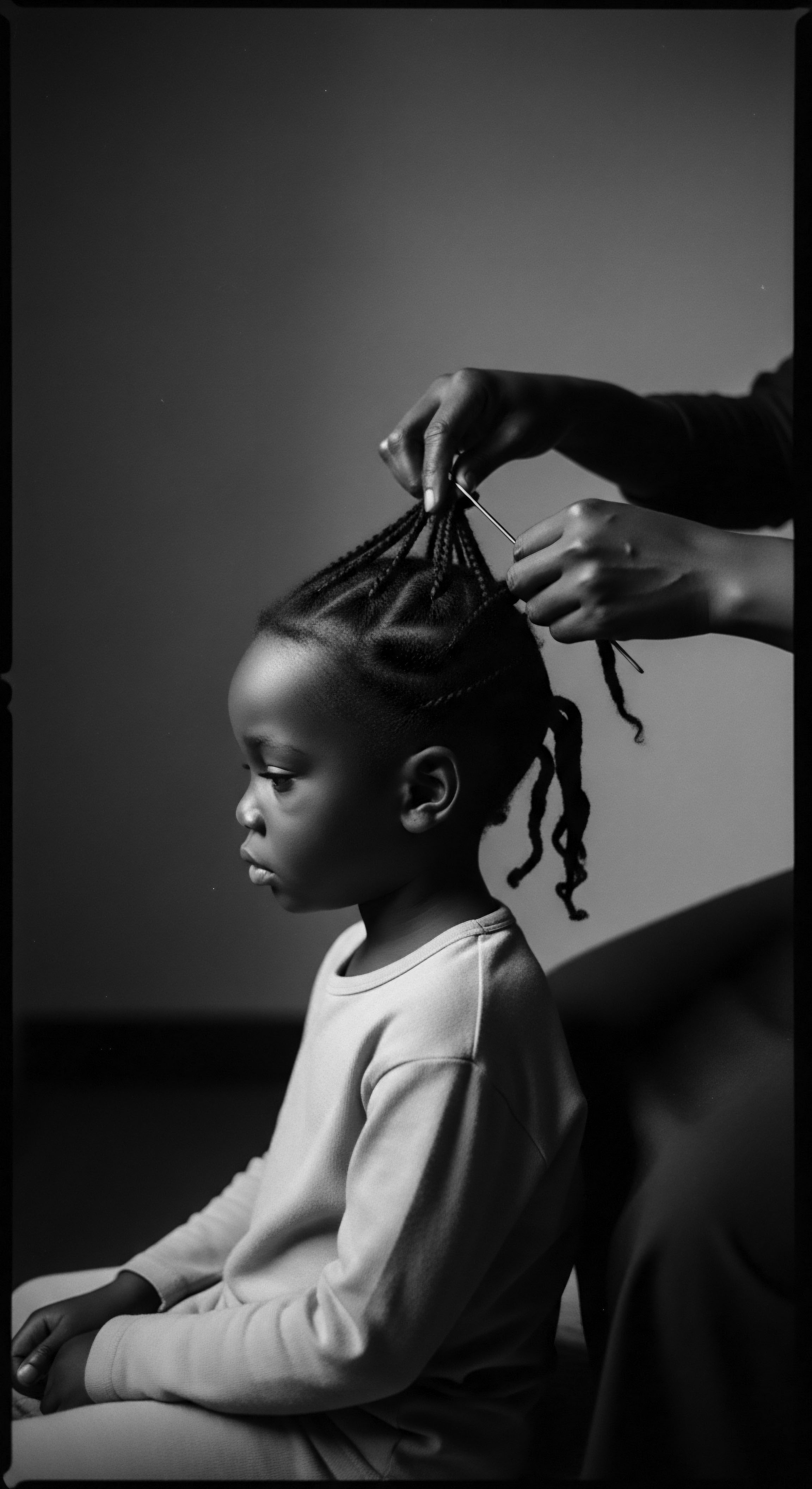

Hair Braiding
Meaning ❉ Hair Braiding is the ancient art of interweaving hair strands, a practice profoundly significant to textured hair heritage, symbolizing identity, communication, and resilience.

In What Ways Do Traditional Braiding Practices Connect Contemporary Textured Hair Care to Its Heritage?
Traditional braiding practices link contemporary textured hair care to its heritage through ancestral wisdom, cultural communication, and resilient identity.

How Did Ancient Braiding Protect Hair?
Ancient braiding protected textured hair by minimizing manipulation, sealing moisture, and serving as a profound cultural and survival heritage.

What Is the Cultural Meaning of Braids in Textured Hair Heritage?
Braids in textured hair are a profound cultural language, symbolizing identity, historical resilience, and ancestral wisdom within Black and mixed-race heritage.

Hair Braiding Resistance
Meaning ❉ Hair Braiding Resistance is the intrinsic strength of textured hair enabling complex braids, symbolizing cultural fortitude and historical defiance.

Braiding Identity
Meaning ❉ Braiding Identity is the profound cultural, historical, and personal meaning embedded within braided textured hair, reflecting lineage and self-expression.

Braiding Practices
Meaning ❉ Braiding Practices are ancient, culturally significant techniques of interweaving hair, deeply rooted in the heritage and resilience of textured hair communities.

Braiding as Resistance
Meaning ❉ Braiding as Resistance is the profound act of styling textured hair to assert identity, preserve heritage, and defy oppressive beauty standards.

Braiding Cultural Significance
Meaning ❉ The Braiding Cultural Significance delineates the historical, communal, and identity-affirming meanings embedded within braided textured hair across Black and mixed-race cultures.
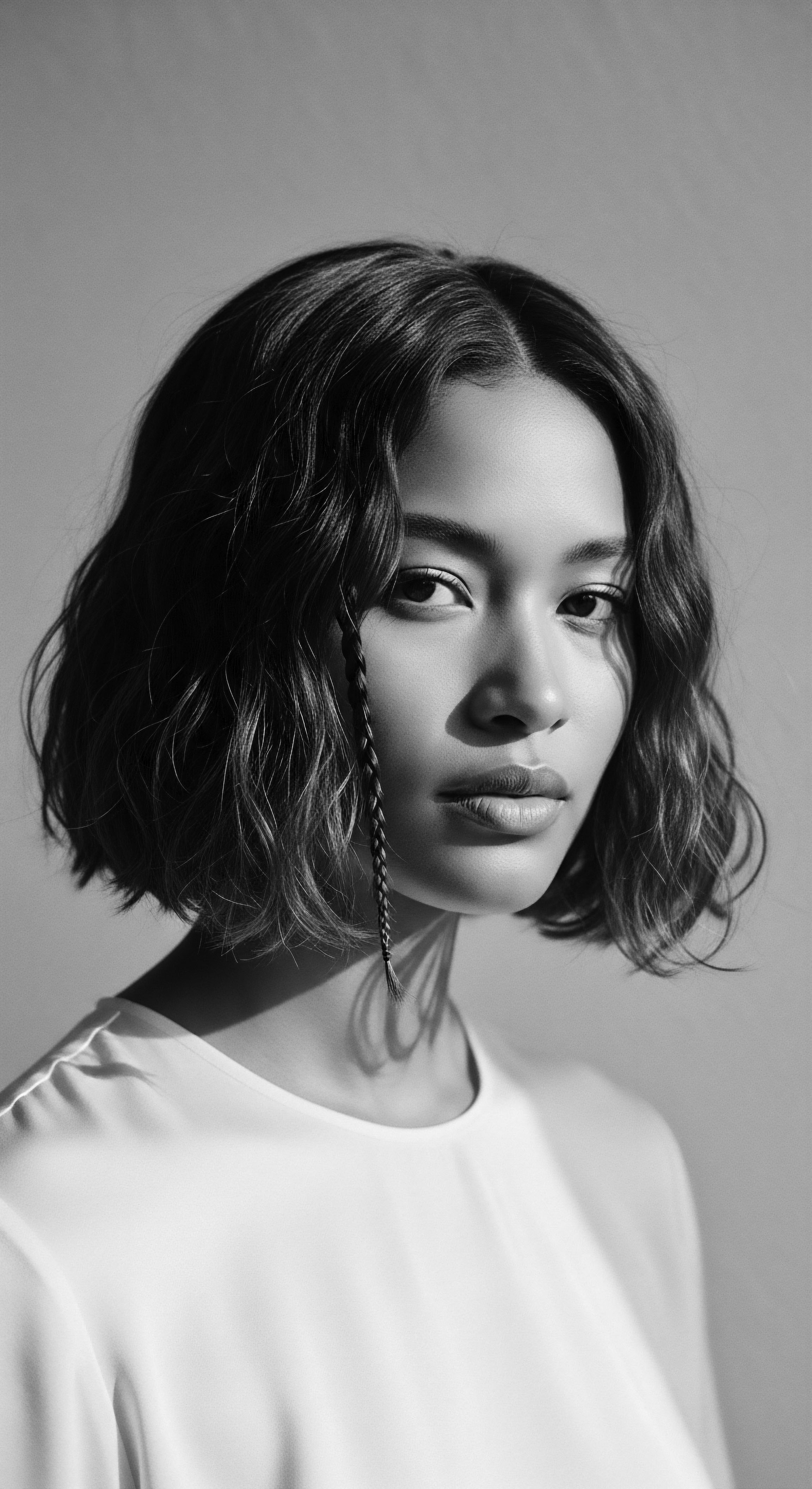

What Is the Role of Cultural Legacy in Textured Hair Care Decisions Today?
Cultural legacy profoundly shapes textured hair care by influencing styling choices, product selection, and identity expression, rooted in ancestral wisdom and historical resilience.
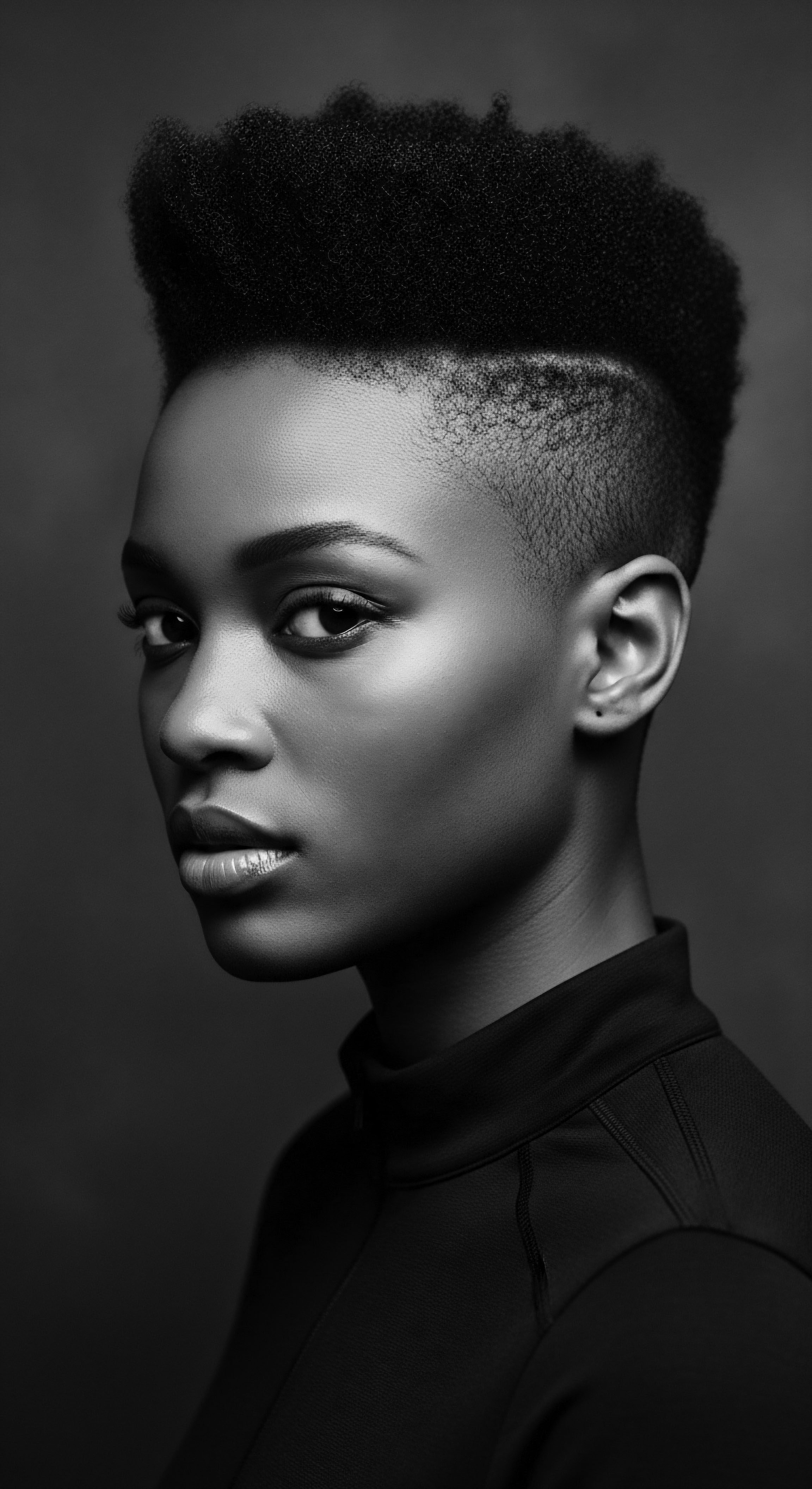

What Is the Cultural Significance of Braiding in Textured Hair Heritage?
Braiding textured hair is a powerful cultural expression, embodying heritage, resistance, and identity for Black and mixed-race communities.
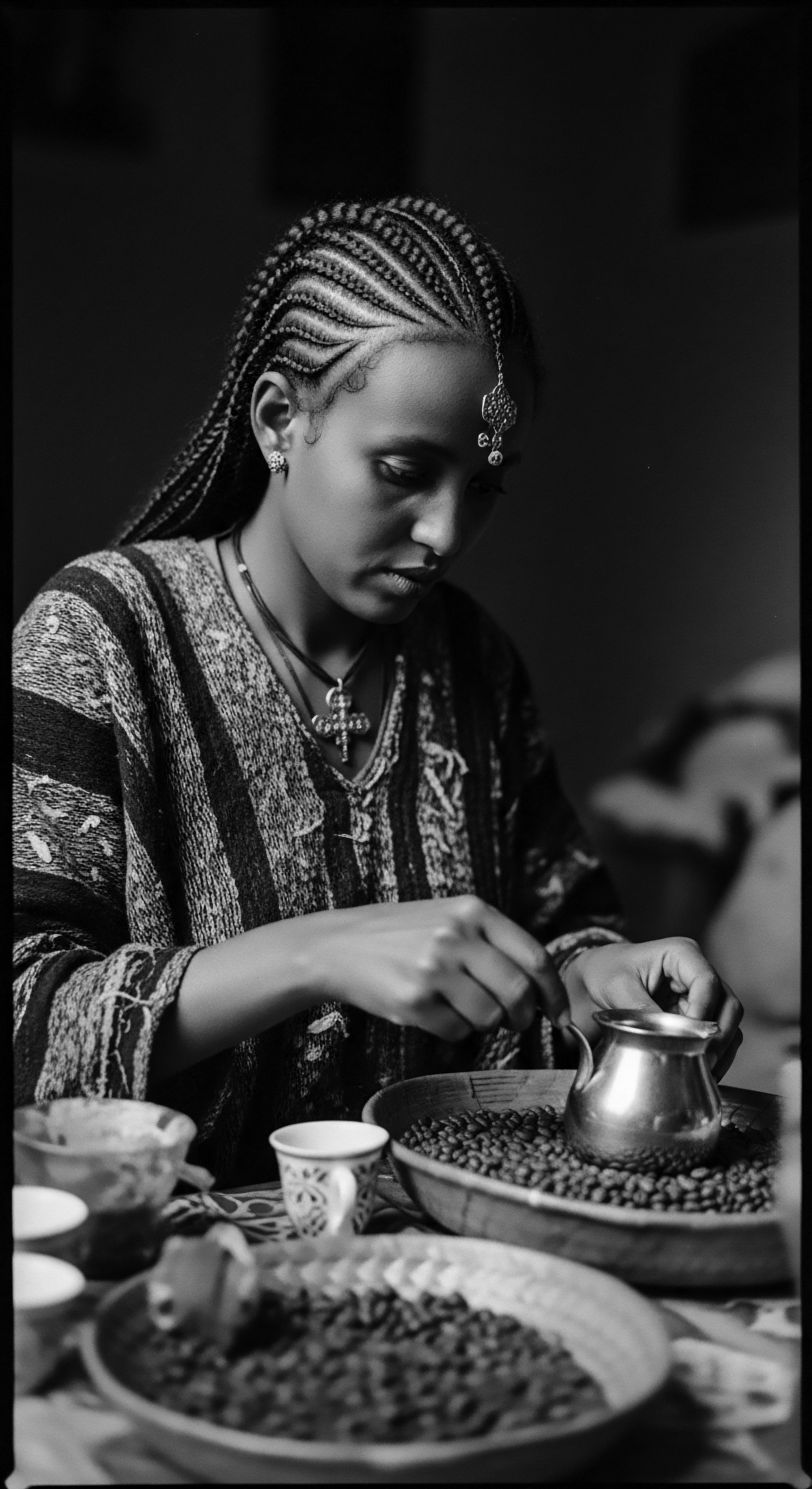

How Did Ancestral Communities Shield Textured Hair?
Ancestral communities shielded textured hair through protective styles, natural emollients, and coverings, deeply connecting to cultural heritage.

What Specific Ancestral Oils Benefit Textured Hair?
Ancestral oils like shea butter, coconut, red palm, and argan offer deep nourishment and protection, rooted in centuries of textured hair heritage.

What Is the Cultural Significance of Oiling Textured Hair?
Oiling textured hair signifies a profound connection to ancestral practices, embodying a heritage of care, cultural identity, and resilience.
In What Ways Did Braiding Communicate Heritage and Resistance during Slavery?
Braiding transformed textured hair into a discreet language, conveying heritage and vital messages of resistance for enslaved individuals.

African Diasporic Care
Meaning ❉ African Diasporic Care encompasses the historical and contemporary practices, wisdom, and communal rituals for nurturing textured hair.

How Did Ancient Styling Practices Influence Modern Hair Care?
Ancient styling practices profoundly shaped modern hair care by prioritizing protection and nourishment for textured hair, reflecting a living heritage.

In What Ways Did Braiding Become a Tool of Resistance during the Transatlantic Slave Trade?
Braiding was a profound act of resistance during the transatlantic slave trade, encoding escape maps and sustaining heritage.

Can the Scientific Properties of Textured Hair Explain Ancestral Braiding Practices?
Ancestral braiding practices intuitively leveraged textured hair's unique properties, like its coiling and elasticity, for protection and cultural expression.

What Role Did Hair Braiding Play in Resistance during Slavery?
Hair braiding became a clandestine tool, weaving vital information and cultural perseverance into acts of resistance.

What Ancestral Hair Practices Protected Strands through Generations?
Ancestral hair practices protected strands through generations by combining meticulous care, culturally significant styling, and potent natural ingredients.
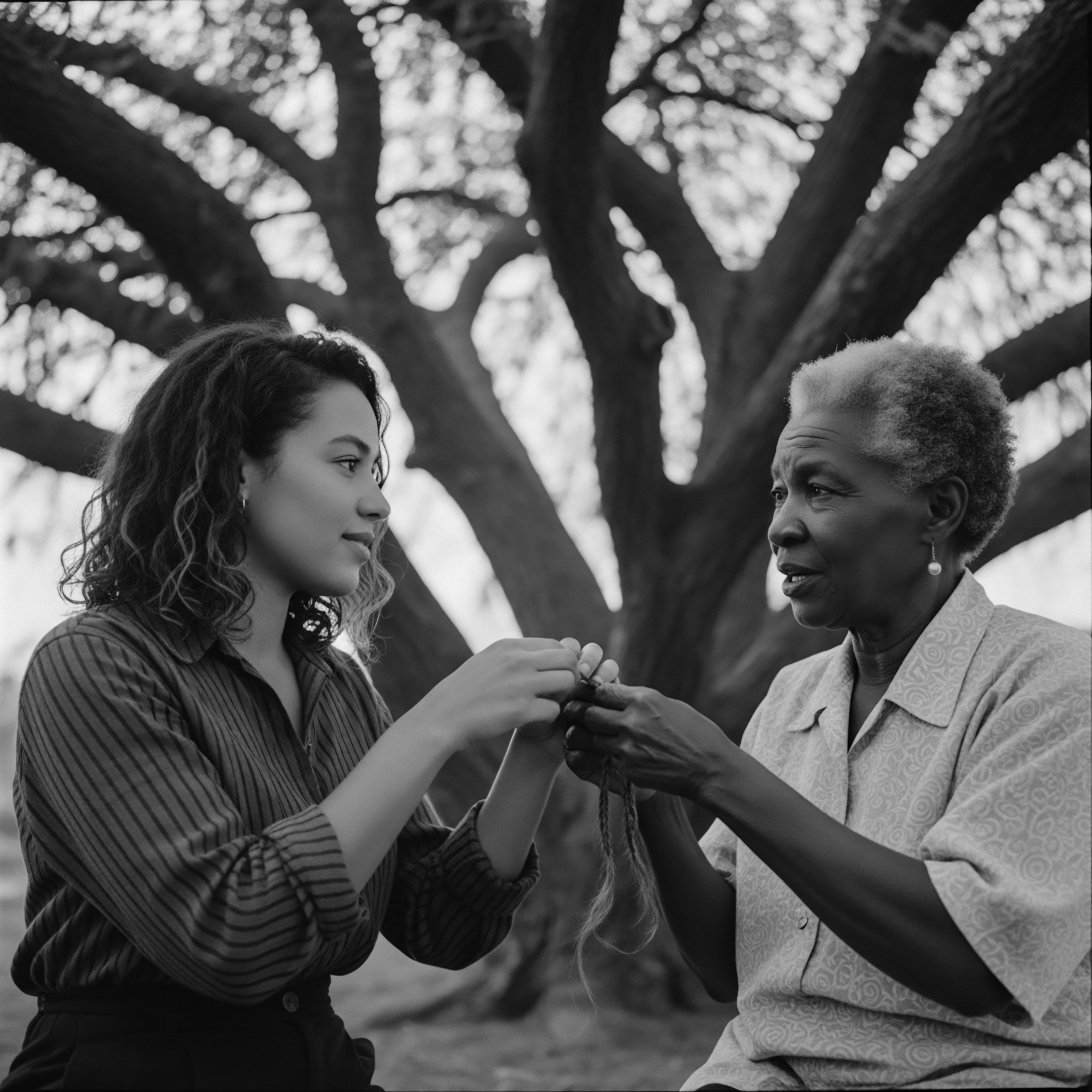

How Far Back Do Textured Hair Braiding Traditions Extend?
Textured hair braiding traditions extend back over 30,000 years, rooted in African heritage as markers of identity, communication, and spiritual connection.

In What Ways Did Protective Braiding Serve as a Means of Resistance during Enslavement?
Protective braiding during enslavement served as a vital, covert means of resistance, encoding escape routes and preserving cultural identity.

How Did Braiding Become a Resistance Act?
Braiding became a resistance act by silently preserving identity, communicating covert messages, and challenging oppressive beauty norms, rooted deeply in textured hair heritage.

Braiding Resistance
Meaning ❉ Braiding Resistance is the inherent strength and cultural defiance of textured hair, nurtured through ancestral braiding practices for protection and identity.

What Was the Role of Hair Braiding in Resistance during the Transatlantic Slave Trade?
Hair braiding served as a vital, covert system of communication and preservation of textured hair heritage during enslavement.
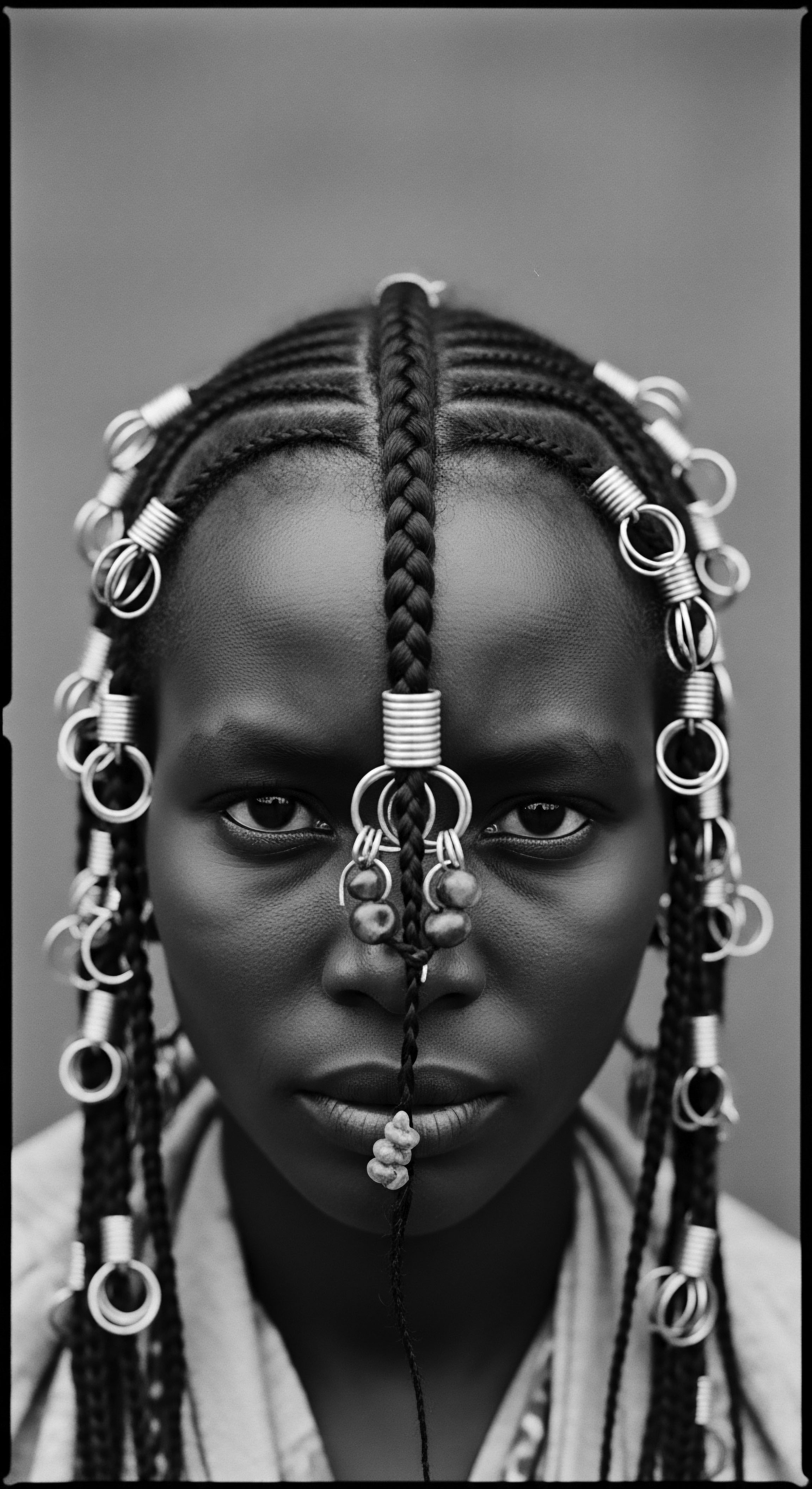

In What Ways Did Braiding Become a Tool for Resistance during Historical Oppression?
Braiding became a powerful tool of resistance during historical oppression, concealing escape routes and cultural heritage within textured hair.

What Ancient Practices Connect Deeply to Textured Hair’s Biological Heritage?
Ancient practices directly connect to textured hair's biological heritage through protective styling, natural ingredient use, and communal rituals that honored its unique structure and cultural significance.

Resistance Braiding
Meaning ❉ Resistance Braiding is a practice of interweaving hair, deeply rooted in ancestral wisdom, designed for protective care and cultural preservation of textured strands.
