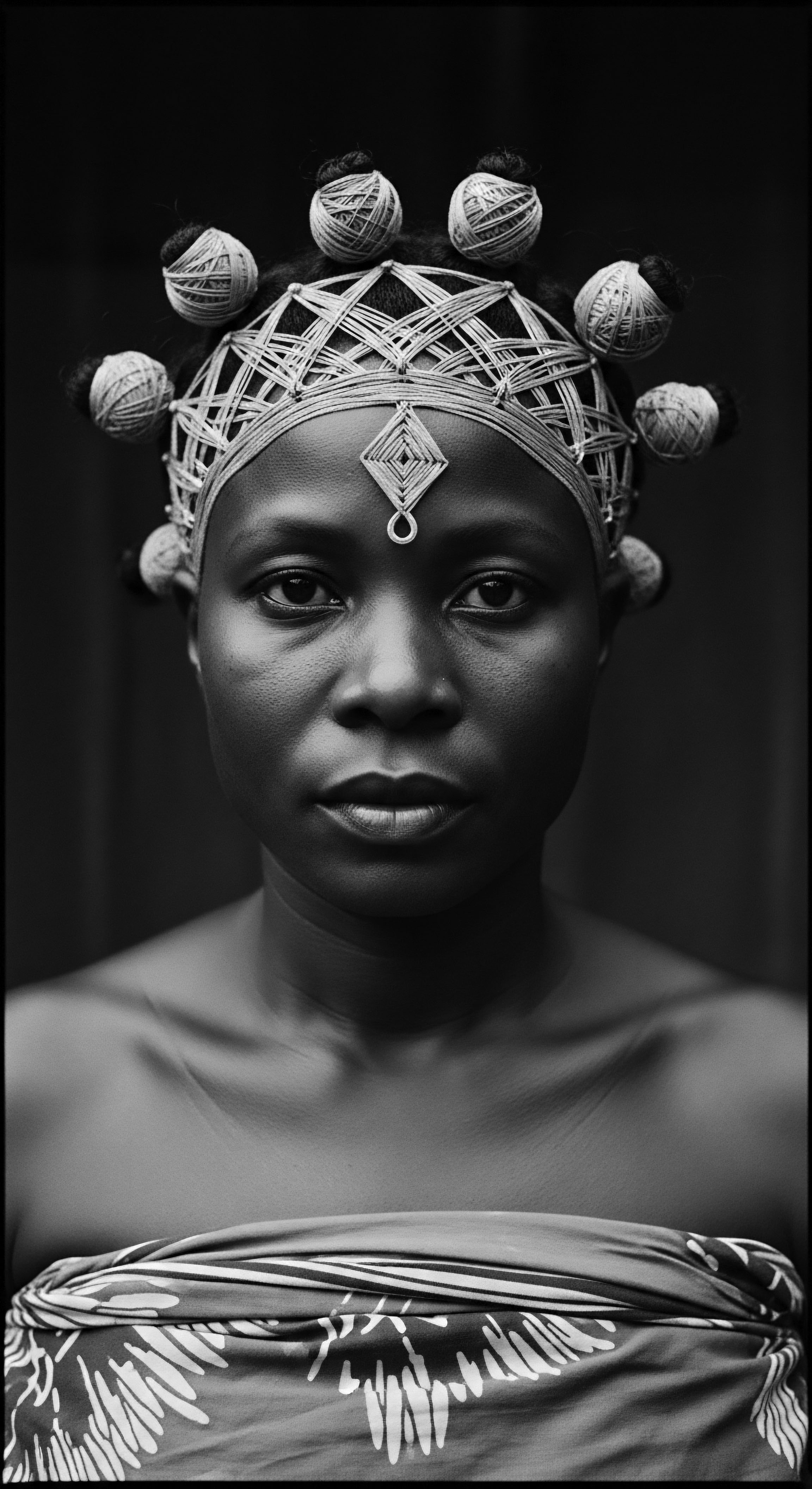
What Traditional African Terms Describe Textured Hair?
Traditional African terms for textured hair often signify its cultural role, spiritual connection, and unique physical characteristics, revealing a rich heritage.

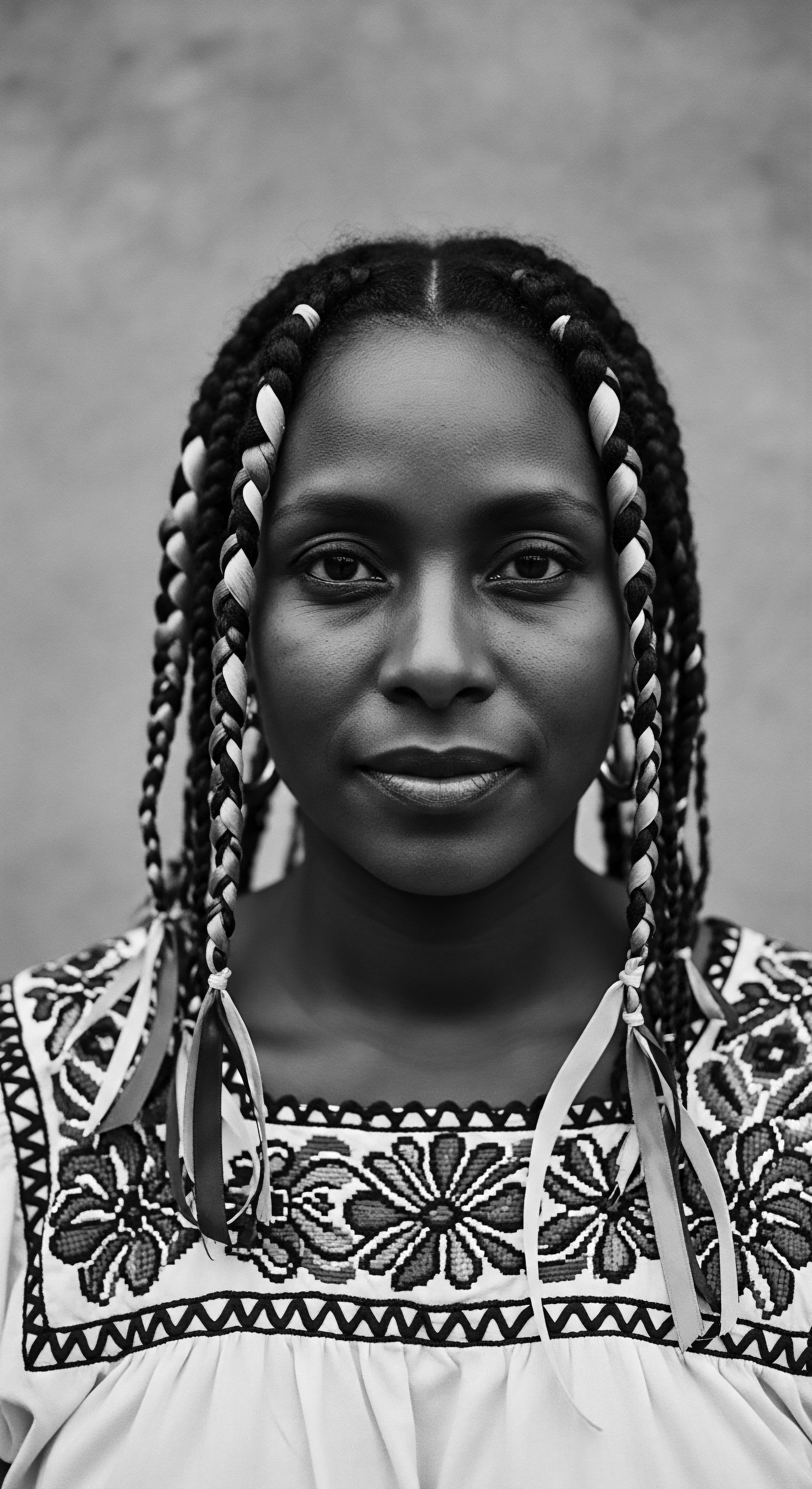
Can Understanding Hair Heritage Change Our Self-Perception?
Understanding hair heritage shifts self-perception, grounding personal identity in the rich history of textured hair and ancestral wisdom.

In What Ways Did Historical Textured Hair Practices Influence Cultural Identity?
Historical textured hair practices deeply influenced cultural identity by acting as social markers, spiritual links, and enduring symbols of resistance and belonging.

In What Ways Did Textured Hair Practices Serve as Resistance against Oppression?
Textured hair practices served as resistance by covertly communicating defiance, asserting cultural heritage, and affirming selfhood against oppressive forces.

What Historical Nutrient Deficiencies Weakened Textured Hair?
Historical nutrient deficits, stemming from disrupted ancestral foodways, significantly weakened textured hair, a legacy still resonant in its heritage and care.
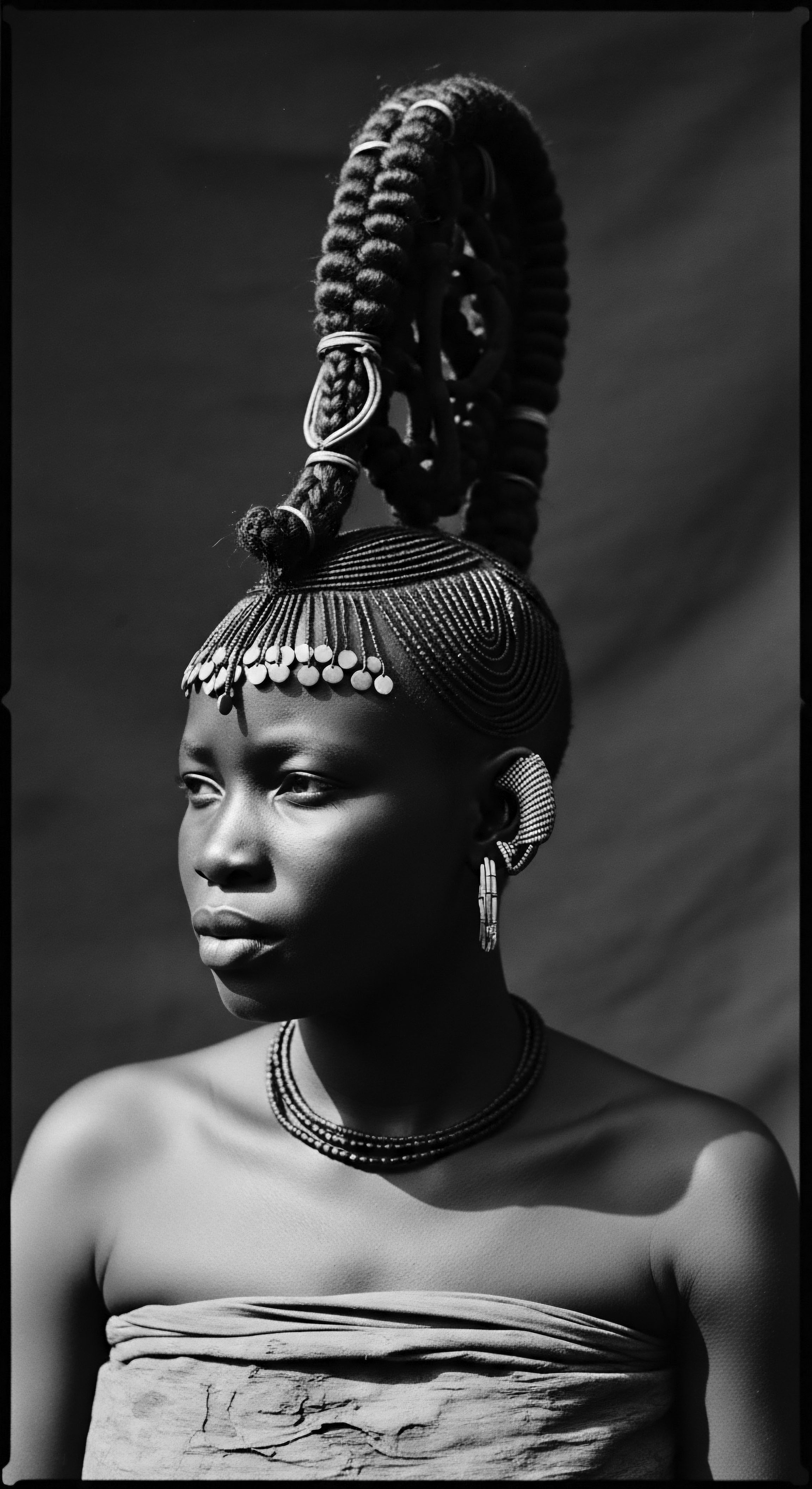

Kabbalah Hair Meaning
Meaning ❉ Kabbalah Hair Meaning interprets hair, especially textured hair, as a sacred conduit for ancestral wisdom, spiritual energy, and personal identity.
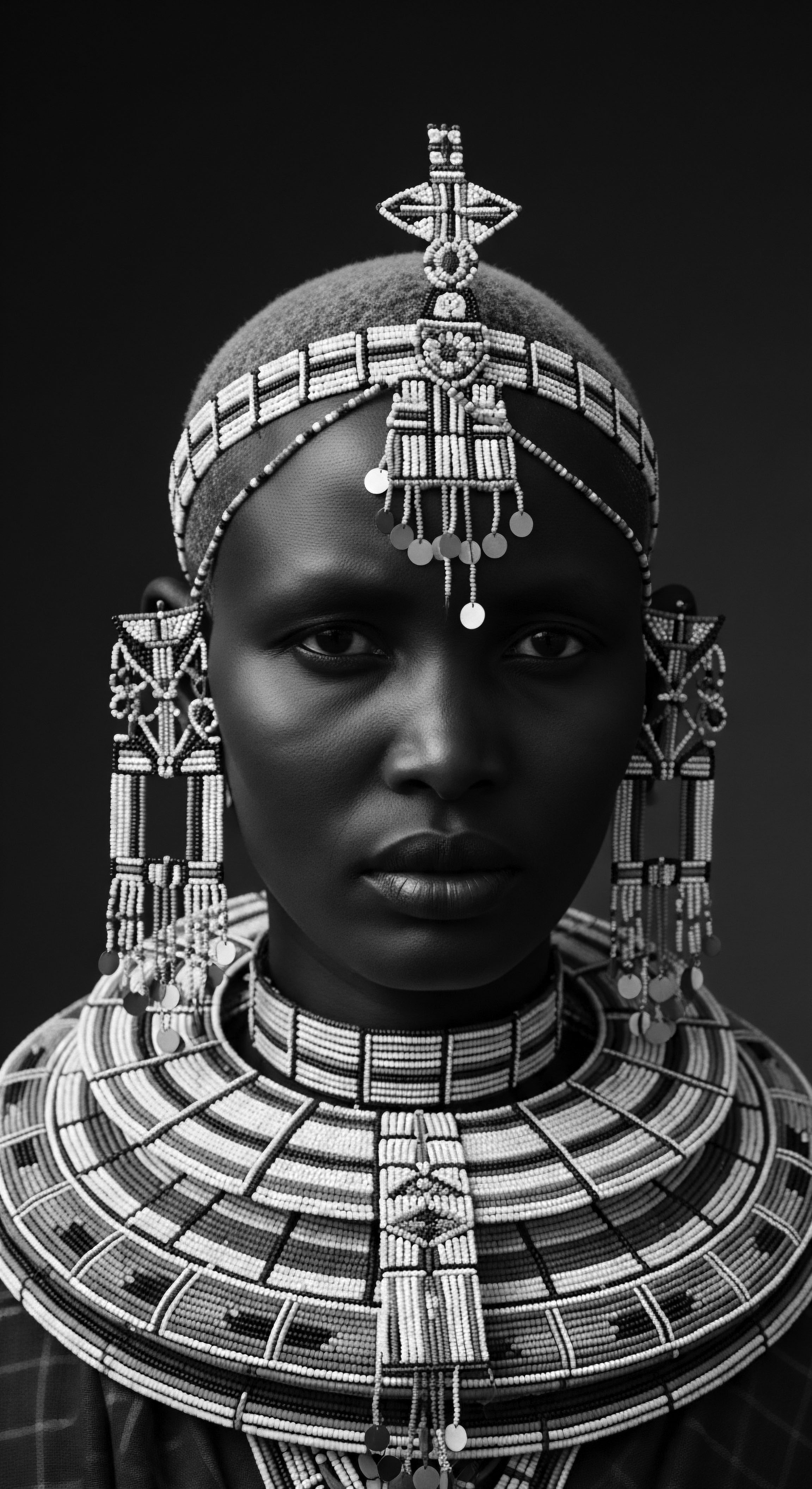

How Does Textured Hair Heritage Connect to Cultural Identity?
Textured hair heritage profoundly links to cultural identity through ancestral practices, historical resistance, and communal wellbeing.
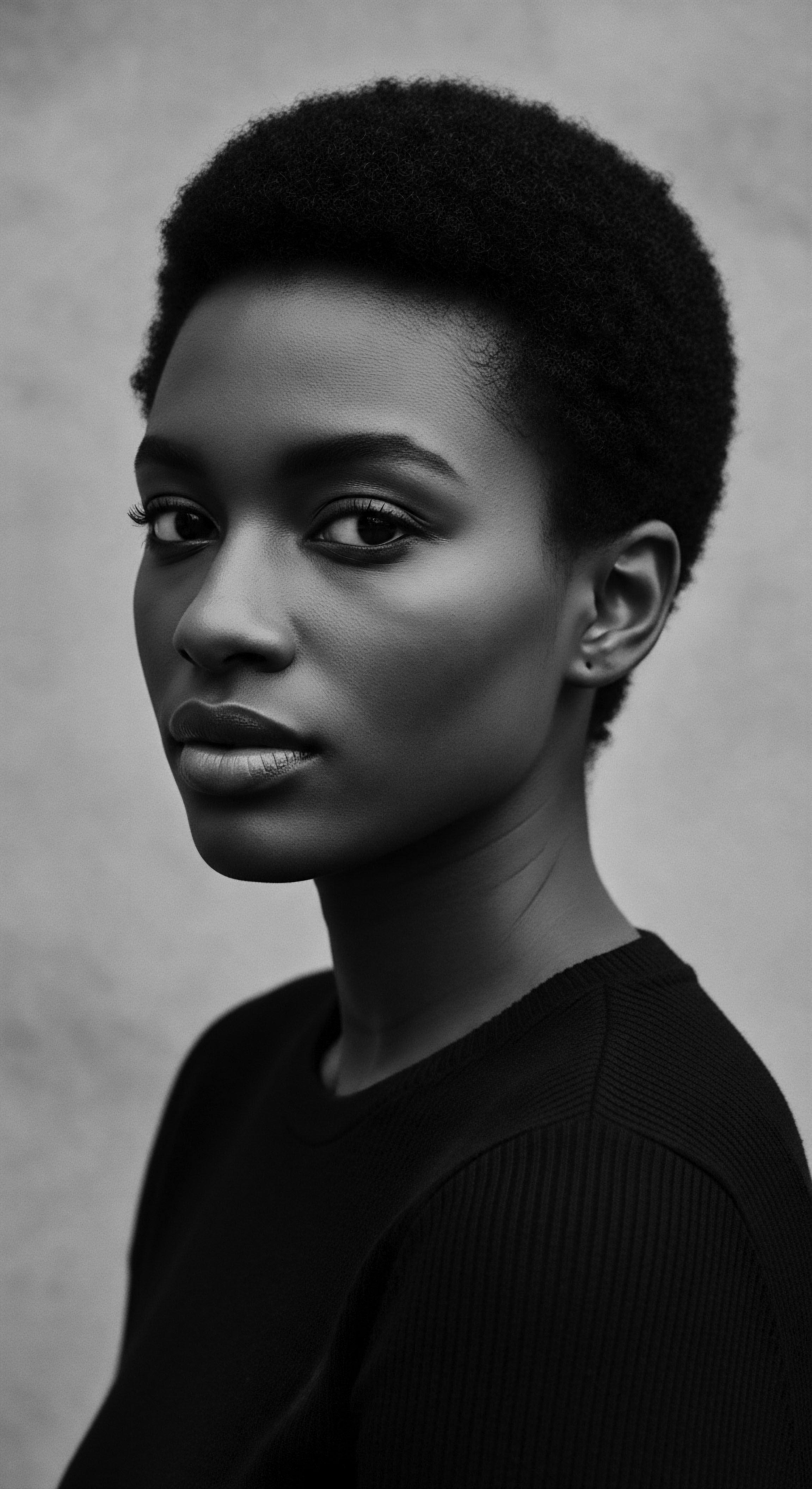
How Does Hair Texture Connect to African Heritage?
Hair texture directly connects to African heritage, serving as a profound marker of identity, resilience, and ancestral wisdom.
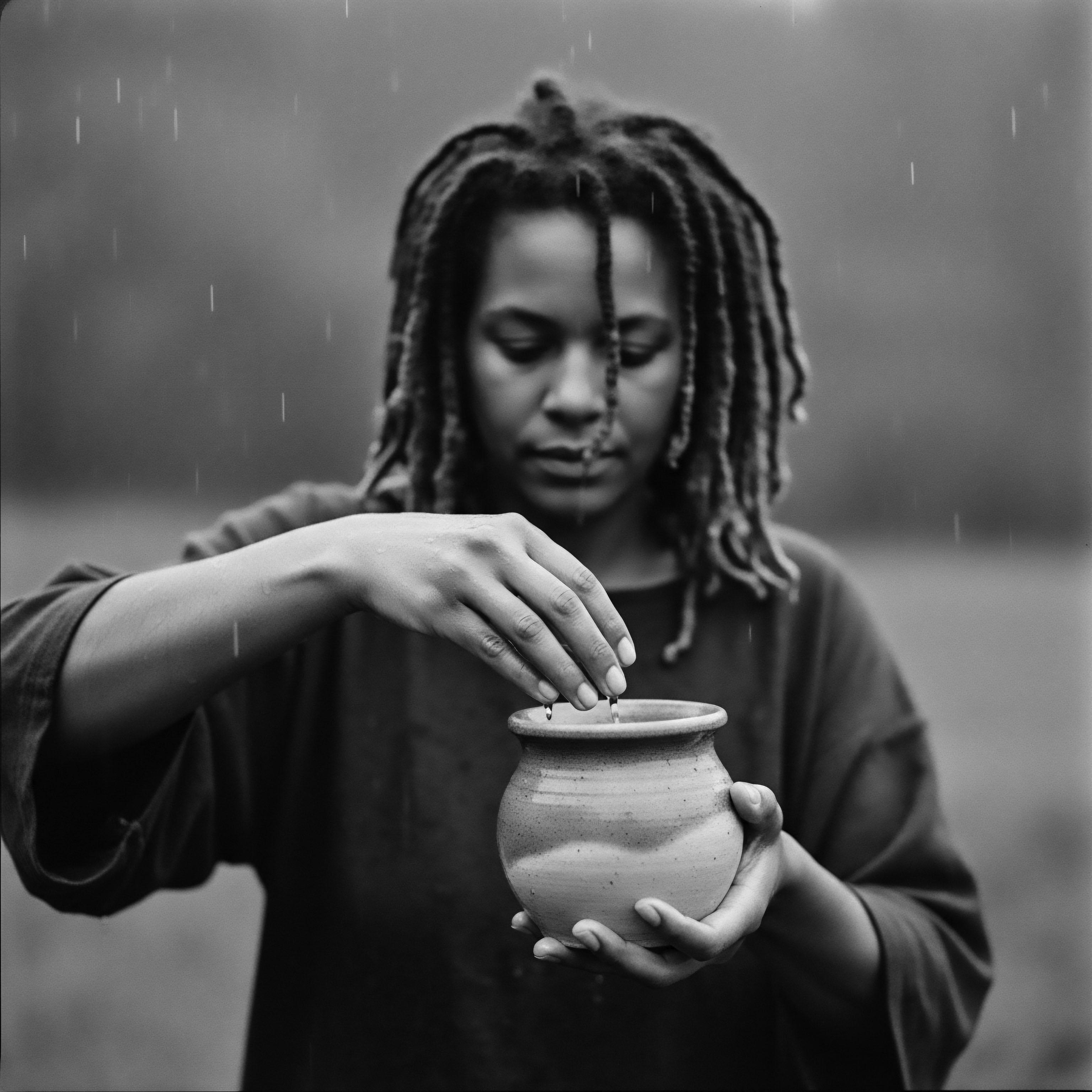

How Does Hair Texture Link to Ancient African Cultures?
Textured hair’s profound link to ancient African cultures embodies a living heritage of identity, communication, and resilience.
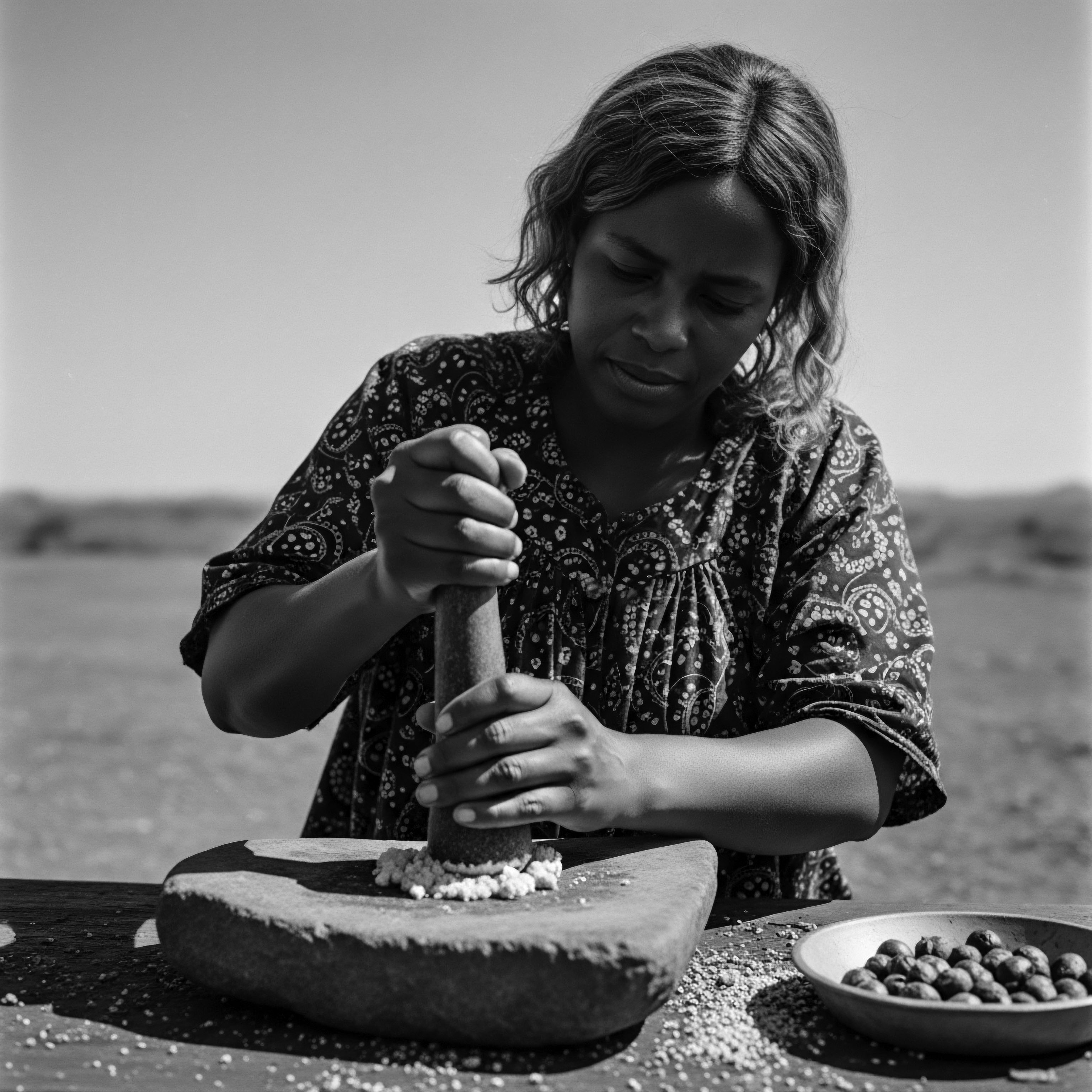

What Is the Ancestral Meaning of Hair Tools in African Heritage?
Ancestral African hair tools embody heritage, acting as conduits for cultural transmission, identity markers, and symbols of enduring resilience.

Can Textured Hair Care Heal Generational Trauma?
Textured hair care offers a pathway to heal generational trauma by reclaiming heritage, fostering self-acceptance, and celebrating cultural identity.

What Is the Biological Basis of Textured Hair’s Adaptation?
Textured hair’s biology adapted in equatorial Africa for protection and water conservation, intrinsically linking its heritage to survival.

What Is the Long-Term Impact of CROWN Act on Student Identity and Well-Being?
The CROWN Act protects textured hair in schools, affirming student identity and well-being rooted in cultural heritage.

How Did Headwraps Become a Symbol of Cultural Resilience and Ancestral Connection?
Headwraps embody cultural resilience and ancestral connection by protecting textured hair, communicating heritage, and symbolizing resistance.

What Historical Acts of Resistance Involved Hair Practices?
Historical acts of resistance involving hair practices allowed enslaved and oppressed communities to preserve identity and communicate defiance.

How Did Ancient African Hair Practices Influence Identity?
Ancient African hair practices deeply informed identity, signaling status, spirituality, and lineage within textured hair heritage.
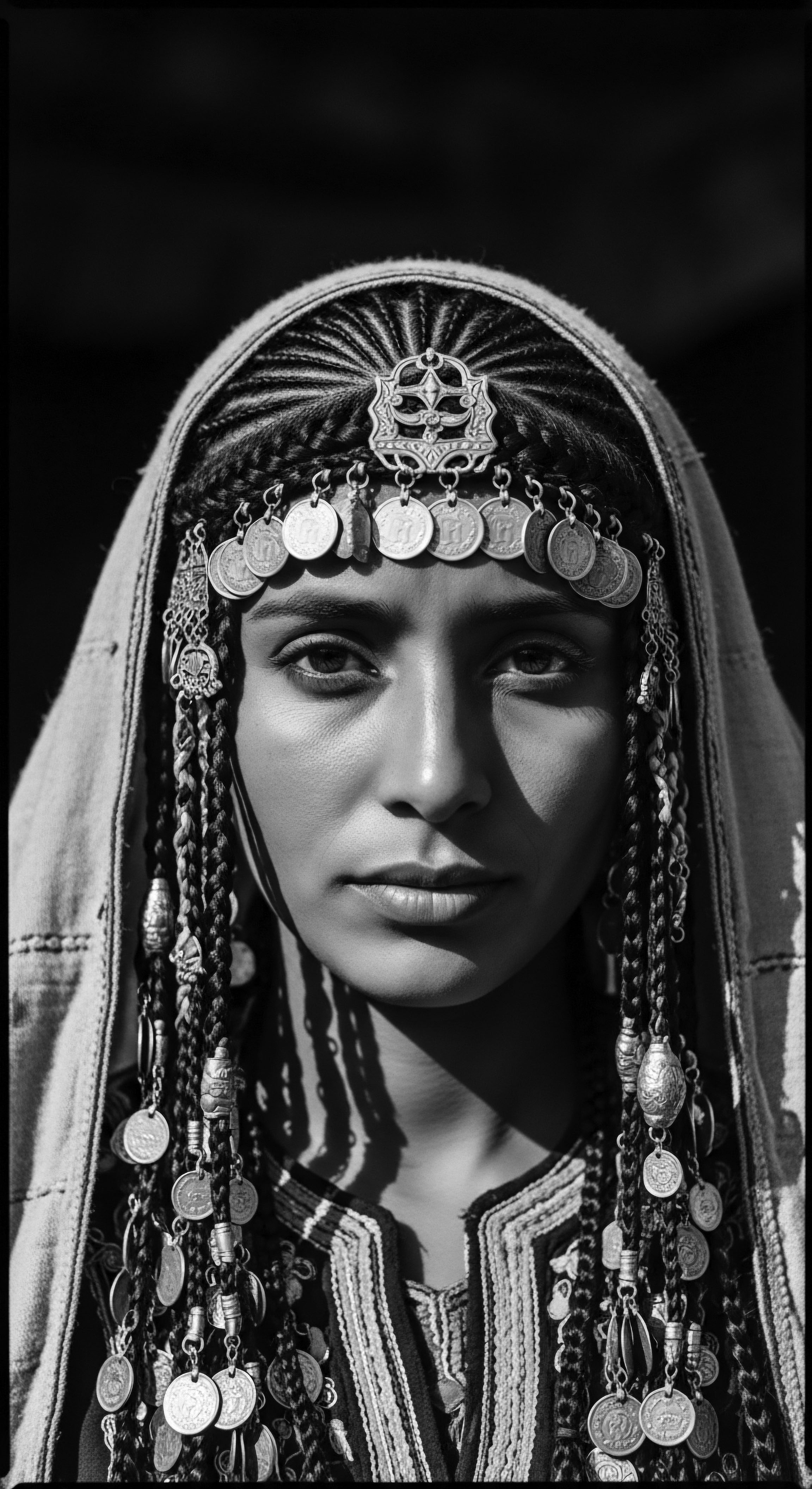

What Historical Connections Exist between Textured Hair and Community Identity?
Textured hair's historical connections to community identity are rooted in ancient African communication and resilience.

In What Ways Did Ancient Plants Contribute to Textured Hair Moisture from a Heritage Viewpoint?
Ancient plants provided crucial moisture to textured hair through their humectant, emollient, and protective properties, rooted in ancestral heritage and cultural practices.

In What Ways Did Ancient African Hair Practices Influence Community Identity and Spiritual Connection?
Ancient African hair practices were intrinsic to communal identity and spiritual connection, signifying status, age, and ancestral ties.
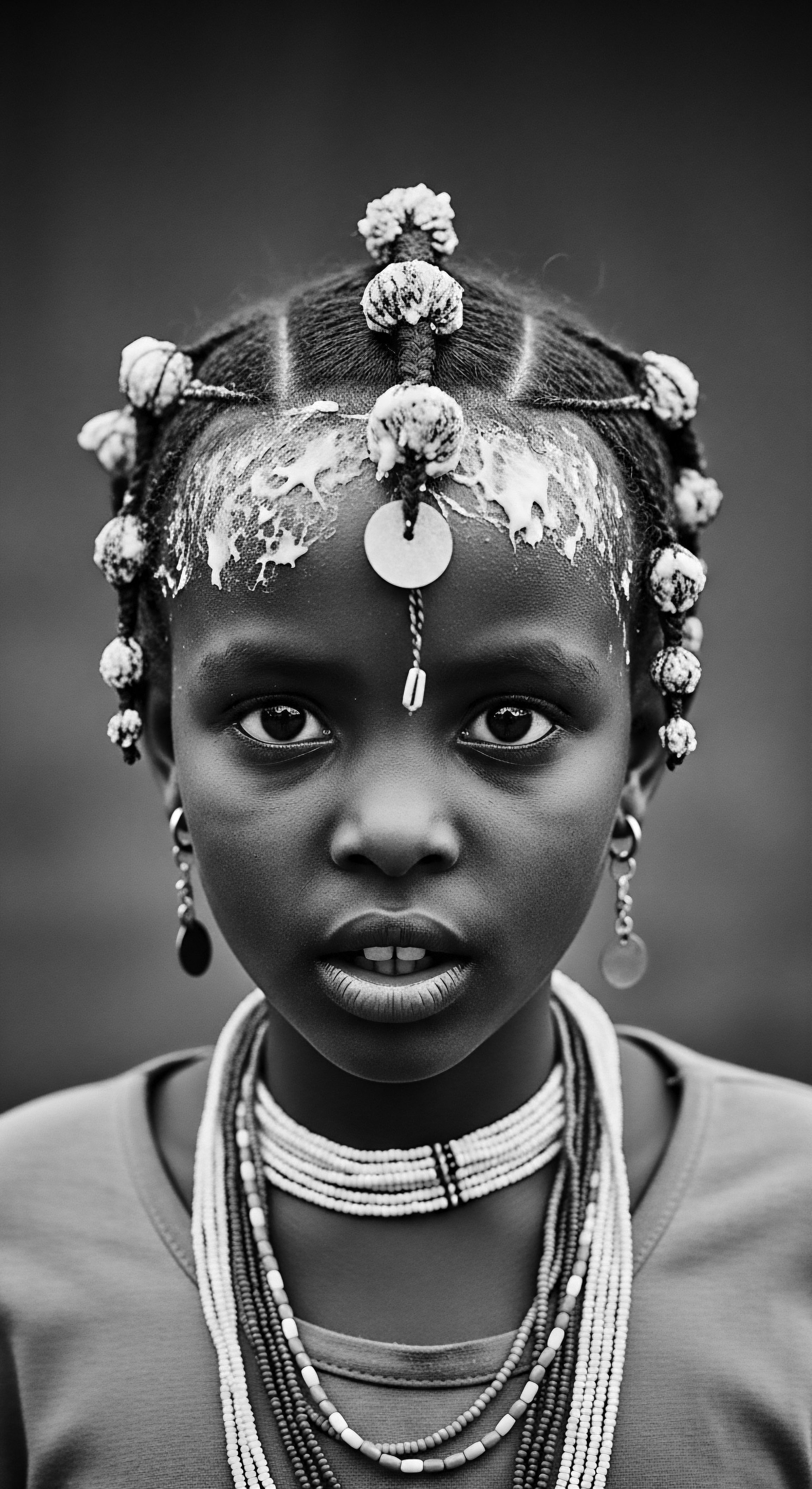

What Historical Communication Was Possible through Braided Hair?
Braided hair served as a deep communicative system, conveying identity, status, spiritual beliefs, and even hidden escape routes, profoundly connecting to textured hair heritage.

How Did Ancient African Hair Practices Reflect Community Bonds?
Ancient African hair practices were intimate communal acts, building profound social ties and preserving ancestral identity through shared rituals.

In What Ways Did Enslaved Communities Use Braids for Resistance and Communication?
Enslaved communities used braids as covert maps and carriers of vital provisions, a testament to enduring textured hair heritage and silent resistance.

What Historical Role Did Textured Hair Play in Social Identity?
Textured hair historically conveyed social standing, spiritual connection, and tribal belonging, later becoming a profound symbol of resilience and heritage.

What Roles Did Textured Hair Customs Play in Cultural Resistance during Enslavement?
Textured hair customs served as covert communication, identity preservation, and a profound act of cultural resistance during enslavement.
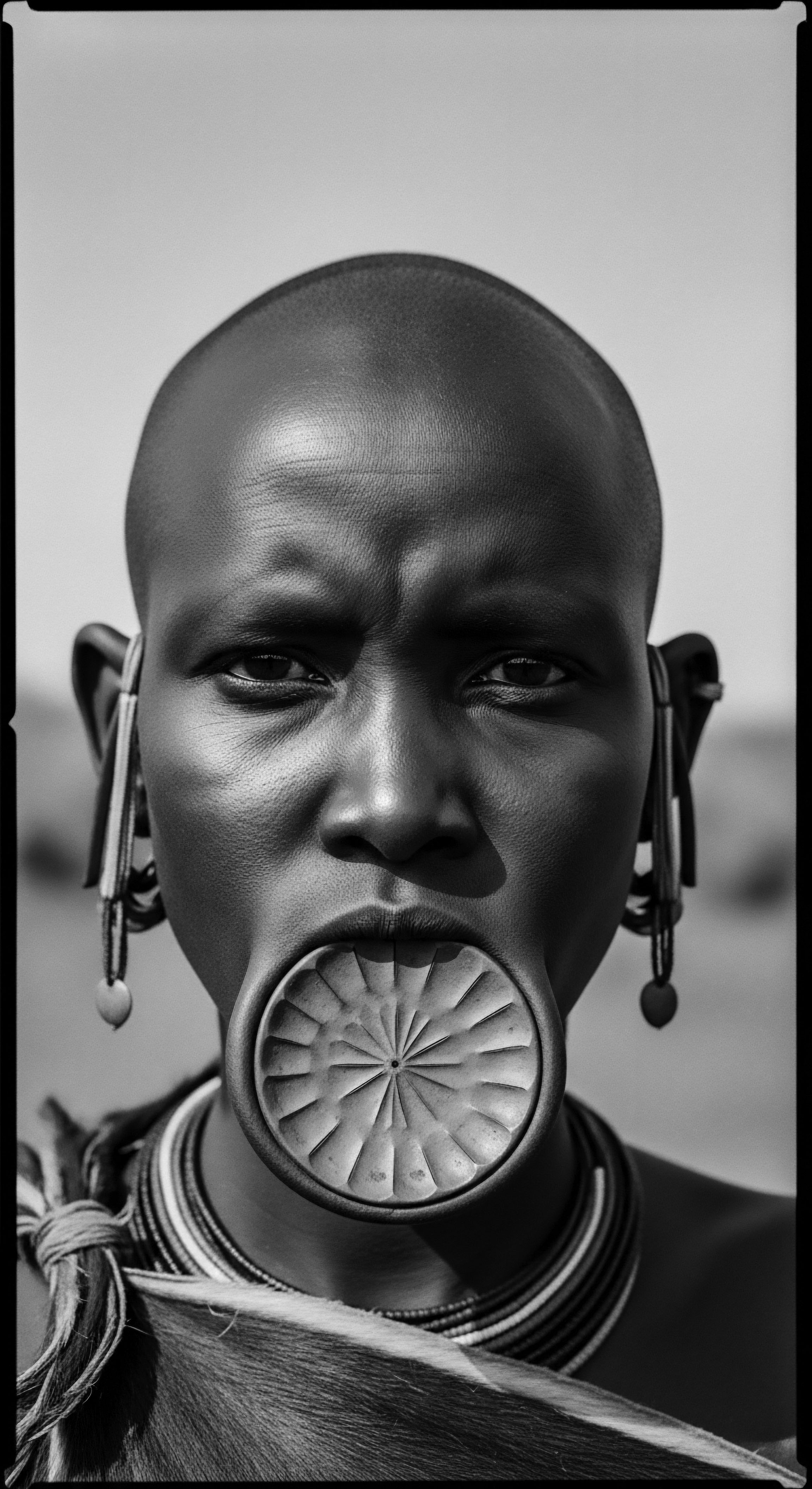

How Did Textured Hair Styles Symbolize Identity across African Cultures?
Textured hair styles in African cultures symbolized social status, spiritual beliefs, and tribal identity, deeply rooting individuals in their heritage.
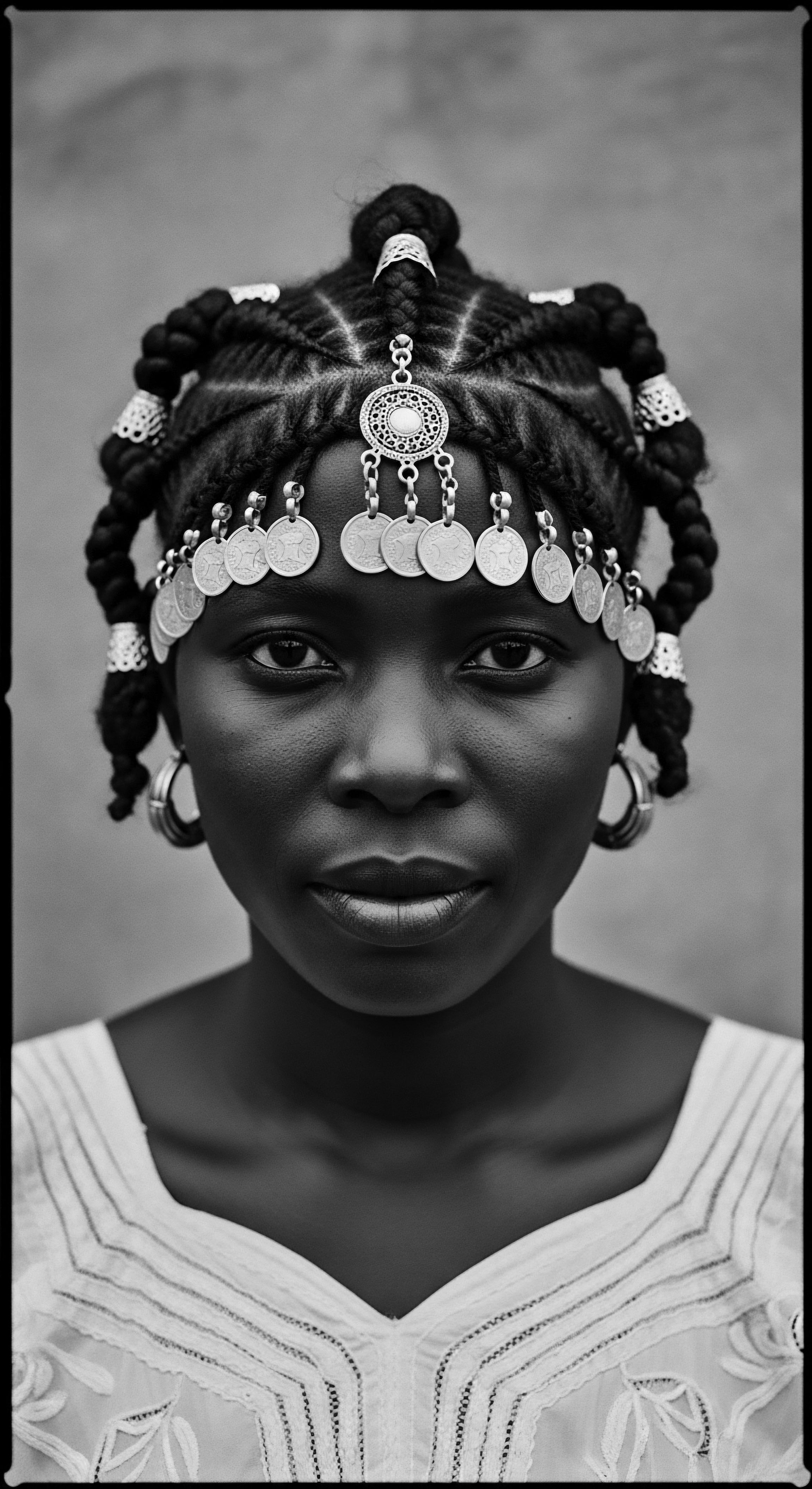

In What Ways Did Braids Symbolize Social Standing in African Heritage?
Braids in African heritage conveyed diverse social standings, from age and marital status to wealth and spiritual roles, embodying a rich cultural lexicon.
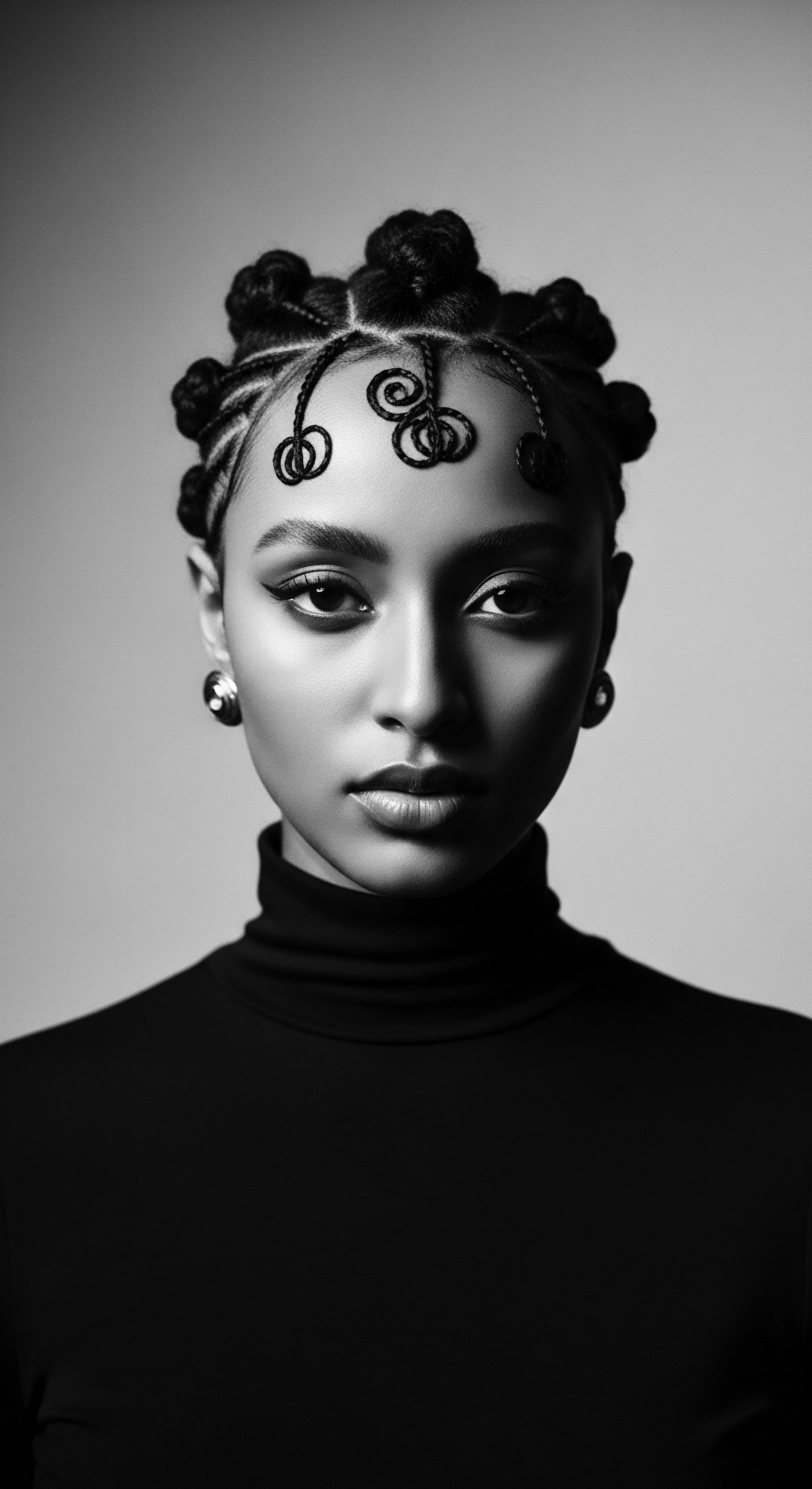

What Traditional Roles Did African Hairstyles Signify?
African hairstyles served as a complex language, communicating social status, age, spiritual beliefs, and tribal identity, deeply connected to textured hair heritage.

What Historical Meanings Did Braided Patterns Convey in African Societies?
African braided patterns historically conveyed identity, status, and spiritual beliefs, becoming powerful symbols of textured hair heritage.
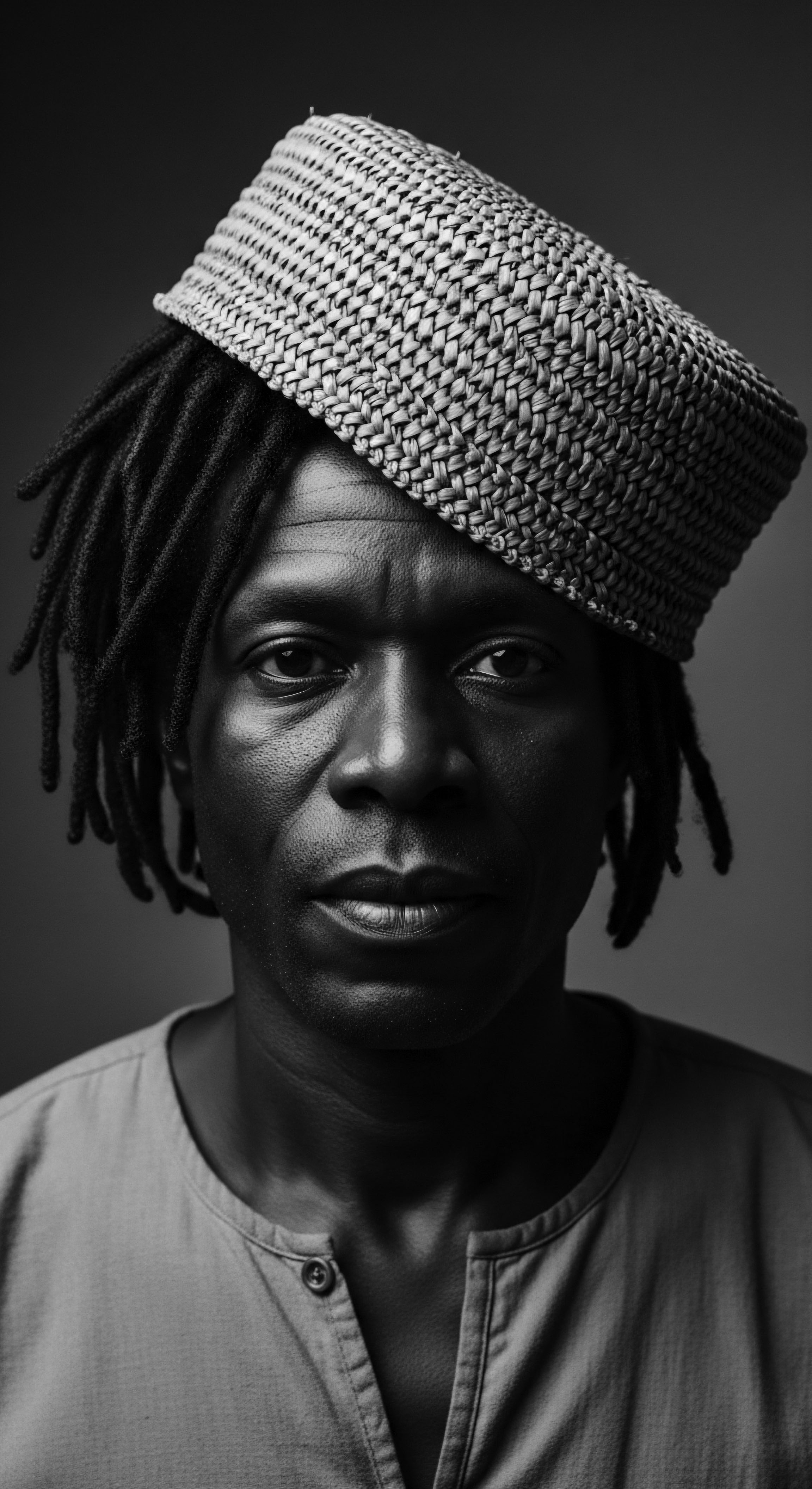

What Enduring Cultural Meanings Are Embedded in African Hair Covering Practices and Materials?
African hair coverings embody a rich heritage of identity, status, spirituality, and resistance, reflecting the profound cultural meanings woven into textured hair.

