
How Does Shea Butter’s Heritage Connect to Economic Autonomy for Women?
Shea butter’s heritage, deeply woven into textured hair care, provides a pathway to women's economic autonomy through traditional practices and cooperative ventures.

Why Do Headwraps Protect Textured Hair?
Headwraps safeguard textured hair by reducing friction and maintaining moisture, continuing a deep ancestral tradition of care.

Why Is Hair Culturally Significant in African Heritage?
African hair’s significance stems from its historical role in identity, status, spirituality, and a living connection to heritage.

Lukasa Memory Boards
Meaning ❉ The Lukasa Memory Board is a Luba mnemonic device, a tactile artifact encoding complex historical and cultural narratives.

How Does Shea Butter Support Textured Hair Heritage?
Shea butter supports textured hair heritage by providing ancestral moisture and protection, connecting modern care to ancient African traditions.

Kilongo Headrests
Meaning ❉ The Kilongo Headrests are sculpted tools, predominantly from the Luba people, symbolizing ancestral heritage, social identity, and hair protection.

African Hair Cleansers
Meaning ❉ African Hair Cleansers signify traditional, often plant-based, methods and materials used for purifying textured hair, deeply rooted in heritage and community.

Ancient African Botanicals
Meaning ❉ Ancient African Botanicals represent a profound repository of plant-based wisdom and practices integral to textured hair heritage and holistic wellness.

Can Ancestral Oils Protect Textured Hair from Damage?
Ancestral oils, rooted in heritage, form a protective barrier for textured hair, reducing damage and honoring centuries of care traditions.

Hair Donation
Meaning ❉ Hair donation is the offering of one's hair to create wigs for those experiencing hair loss, deeply rooted in traditions of communal care and identity.

What Traditional Plant Remedies Are Still Relevant for Textured Hair Today?
Traditional plant remedies, rooted in ancestral wisdom, offer textured hair profound nourishment, strength, and a vibrant connection to heritage.

What Historical Moments Shaped Textured Hair Resilience?
Historical moments, from ancient reverence to acts of resistance and legislative triumphs, have profoundly shaped textured hair's heritage.

Miskito Hair
Meaning ❉ Miskito Hair defines the diverse hair textures and cultural care practices stemming from the Miskito people's Indigenous and African heritage.

Luba Sculpture
Meaning ❉ Luba Sculpture represents a profound artistic tradition from Central Africa, where intricate hairstyles convey identity, status, and spiritual connections within cultural heritage.
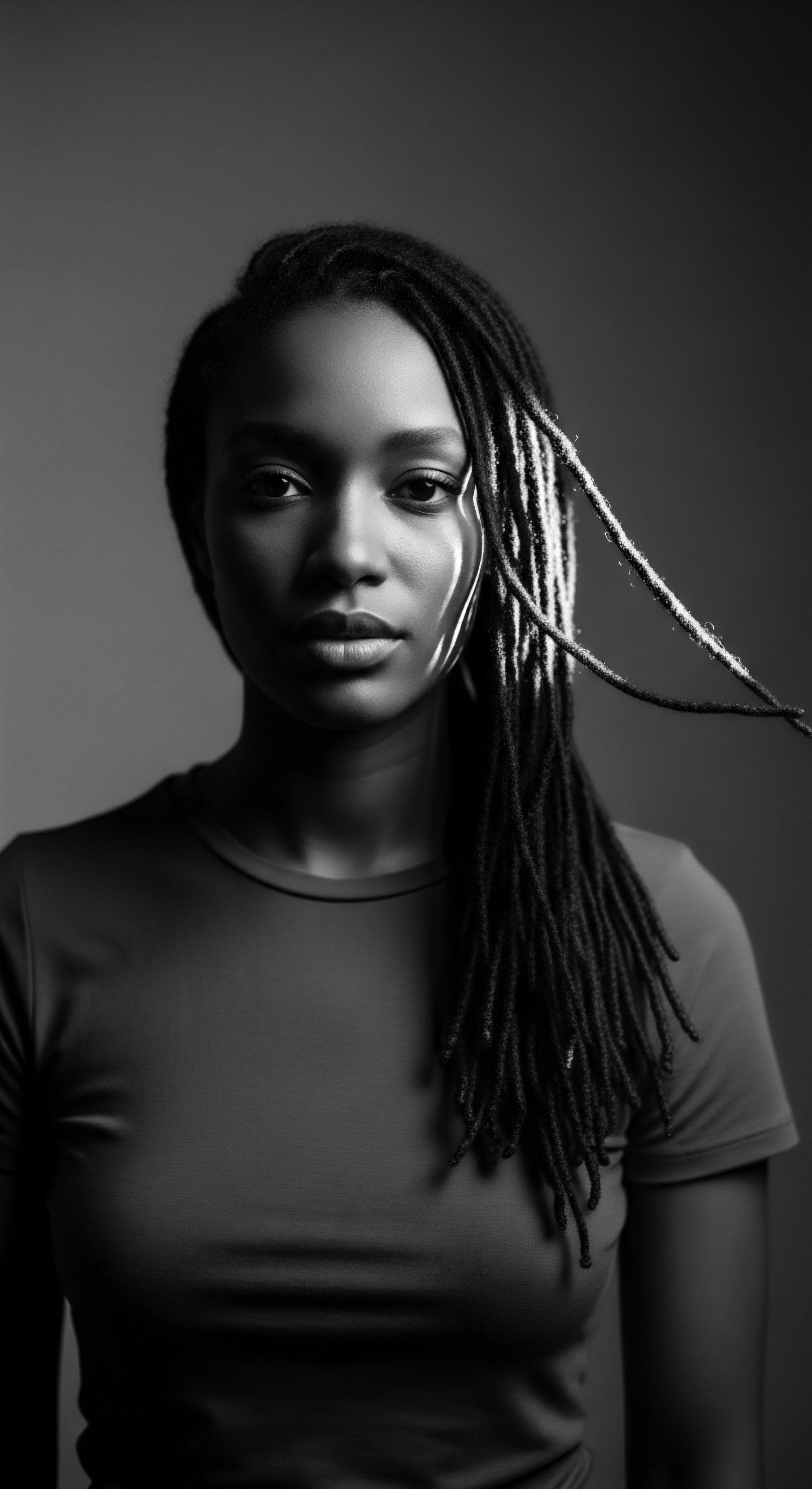
What Historical Role Does Shea Butter Play in Textured Hair Care?
Shea butter holds a deep historical role in textured hair care, rooted in ancestral African practices for protection and nourishment.

How Did Kemetian Hair Practices Relate to African Heritage?
Kemetian hair practices, deeply intertwined with African heritage, showcased intricate styling, ritual care, and symbolic adornment.

Can Shea Butter Help with Textured Hair Breakage and Scalp Health?
Shea butter, deeply rooted in West African heritage, helps textured hair breakage and scalp health by providing moisture, soothing irritation, and strengthening strands.

What Traditional African Practices Maintained Textured Hair Health and Moisture?
Traditional African practices used natural ingredients and protective styles to maintain textured hair health and moisture, honoring heritage.

Maroons Hair Care
Meaning ❉ Maroons Hair Care defines the ancestral, plant-based hair practices of Maroon communities, embodying cultural resilience and deep heritage.

Afro-Descendant Identity
Meaning ❉ Afro-Descendant Identity is a profound declaration of ancestral connection, rooted in history, culture, and the unique heritage of textured hair.

What Traditional Ingredients Hold Scientific Promise for Textured Hair?
Traditional ingredients offer scientifically backed benefits for textured hair, rooted in ancestral practices of moisture, strength, and scalp health.

What Is the Evolutionary Significance of Textured Hair for Sun Defense?
Textured hair's unique structure, particularly tight coils, evolved in equatorial Africa to shield the scalp from intense solar radiation, aiding brain thermal regulation.

Nok Terracotta
Meaning ❉ Nok Terracotta refers to ancient West African sculptures offering a profound visual record of early textured hair artistry and cultural significance.

What Historical Significance Do Textured Hair Remedies Hold for Cultural Identity?
Textured hair remedies embody a profound heritage, linking ancestral wisdom, resistance, and self-expression across generations.

What Ancestral Oils Aided Textured Hair Health?
Ancestral oils, deeply rooted in heritage, nourished textured hair through moisture, protection, and cultural rituals.

Which Historical Oils Are Best for Textured Hair?
Ancestral oils like shea butter, palm oil, and moringa oil were historically vital for textured hair health and cultural expression.

Can Traditional African Ingredients Validate Modern Hair Science for Textured Hair?
Traditional African ingredients offer robust scientific validation for textured hair care, rooted in centuries of ancestral wisdom.

What Historical Oils Nourished Textured Hair?
Historical oils like shea butter, castor oil, and argan oil nourished textured hair through ancient African and diaspora heritage.

Afro Culture
Meaning ❉ Afro Culture is the vibrant cultural heritage of African peoples and their descendants, profoundly expressed through the ancestral wisdom and enduring resilience of textured hair.
