
What Historical Examples Show Botanical Efficacy for Textured Hair Heritage?
Historical botanical examples show plants like shea butter, rhassoul clay, and Chebe powder effectively nourished and protected textured hair.

What Ancestral Hair Care Practices from Kemet Influence Today’s Textured Hair Heritage?
Kemetian hair practices continue to shape textured hair heritage through protective styles, natural ingredient use, and holistic wellness.

Are Traditional Oiling Methods Scientifically Supported for Textured Hair?
Traditional oiling methods for textured hair align with scientific understanding of moisture retention and protein protection, honoring ancestral heritage.

Head Elongation
Meaning ❉ Head Elongation describes the hair fiber's natural stretch and the cultural practices that reveal and preserve the visible length of textured hair.

Diaspora Challenges
Meaning ❉ Diaspora Challenges represent the historical and ongoing struggles for identity and self-expression faced by dispersed communities, acutely visible in the experiences of textured hair.

Mau Mau Resistance Hair
Meaning ❉ Mau Mau Resistance Hair is the defiant cultivation of natural, loc'd hair by Kenyan freedom fighters against colonial rule, symbolizing identity and liberation.
African Bereavement
Meaning ❉ African Bereavement is the culturally specific and deeply ritualized process of mourning and loss, intricately tied to hair symbolism and identity.

What Natural Ingredients from Ancient Practices Condition Textured Hair?
Ancient traditions used natural ingredients like shea butter and plant oils to condition textured hair, rooted in heritage.

How Do Historical Styling Practices Inform Modern Textured Hair Care?
Historical styling practices inform modern textured hair care by providing a heritage of protective methods and natural ingredients.

Why Did Ancient Protective Styles Become so Important for Textured Hair?
Ancient protective styles became vital for textured hair by meeting biological needs, preserving heritage, and serving as cultural expressions.

Why Was Head Covering Important in African Heritage?
Head covering in African heritage signified identity, protection, and spiritual connection for textured hair.

What Ancestral Styling Techniques Supported Textured Hair Health and Heritage?
Ancestral styling techniques focused on gentle protective methods, natural ingredients, and holistic well-being to sustain textured hair health and honor heritage.

Ebers Papyrus Hair
Meaning ❉ A unique designation for ancient Egyptian hair wisdom, reflecting documented care practices and their lasting influence on textured hair heritage.

What Types of Clay Were Traditionally Used for Textured Hair?
Traditional textured hair care often used clays like rhassoul, bentonite, and kaolin for cleansing, conditioning, and cultural adornment.

Can Jamaican Black Castor Oil Benefit Fine Textured Hair?
Jamaican Black Castor Oil, deeply rooted in textured hair heritage, may aid fine strands by improving scalp health and strengthening delicate fibers.
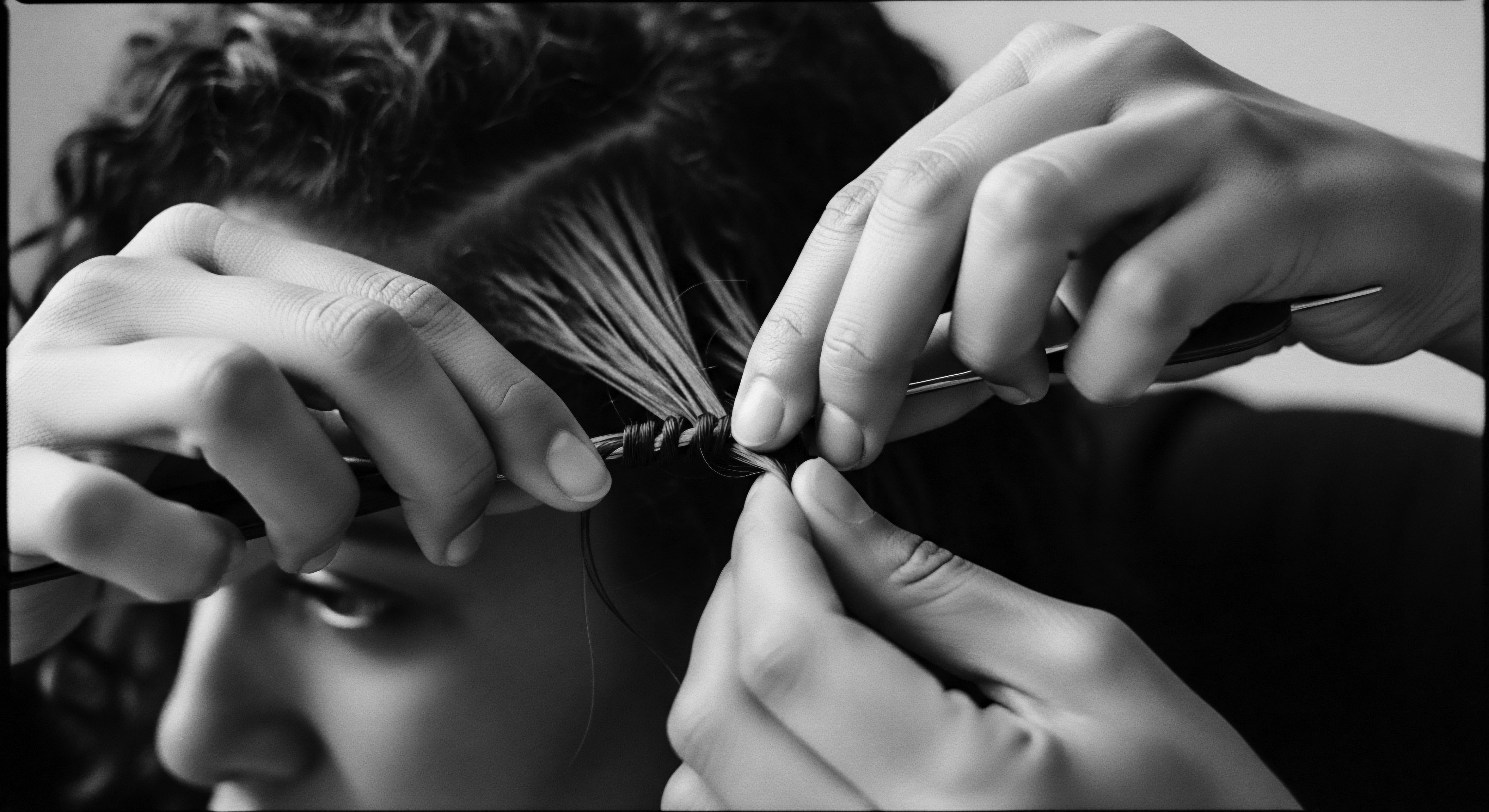

How Do Traditional Braiding Techniques Support Modern Textured Hair Health and Growth?
Traditional braiding secures textured hair, reducing manipulation and breakage, directly supporting health and length through inherited protective heritage.

Head Shape
Meaning ❉ Head shape denotes the skull's contours and its integral connection to hair biology, ancestral practices, and cultural identity.

What Mineral Components Allow Earth-Derived Products to Cleanse Textured Hair?
Earth's mineral components, rooted in ancestral practices, gently cleanse textured hair by drawing out impurities and honoring its natural structure.

Bacuri Oil
Meaning ❉ Bacuri Oil is a nourishing lipid from Amazonian seeds, prized for its unique absorption and heritage in textured hair care traditions.

What Scientific Insights Align with Historical Textured Hair Oiling Rituals?
Historical textured hair oiling rituals align with modern science by deeply nourishing the scalp, fortifying strands, and protecting unique curl patterns, all rooted in ancestral wisdom.

How Did Ancient Practices Shape Textured Hair Ideals?
Ancient practices shaped textured hair ideals by embedding deep cultural, spiritual, and communal meanings within each strand's heritage.

How Did Ancient Hair Braiding Techniques Connect to Cultural Heritage?
Ancient hair braiding connected to cultural heritage by conveying identity, social status, and spiritual beliefs, preserving ancestral knowledge for textured hair communities.

What Historical Biases Does Hair Discrimination Legislation Counter for Textured Hair?
Hair discrimination legislation counters historical biases that devalued textured hair, affirming its connection to Black and mixed-race heritage.

Friction Protection
Meaning ❉ Strategies to minimize abrasive forces on hair strands, deeply rooted in the cultural and biological heritage of textured hair.

How Does Black Hair Heritage Reflect Spiritual Resilience?
Black hair heritage embodies spiritual resilience through ancestral practices, cultural resistance, and its deep connection to identity.

Shanivar Teli
Meaning ❉ Shanivar Teli denotes the Bene Israel, historically oil-pressers, whose Sabbath observance links to universal heritage of hair oiling and care.

Landy Silk Heritage
Meaning ❉ The Landy Silk Heritage recognizes silk's historical and ongoing role in protecting and honoring textured hair, rooted in ancestral wisdom and cultural continuity.

What Is the Cultural Meaning of Headwraps for Textured Hair Heritage?
Headwraps for textured hair represent a profound cultural legacy, weaving together practical care, ancestral resistance, and vibrant identity.

Ancient Henna
Meaning ❉ Ancient Henna defines the historical botanical dye from Lawsonia inermis, a cornerstone of ancestral hair care and cultural identity.

