practices.

How Do Ancestral Oils Attract Moisture to Textured Hair?
Ancestral oils moisturize textured hair by sealing strands and internal strengthening, a heritage-rich practice.

Can Modern Science Validate the Heritage Practices of Textured Hair Oiling?
Modern science affirms that heritage oiling for textured hair provides significant moisture retention and breakage reduction.